Expressions
An expression is a combination of values, variables, operators, and functions that can be evaluated to produce a result. Think of it as a sentence of instructions that we tell inorigo®, and to get an answer from these instructions we need to write it in a language that inorigo® understands, i.e., expressions.
Overview
Expressions allow you in this way to customize and transform your data from the information you have to the information that you need. They can help you reduce the need for additional attributes and enable you to, for example, apply logic, use formulas, manipulate dates, or filter items.
Where can we use expressions?
Expression can be applied in some way for most modules in inorigo®. Look for an “Expression” text box for where you can add an expression. This can for example be in attribute automation in Model Builder or calculated columns in Knowledge Set Builder.
How to use expressions
Expressions can be as simple as a single value or variable, or they can be more complex, involving multiple values, functions, and operators. Some common types of expressions include Mathematical expressions (such as 2 + 3), logical expressions (such as x > y or a == b), and string expressions (such as "Hello, " + “name”).
A good use for expressions is to manipulate the data that you have created in Model Builder in other modules such as Application Builder and Knowledge Set Builder, but you can also, to some extent, use them in Model Builder. Note that the trickiest part about learning how to use expressions will be understanding how each available function works.
We have categorized the available functions according to their use in this documentation along with descriptions on how you can apply them in expressions.
Vocabulary
Boolean
A value that is either true or false.
Double
A number with decimals, for example 22.343.
Integer
A positive or negative whole number, including 0.
Expression
A combination of variables, constants, operators, and functions that are put together in a single statement to be evaluated.
Function
Always contains $ + Function name and a start and closing parentheses (). All functions are expressions but not all expressions contain functions.
GID
Global Identifier. A way for inorigo® to identify objects.
Input
The data we give to inorigo® to process.
Null
Means that something is undefined. It has no value but note it is not equal to zero.
Output
The result we get back from inorigo® from the processing.
Operate
An action that is carried out to accomplish a given task
Inward function
A function that is enclosed within another function.
Example: $FORMAT_DATE**($GET(**{p0},"StartDate"**)**"DATE_LONG")
Outward function
The surrounding function that encloses another function.
Example: $FORMAT_DATE($GET({p0},"StartDate"), "DATE_LONG")
Operator
A character that represents a mathematical or logical action, such as +, -, = or >.
Parse
Converting information into a format. This so to make something understandable for inorigo®.
Parameter
The variable listed inside the parentheses in the function definition.
Argument
The value that are sent to the function when it is called.
Example: X=3, here the 3 is the argument and X is the parameter.
Variable
Container for storing data values.
Constant
A fixed value, for example the number 5. The value does not change and is predefined.
String
A sequence of characters, for example “Hello world”.
Substring
A string that is part of another string. "Hel" is for example a substring of "Hello World".
Syntax
The concept/rules of how different elements in an Expression should be combined in order for it to run correctly.
Zero based Index
A way of numbering in which the initial element of a sequence starts at the index 0 rather than the usual index 1.
$ Functions - Summary List
inorigo® has a number of Built-in functions, which are listed below in alphabetical order.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ABS | Calculates the absolute value of a double value. |
| ACOS | Calculates the arc cosine of a number. |
| ADDAY | Add days to a given date. |
| ADDHOUR | Add hours to a given date. |
| ADDMILLIE | Add milliseconds to a given date. |
| ADDMINUTE | Add minutes to a given date. |
| ADDMONTH | Add months to a given date. |
| ADDSECOND | Add seconds to a given date. |
| ADDWEEK | Add weeks to a given date. |
| ADDYEAR | Add years to a given date. |
| AGGREGATE | Performs an aggregation on a collection of items. |
| ASCIITOSTRING | Returns a String object representing the specified decimal ASCII character. |
| ASIN | Calculates the arc sine of a number. |
| ATAN | Calculates the arc tangent of a number. |
| ATINDEX | Returns the value at specified (zero-based) index of a list or array. |
| AVG | Calculates the average of the given arguments. |
| CALL | Executes an Inorigo Method and returns the first output of the method. |
| CEIL | Calculates the smallest (closest to negative infinity) double value that is greater than or equal to the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer. |
| COALESCE | Return the first non null value. |
| CONTAINS | Checks if one is contained within two. |
| COS | Calculates the cosine of a number. |
| COSH | Calculates the hyperbolic cosine of a number. |
| COT | Calculates the cotangent of a number (1/tan(n)). |
| CSC | Calculates the cosecant of a number (1/sin(n)). |
| DATE_LONG | Formats a timestamp according to Formats a timestamp according to DateTimeLayout.DATE_LONG format. |
| format. | |
| DATE*SHORT | Formats a timestamp according to DateTimeLayout.DATE_SHORT format. |
| DATEADD | Adds to a given date depending on DatePart. |
| DATEFORMAT | Formats a timestamp as a string. |
| DATEPART | Returns the desired date part of a timestamp. |
| DATETIME_LONG | Formats a timestamp according to DateTimeLayout.DATETIME_LONG format. |
| DATETIME_SHORT | Formats a timestamp according to DateTimeLayout.DATETIME_SHORT format. |
| DAY | Calculate the day of a date, or the current day if no date argument is passed. |
| DAYNAME | Calculate the day name of a date, or the current day name if no date argument is passed. |
| DEFINITIONS | Returns a list of definition IDs for one or several instances. |
| DISTINCT | Performs a distinct operation on a collection of items. |
| DISTINCTBYCOLUMNS | Creates a Data Set containing column matched unique rows. |
| E | Calculates the double value that is closer than any other to e, the base of the natural logarithms. |
| EVALUATE | The function can replace method calls and enhance performance substantially, particularly if used in a calculated column in a knowledge Set with many rows. |
| EXP | Calculates Euler's number e raised to the power of a number. |
| EXPR | Evaluates an expression |
| FILTER | Performs a filter operation on a collection of items. |
| FILTERNULL | Remove null values from a collection of items. |
| FINDMANY | Returns all GlobalIDs matching the supplied criterias. |
| FINDONE | Returns one GlobalID matching the supplied criterias. |
| FINDSTR | Returns the index of a substring within a string. |
| FLOOR | Calculates the largest (closest to positive infinity) double value that is less than or equal to the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer. |
| FOREACH | Executes an expression for each item in a collection of items. |
| FORMAT_DATE | Formats a timestamp as a string. |
| FORMAT_NUMBER | Formats a number using the current locale. |
| GET | Returns an Attribute Value. Can also be used to get a hash map value. |
| GID | Creates a GlobalID. |
| HOUR | Calculate the hour of a date, or the current hour if no date argument is passed. |
| HTML_ENCODE | Makes a string safe to present on web. |
| IFNULL | Returns second or third argument, depending on wether first argument is null. |
| IIF | Returns second or third argument, depending on boolean first argument. |
| IS_AUTHORIZED | Check entity for authorization. |
| ISNULL | Returns wether first argument is null. |
| KNOWLEDGE_SET | Executes a Knowledge Set. |
| LEFT | Returns the leftmost _n* characters of a string. |
| LOAD | Deprecated. |
| LOG | Calculates the natural logarithm (base e) of a number. |
| LOG10 | Calculates the base 10 logarithm of a number. |
| LOOKUP | Performs a lookup by attribute values. |
| LOOP | Executes an expression for each item in a collection of items. |
| MAX | Calculates the greater double value of two numbers. |
| MILLISECOND | Calculate the millisecond of a date, or the current millisecond if no date argument is passed. |
| MIN | Calculates the smaller double value of two numbers. |
| MINUTE | Calculate the minute of a date, or the current minute if no date argument is passed. |
| MONTH | Calculate the month of a date, or the current month if no date argument is passed. |
| MONTHNAME | Calculate the month name of a date, or the current month name if no date argument is passed. |
| NOW | Calculates the current date and time. |
| NTH | Returns the n:th object in a list or the n:th letter in a string. |
| NULL | Returns null. |
| OBJECT | Returns an GlobalID using the supplied identification. |
| PACK | Returns a list of the arguments supplied. |
| PARTNERS | Returns a list of partner Global Identifiers. |
| PERCENT | Creates dataset with added percentage column(s). |
| PI | Calculates the double value that is closer than any other to pi, the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter. |
| POW | Calculates the double value of the first number raised to the power of the second number. |
| QUARTER | Calculate the quarter of a date, or the current quarter if no date argument is passed. |
| QUARTERNAME | Calculate the quarter name of a date, or the current quarter name if no date argument is passed. |
| REFERENTS | Returns Attribute Value referents for a given instance. |
| REPLACEREGEX | The function can replace method calls and enhance performance substantially. |
| REPLACESTR | Replace part(s) of a string. It is used to replace parts of a string using a regular expression. |
| RIGHT | Returns the rightmost n characters of a string. |
| ROUND | Rounds the first argument to the number of decimals specified by the second argument, using the HALV_EVEN rounding mode. |
| SEC | Calculates the secant of a number (1/cos(n)). |
| SECOND | Calculate the second of a date, or the current second if no date argument is passed. |
| SELECT | Select rows and columns from a Dataset or a List of Dataset rows. |
| SERIAL_NO | Generates the next serial number for the given pool. |
| SIN | Calculates the sine of a number. |
| SINH | Calculates the hyperbolic sine of a number. |
| SIZE | Performs a size operation on a value. |
| SORT | Performs sorting on a collection of items. |
| SQRT | Calculates the square root of a number. |
| STRING_JOIN | Returns a string built from a list of items, with specified delimiter and optional prefix and suffix |
| STRINGFORMAT | Performs a string.format() operation. |
| SUBCLASSES | Returns a list of subclasses. |
| SUBSTR | Returns a substring of the first input string. |
| SUM | Returns summary of values. |
| SUPERCLASSES | Returns a list of superclasses. |
| TAN | Calculates the tangent of a number. |
| TANH | Calculates the hyperbolic tangent of a number. |
| TIME_SHORT | Formats a timestamp according to DateTimeLayout.TIME_SHORT format. |
| TIME_SHORT_MILLIES | Formats a timestamp according to DateTimeLayout.TIME_SHORT format. |
| TIMESPAN | Calculates the timespan between two timestamps or a duration. |
| TO_COORDINATE | Creates a valid Coordinate for use in maps. |
| TOARRAY | Creates an array of the supplied input. |
| TODATE | Parse argment to timestamp. |
| TODATETIME | Parse argment to timestamp. |
| TODOUBLE | Parse argment to double |
| TOGLOBALID | Creates a GlobalID. |
| TOINT | Parse argment to integer |
| TOLIST | Creates a List of the supplied input. |
| TOLONG | Parse argment to long |
| TOLOWER | Turns a string into lower case. |
| TOLOWERCASE | Turns a string into lower case. |
| TOSTRING | Returns argument as its string representation. |
| TOULONG | Parse argment to unsigned long (BigInteger) |
| TOUPPER | Turns a string into upper case. |
| TOUPPERCASE | Turns a string into upper case. |
| TRANSLATE | Translates a text. |
| TRIM | Removes leading and trailing spaces from a string. |
| VELOCITY_IFRAME | Returns an IFRAME HTML tag for a Velocity page. |
| VELOCITY_URL | Returns an URL for a Velocity page. |
| WEEK | Calculate the week of a date, or the current week if no date argument is passed. |
| YEAR | Calculate the year of a date, or the current year if no date argument is passed. |
| YEAR_QUARTER | Calculate the year and quarter name of a date, or the current year and quarter name if no date argument is passed. |
Legacy Expression Editor
The below are relevant for the Model Builder and Application builder
Expression Editor
The Expression Editor will simplify the readability of expressions as it checks for inconsistencies and helps you with some guidance and basic validations to create the expression.

Note, the Visible option is not always available, it depends on the context expression is used, e.g. it is useful when writing expressions for map Info panel.
The Functions context menu options will show all the available Expression Functions

and they are inserted in Expression field as they are selected.
There are a few shortcuts to some of the most common operations/variables/functions used;
| Ctrl-G | $GET |
| Ctrl-I | @item (the Source object in map configuration) |
| Ctrl-N | “name” |
| Ctrl-R | @record |
Variables – Verso View will give the list of available default variables, user defined variables and dataset(s) as input to new Expression Variables in view;

Example that shows the available items defined in view
Refresh this menu
Sometimes the contents of the context menu are not updated, especially for some Variables and Datasets that require calculations to be updated, hence the Refresh option to update the list.
Expression Reference Guide
Advanced Functions
$CALL
Executes an Inorigo Method and returns the first output of the method.
Input:
String methodName , Any param1, Any param2,...
Output:
Any
Usage:
$CALL(Target Global Identifier [, method input, ...])$CALL(Method Unique Identifier [, method input, ...])$CALL(Method Fully Qualified Name [, method input, ...])
Example:
$call("MyChange/HelloWorld", "Hey", "You"). This will run the method "HelloWorld" in the process object "MyChange" and give "Hey" and "You" as input variables.
$Coalesce
Return the first non null value.
Input:
Object or list/collection
Output:
Any
Usage:
$COALESCE(@NULL, 1, 2, "test") → 1
Example:
We have Instance of the definition Person in a filter box. The below expression will output the first non null item in the selected lis
This expression is first checking if the first selected item in p0 is null via $NTH({p0}, 0), if null, it will return "Nothing is selected in p0!" but if any value is found it will return the first non null item.
$EXPR
Evaluates an expression
Input:
String expression
Output:
Any
Usage:
$EXPR("Hello inner world.").
$IS_AUTHORIZED
Check entity for authorization.
Input:
- Entity or Entity ID.
- Action (Read / Update / Create / Delete / Execute).
- Optional User ID. If empty, current user is used.
Output:
- True or False.
Usage:
$IS_AUTHORIZED(@item, "Read")
$IS_AUTHORIZED(@item, "Read", @USER_ID)
$IS_AUTHORIZED(@item, "Read", "F973B5C0-21B3-D4AB-870D-A42201230315")
Example:
We have a filter box (p0) containing Instances of the definition Person which we are showing in a result matrix by using p0.all.
We add the below expression as a calculated column which will check if the current user is able to delete each of the Instances in the p0:
$KNOWLEDGE_SET
Executes a Knowledge Set. Returns the execution result as a DataSet, suitable for further processing
Usage:
$KNOWLEDGE_SET(@KsID).
$KNOWLEDGE_SET("7f69e05c-5adc-4bce-a88b-0640c84792e5").
Example:
We have a Knowledge Set containing Instances from the definition Person with the attribute Columns below:
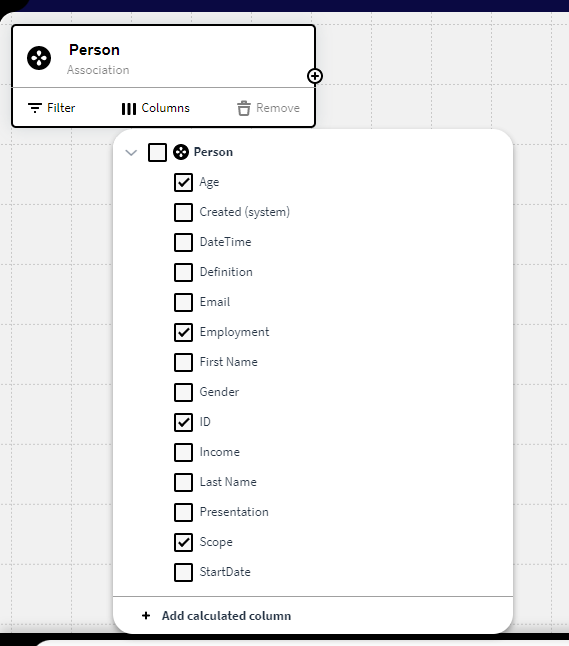
We want to view this data structure in Application Builder as well. So we add our below expression and input the ID of the Knowledge Set to a Result Matrix in Application Builder:
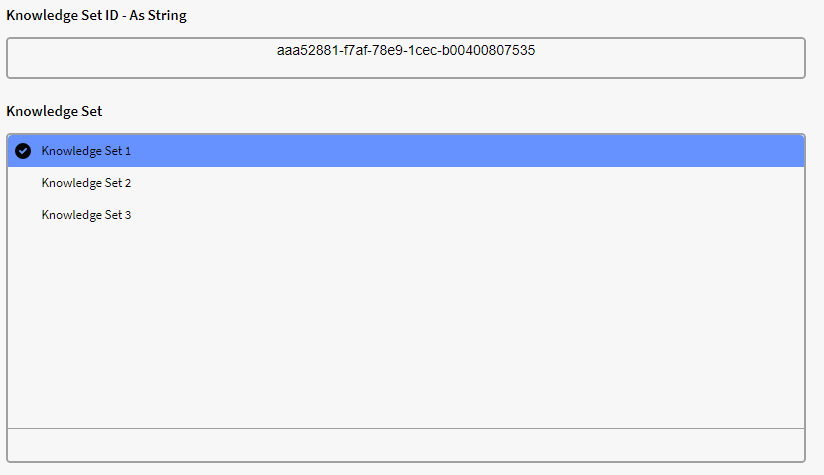
$KNOWLEDGE_SET(aaa52881-f7af-78e9-1cec-b00400807535)
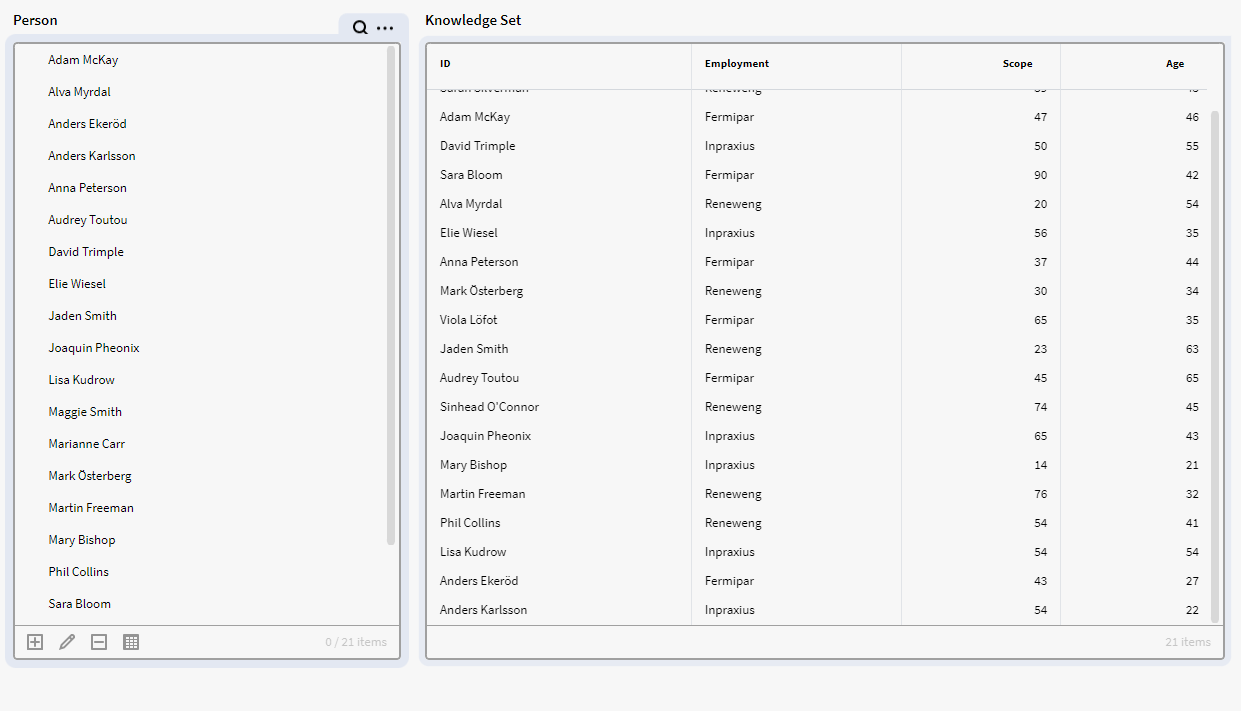
This will result in below view:
$Null
Returns null.
Usage:
$NULL().
$SERIAL_NO
Generates the next serial number for the given pool.Returns a number of type long
Usage:
$SERIAL_NO("GENERAL_POOL").
$STRINGFORMAT("EMP-%02d", $SERIAL_NO({POOL_NAME}))
Example:
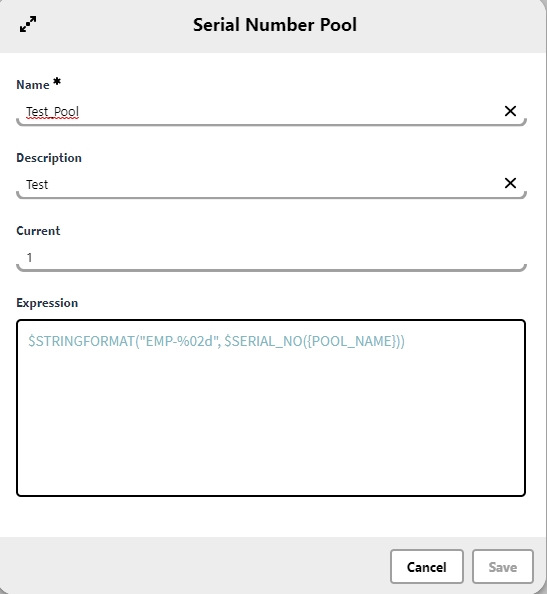
We want to create create an expression that generates serial number for our Serial Pool named Test_Pool. This should then be used in an automation for an attribute called Serial Number within a definition named Person.
We first create the Serial Number Pool in System Management;
We then call the Serial Number Pool we just created in the automation panel within the attribute:
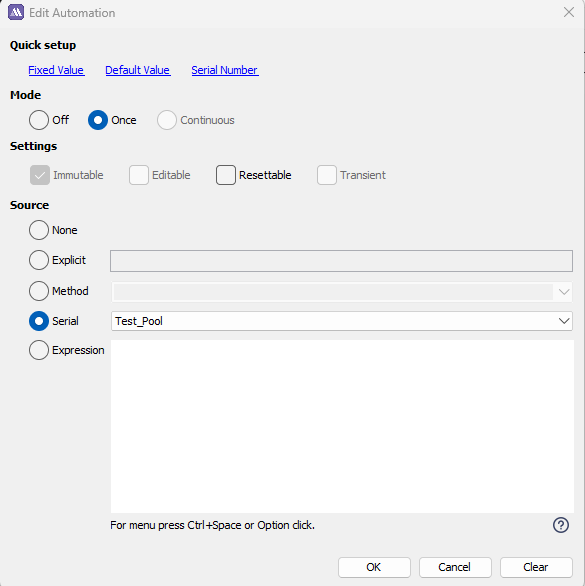
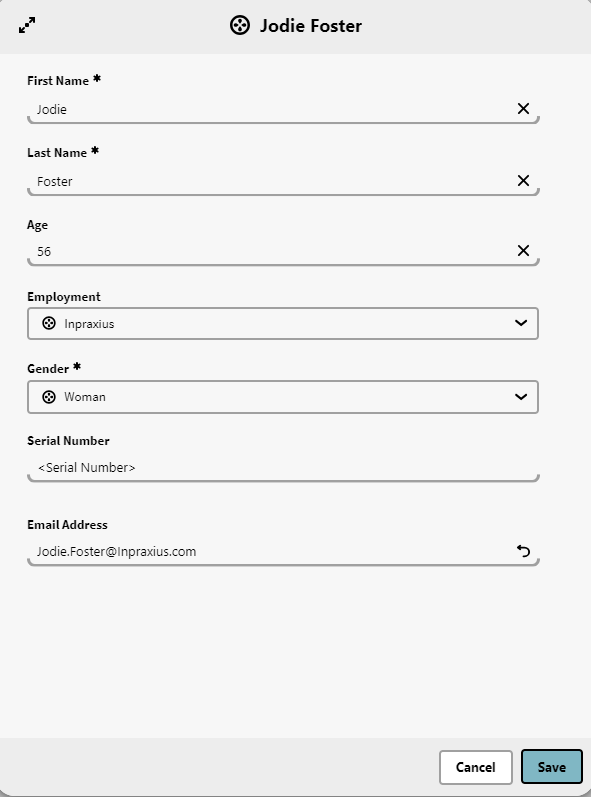
When we create a new Instance for the definition we can see the Serial Number attribute. Note that it will not generate until we save the instance.
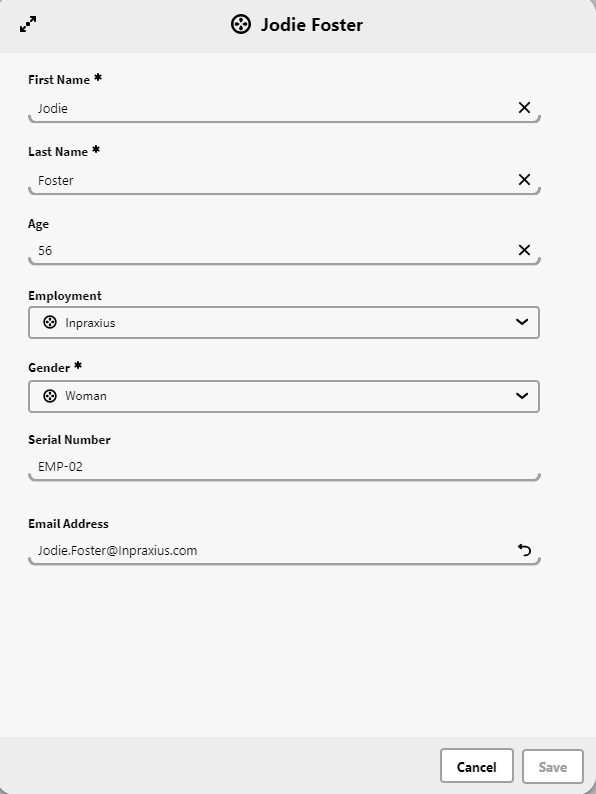
Now we have saved the new instance and we can see the generated Serial Number:
$TO_COORDINATE
Creates a valid Coordinate for use in maps.
Usage:
$TO_COORDINATE(@MyLatitude, @MyLongitude).
$TO_COORDINATE(@MyStringCoordinate).
$VELOCITY_IFRAME
Returns an IFRAME HTML tag for a Velocity page.
Usage:
$VELOCITY_IFRAME("de305d54-75b4-431b-adb2-eb6b9e546014") $VELOCITY_IFRAME("HelloWorld.html")
$VELOCITY_IFRAME("de305d54-75b4-431b-adb2-eb6b9e546014","RUNTIME_ID=" + @RUNTIME_ID + "&CLICK="+@CLICK)
$VELOCITY_URL
Returns an URL for a Velocity page.
Usage:
$VELOCITY_URL("de305d54-75b4-431b-adb2-eb6b9e546014") $VELOCITY_URL("HelloWorld.html")
$VELOCITY_URL("de305d54-75b4-431b-adb2-eb6b9e546014","RUNTIME_ID=" + @RUNTIME_ID + "&CLICK="+@CLICK)
Aggregation functions
<br>
What is an Aggregate function?
These functions operates on a set of values and returns a single value as an output.
Note:
Ignores null values.
Performs an aggregation on a collection of items. Optionally grouped.
<br>
$AGGREGATE
Performs an aggregation on a collection of items. Optionally grouped.
Input:
Items - a collection of items supported by $GET() (i.e GlobalID, DataSetRow, HashMap, SelectorItem etc)
Aggregation Type - case insensitive. (Sum, Count, Average, Median, Min, Max, StdDeviation, Variance, Percentage)
Aggregation Column(s).
Optional - Group Column(s).
Output:
Always returns a DataSet.
Aggregation columns will be suffixed with the type of aggregation (e.g "Income (Sum)").
If no Group column(s) has been supplied a default "Total" column will automatically be generated and aggregation result(s) will start at column 1.
Usage:
$AGGREGATE({Dataset}, "Sum", "Amount")
$AGGREGATE({Dataset}, "Sum", "Amount", "Category")
$AGGREGATE({Dataset}, "Average", "Income", "Gender", "Age")
$AGGREGATE({p0}, "Average", $PACK("Income","Tax"), "Gender", "Age")
$AGGREGATE({p0}, "Median", $PACK("Income","Tax"), $PACK("Gender", "Age"))
Example:
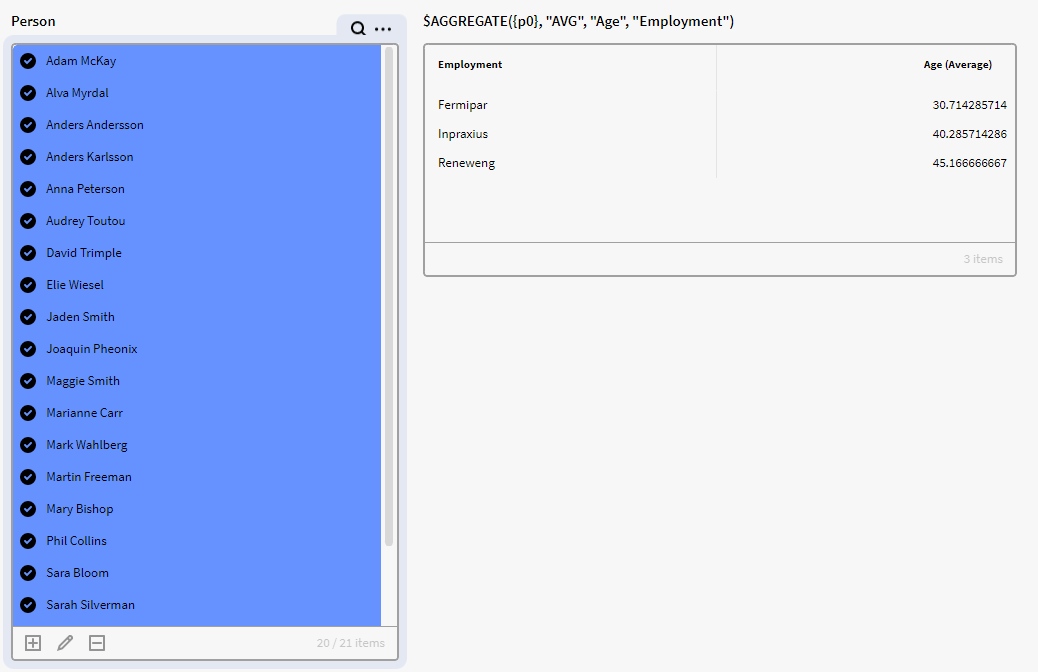
In this example we have a filter box (p0) containing instances of the definition Person with an Employment and Age Attribute. We want to see the average age per Employment in a result matrix.
What we can do to achieve this is to use the aggregate function in an expression where we specify our Aggregation type as "AVG" and then add our Aggregation and group column (Age, Employment) :
$AGGREGATE({p0}, "Average", "Age", "Employment")
<br>
$AVG
Calculates the average of the given arguments.
Input:
List of numbers
Output:
Double
Usage:
$AVG(List of Numbers)
$AVG(List of Dates)
$AVG(List of Entities, attribute name or id)
$AVG(List of Global Identifiers, attribute name or id)
Example:
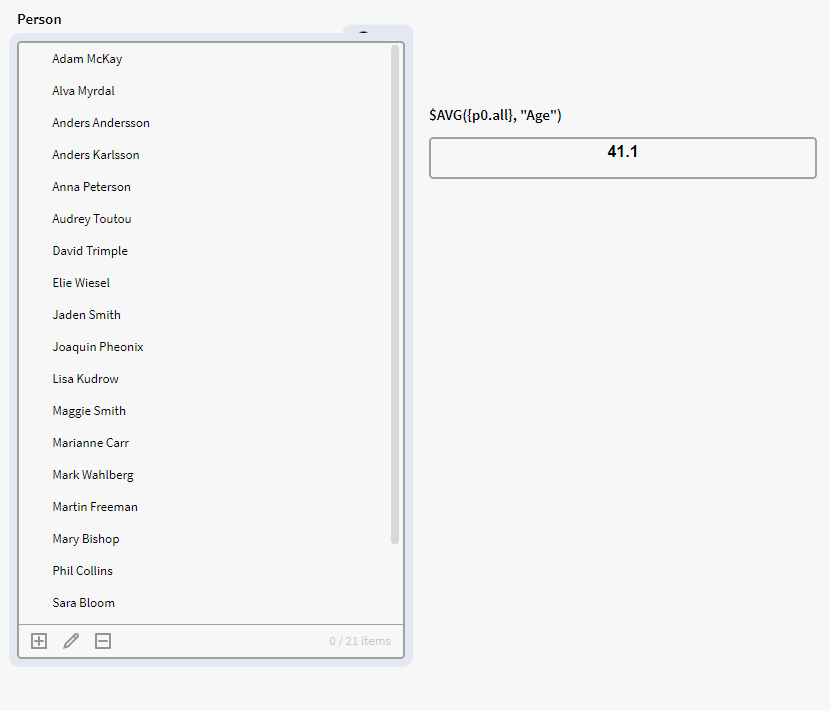
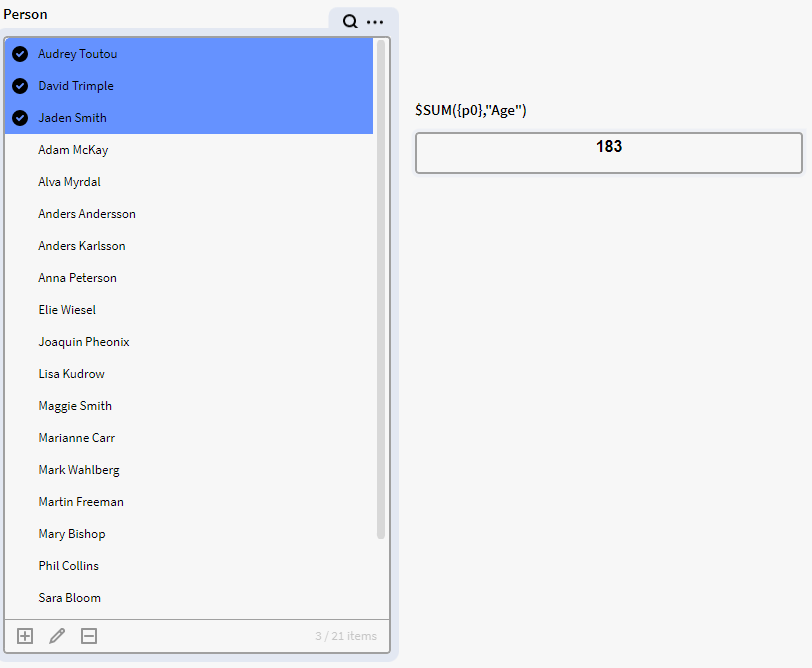
We have a filter box p0 containing instances of the definition Person with an Age attribute. We want to see the average age of all persons in p0. We therefore use the below expression in a calculation box, which tells Inorigo to calculate the average of the all the age attribute values in p0:
$AVG({p0.all}, "Age")
<br>
$MAX
Calculates the greater double value of two numbers.
Input:
Double, Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$MAX(@myFirsNumber,@mySecondNumber)
$MAX(List of Numbers)
$MAX(List of Dates)
$MAX(List of Entities, attribute name or id)
$MAX(List of Global Identifiers, attribute name or id)
Example 1:
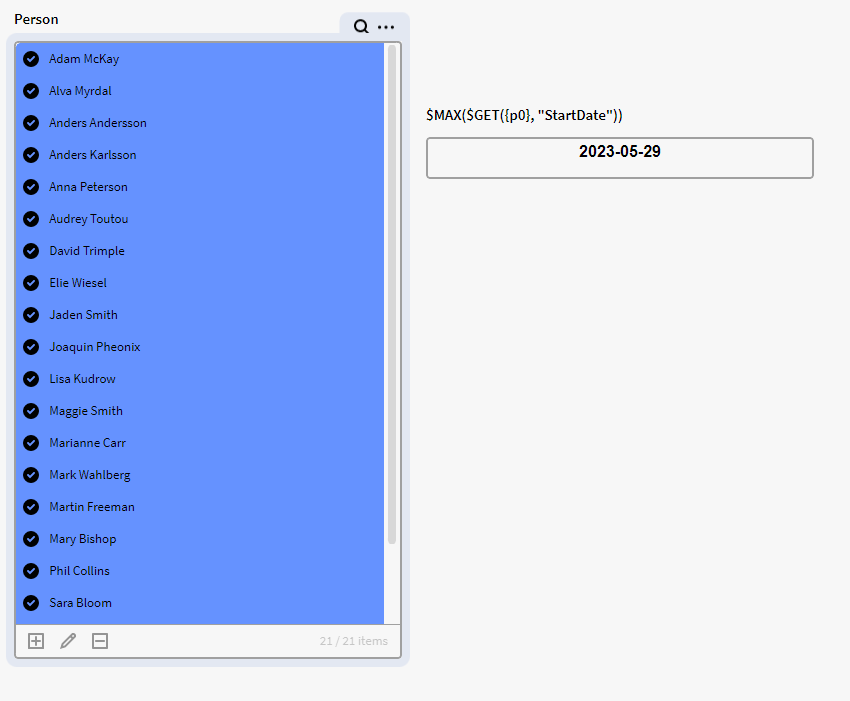
We can use $MAX to return the largest number/date in a list. We have instances of the definition Person listed in the filter box p0 that has the attribute StartDate which consist of a date. Let's say we want to see the latest date in for all these persons in p0, we can then use the below expression in calculation box:
<br>
<br>
Example 2:
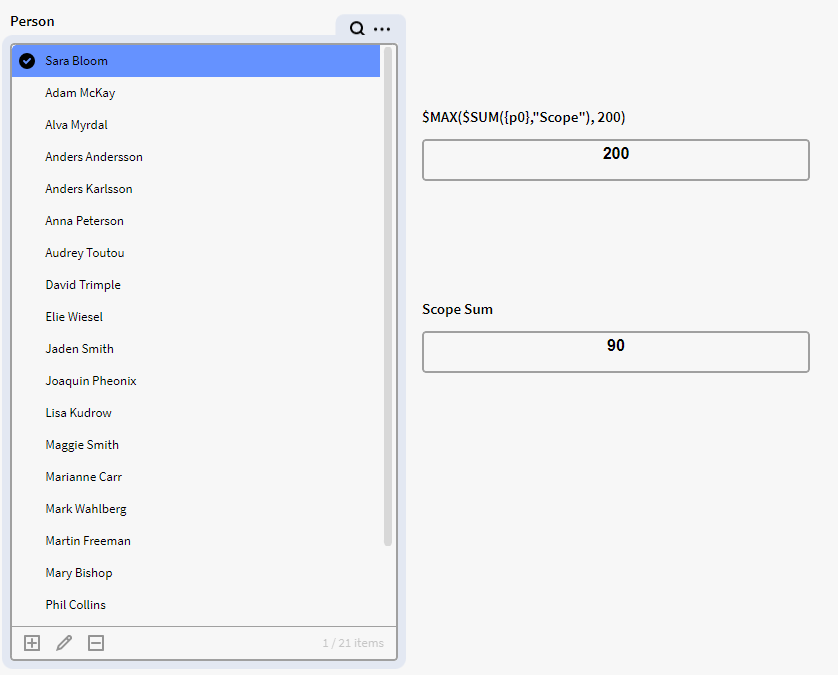
We have instances of the definition Person listed in p0 which have an attribute called Scope. What we want to do is to check if the selected persons in p0 together have a scope value larger than 200. If not then return 200, and if yes then return the sum of the selected scope values. In the first image you can see that we have selected Sara Bloom, which have Scope of 90. But since it's not larger than the 200 we specified it will not change in the top calculation box
<br>
$MAX($SUM({p0},"Scope"), 200)
Returns 200 or the selected sum of Scope in p0, whichever being the largest.
<br>
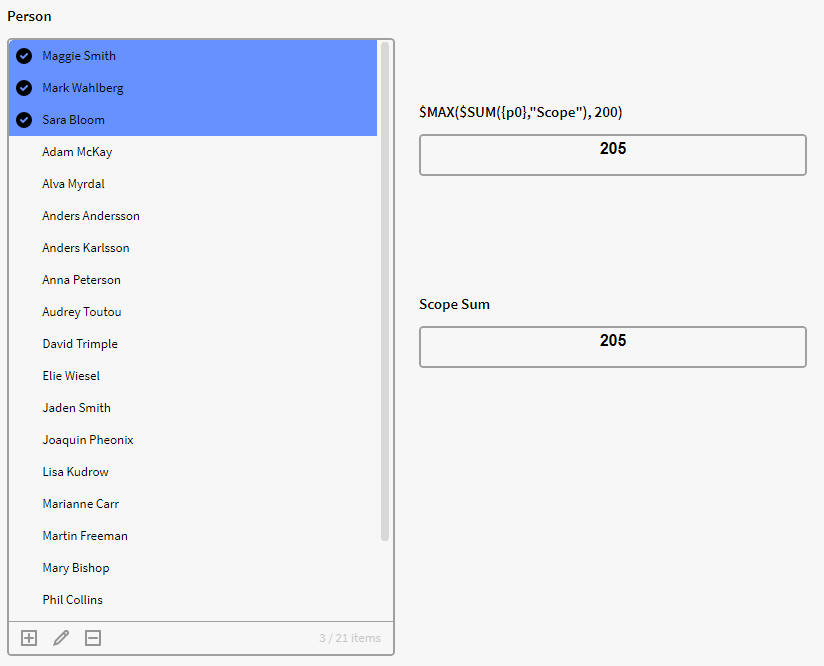
But now we select more people which brings our total scope values to that of 205. The top calculation box now changes to 205 as the sum is over 200.
<br>
$MIN
Calculates the smaller double value of two numbers.
Input:
Double, Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$MIN(@myFirsNumber,@mySecondNumber)
$MIN(List of Numbers)
$MIN(List of Dates)
$MIN(List of Entities, attribute name or id)
$MIN(List of Global Identifiers, attribute name or id)
Example 1
We can use $MIN to return the smallest number/date in a list. Here we have persons instances listed in p0 (Person) which has the attribute StartDate which consist of a date. Let's say we want to see the earliest date in for all these persons in p0, we can then use the below expression in calculation box:
$MIN($GET({p0}, "StartDate"))
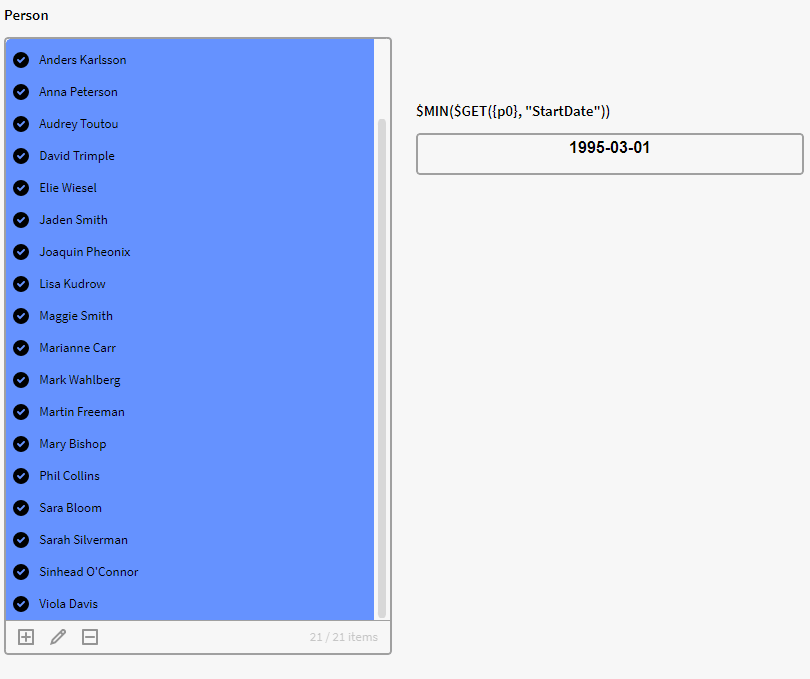
<br>
Example 2
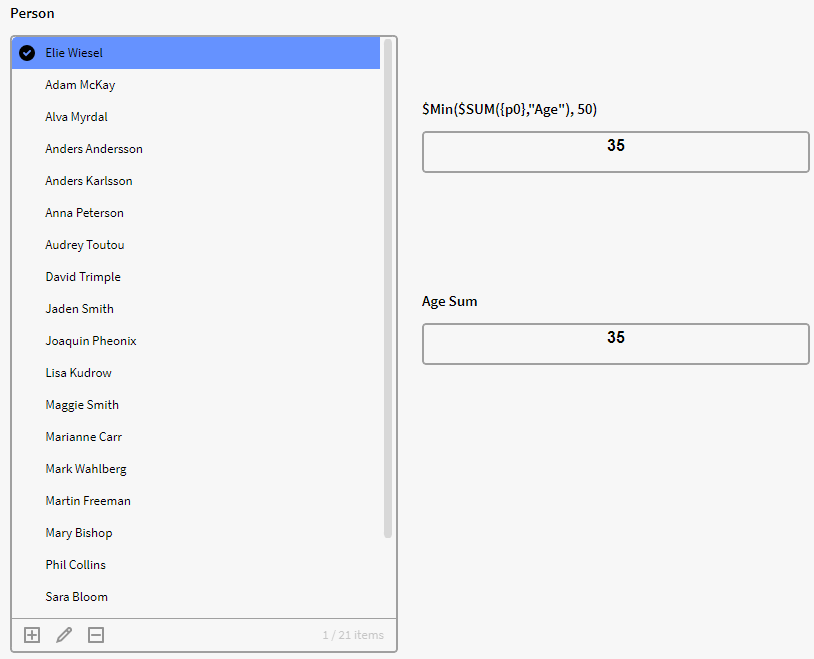
$MIN($SUM({p0},"Age"), 50)
Returns 50 or the sum of p0, whichever being the smallest.
In this example we have a filter box containing instances of the definition Person with the attribute age. We want to see if the sum of the selected ages in the filter box p0 (Person) is below 50, if yes return return the sum of selected ages, if no then return 50.
Here we have only selected one person that have an age of 35, and since it is smaller than 50, the top Calculation box returns the sum of ages selected (35).
<br>
<br>
But here we have selected more people in the filter box which brings our total sum of the ages combined to 98. And since this age sum is larger than 50 the expression will return 50 in the top result Calculation box.
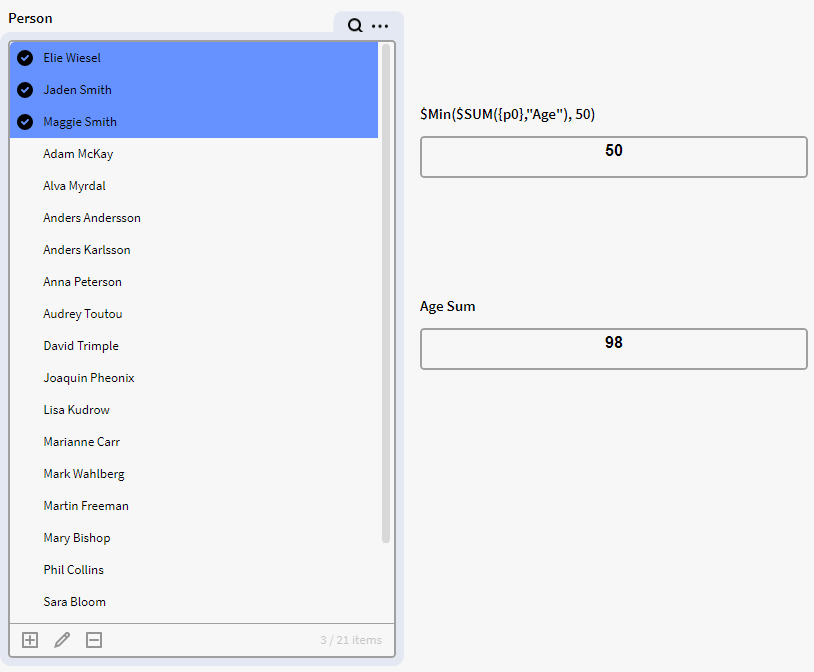
<br>
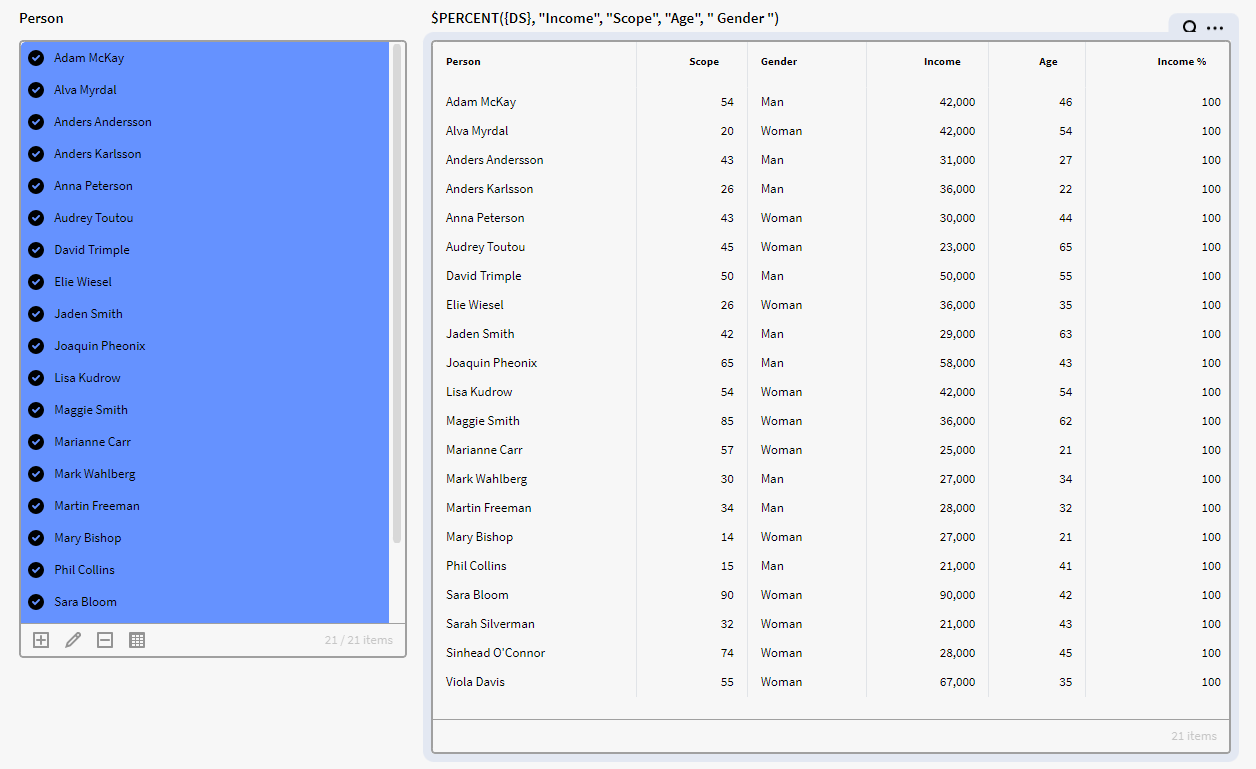
$PERCENT
Creates a dataset with added percentage column(s).
Input:
Items. A collection of DataSet rows, like a normal dataset or the result of an Aggregation
Value Column(s).
Optional - Total Grouping Column(s).
Output:
Always returns a DataSet.
Aggregation columns will be suffixed with % (e.g "Income %").
If no Grouping column(s) has been supplied, the total is simply the sum of all values in the Value column.
Usage:
$PERCENT({Dataset}, "Amount", "Category")
$PERCENT({Dataset}, "Income", "Gender", "Age")
$PERCENT({Dataset}, $PACK("Income","Tax"), "Gender", "Age")
$PERCENT({Dataset}, $PACK("Income","Tax"), $PACK("Gender", "Age"))
Example:
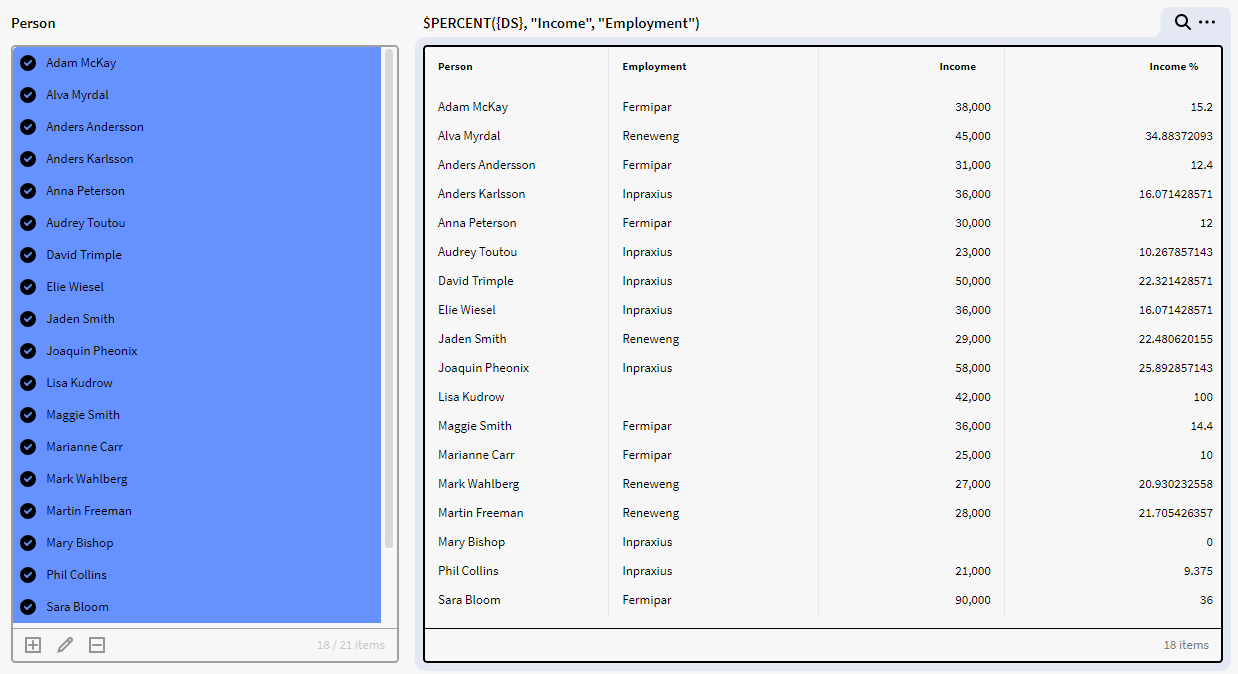
In the below example we have a dataset (DS) containing instances of the definition Person with the attributes Employment, and Income.
<br>
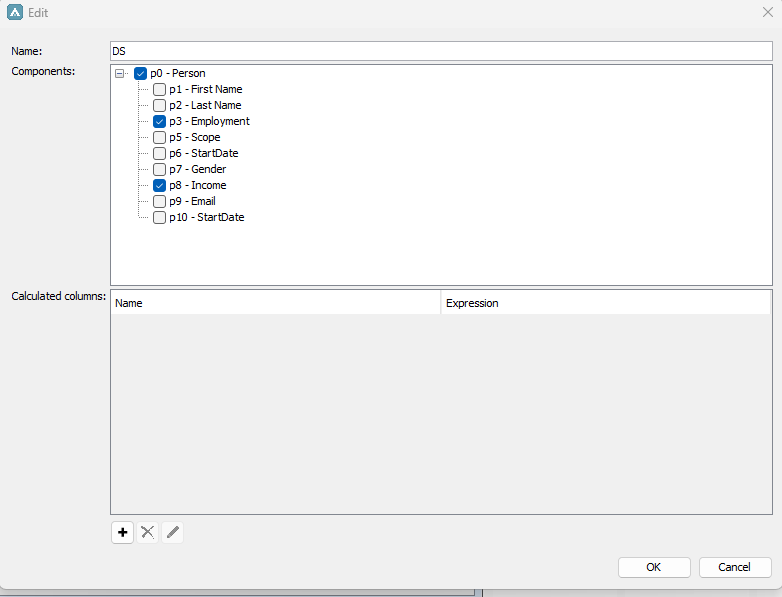
<br>
Using the below expression in a Result Matrix will output the percentage of the total Income per Employment for each row in the dataset DS. Where our dataset is the items input, Income is the value column and Employment is the total grouping column
<br>
$PERCENT({DS}, "Income", "Employment")
<br>
<br>
$SUM
Returns summary of values.
This function is used for summarizing lists, plus a reference to the object attribute value to be summed.
Input:
Collection of numbers or Collection<GID/DataObject>, String attribute
Output:**
Double
<br>
Usage:
$SUM(List of Numbers)
$SUM(List of Dates)
$SUM(List of Entities, attribute name or id)
$SUM(List of Global Identifiers, attribute name or id)
<br>
Example:
In this example we have a filter box p0 containing instances of the definition Person with the attribute age. We want to see the sum of all the selected age attributes values in a calculation box, so we add the below expression. Here p0 is the collection of items input and "Age" is our string attribute:
$SUM({p0}, "Age")
Collection Functions
What is a collection Function?
These functions operate on or return collections.
$CONTAINS
Checks if a string contains another string.
Input:
Look for: Any type.
Look in: String / Collection or Array
Output:
True / False.
Usage:
$CONTAINS("World", "Hello World") -> True
$CONTAINS(@MyGID, {p0}).
$CONTAINS("David", $GET({p0}, "First Name"))
Example:
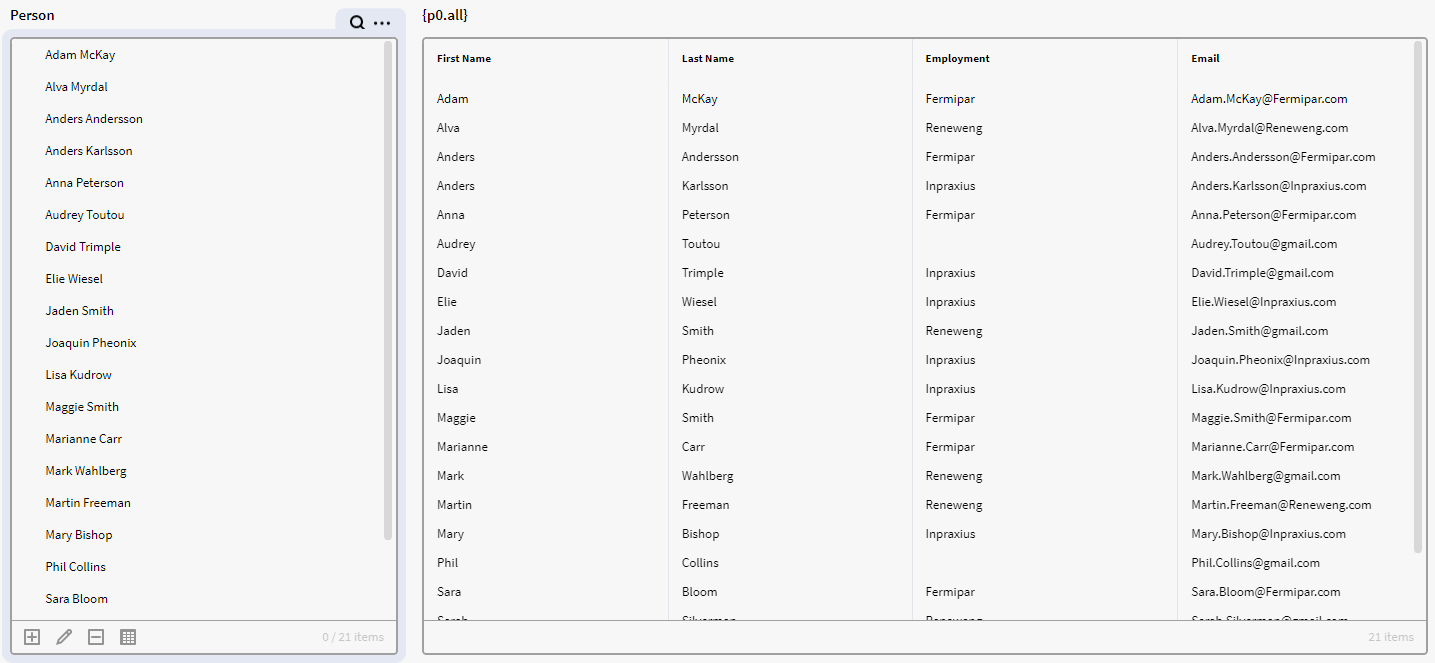
We have a filterbox p0 containing instances of the definition Person with the attribute’s First Name, Last Name, Employment and Email.
Here is the default matrix where we simply have all the items from p0 along with their attribute values. Note that some of these have "gmail" in their email address
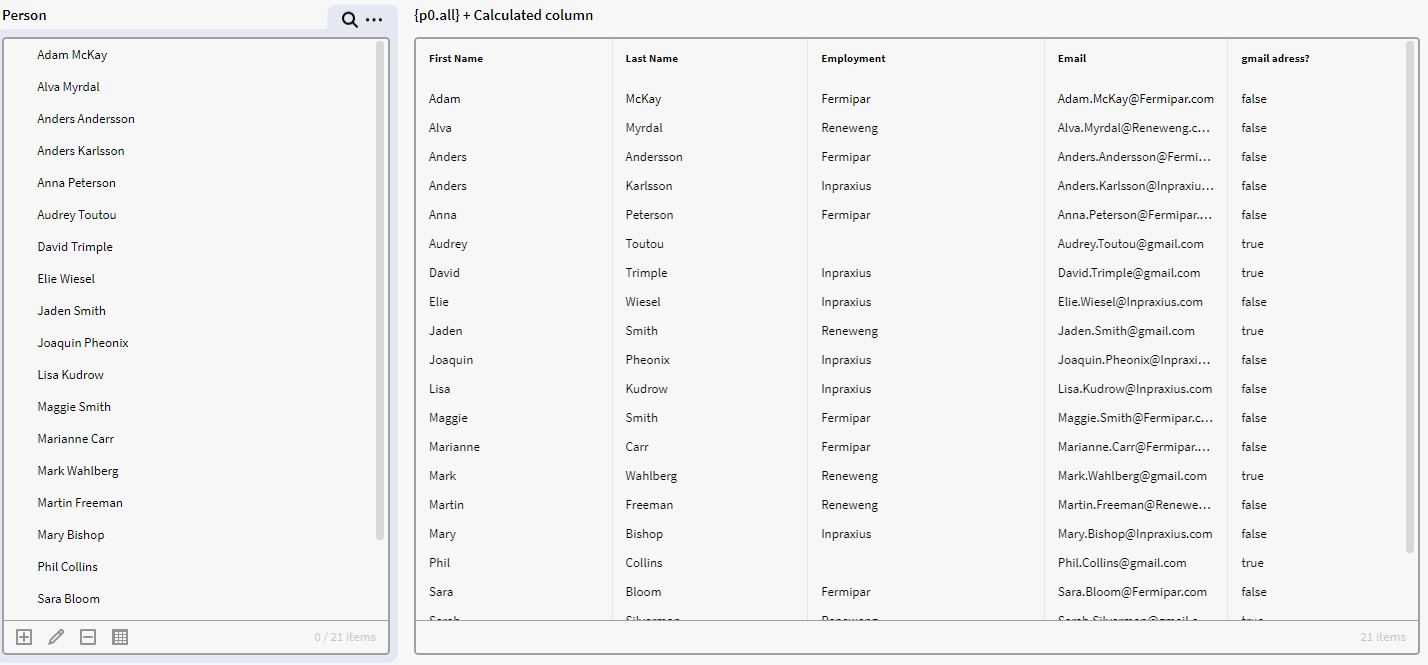
We want to see if any people have a gmail account as their email address. What we can do is see if the email attribute value contains “gmail” via the below expression.
The expression will check if each row in the Email column contains “gmail”. It will then return either true or false for each row.
$CONTAINS("gmail", $GET({record}, "Email"))
$DISTINCT
This function will only return distinct values I.e., duplicate values will not show.
Input:
Items - A collection of items supported by $GET() (i.e GlobalID, DataSetRow, HashMap, SelectorItem etc)
Distinct Column(s).
Output:
Always returns a DataSet.
Usage:
$DISTINCT({DataSet}, "Gender", "Age")
$DISTINCT({p0}, $PACK("Gender", "Age"))
Example:
In the below example we have a Filter Box (p0) containing the Instances from the Definition Person. These Instances have the attribute Employment and Income.
We want to see the distinct incomes per employment from our filter box p0. We therefore use below expression:
$DISTINCT({p0}, "Employment", "Income")
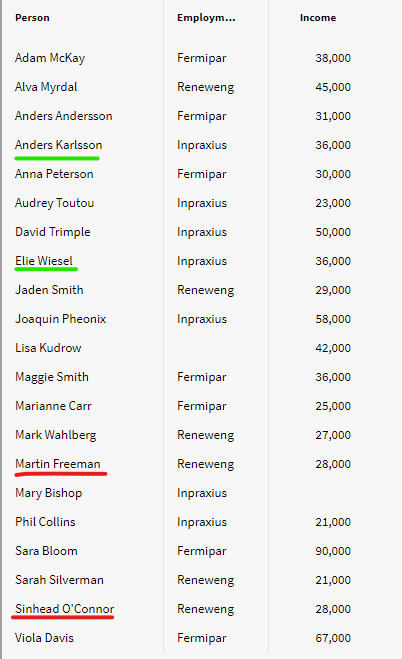
As you can see, we only have 19 rows in the “DISTINCT” matrix using the expression even though we have selected 21 people in the filter box. This is because we have 2 different sets of people that have the same attribute value in Income and Employment, so the expression only returns one distinct value for each of these duplicates.
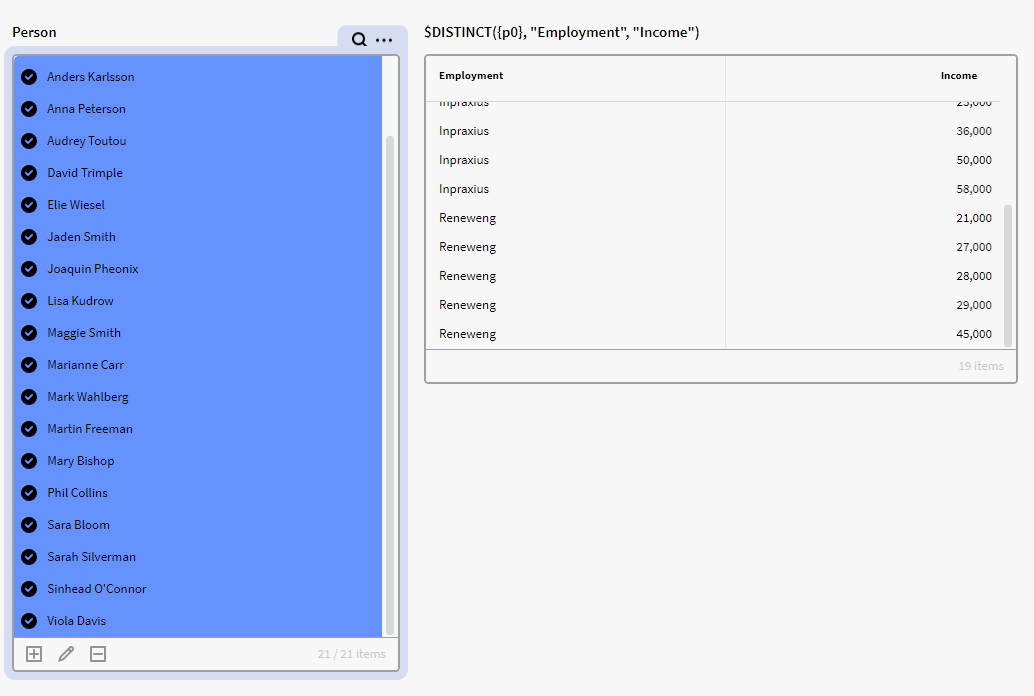
Here are the people with the same income and employment:
$DISTINCTBYCOLUMNS
Creates a Data Set containing column matched unique rows.
Note! The result will contain copies of the distinct rows with ALL original columns.
Input:
Rows. A collection of Data Set Rows (like a dataset).
First? True: Return the first row found. False: Return the last row found (slower).
Distinct Column(s). An invalid column will render an empty result!
Output:
Always returns a DataSet.
Usage:
$DISTINCTBYCOLUMNS({Dataset}, true, "Gender", "Age")
$DISTINCTBYCOLUMNS({Dataset}, true, 1, 3)
$DISTINCTBYCOLUMNS({Dataset}, true, $PACK("Gender", "Age"))
$DISTINCTBYCOLUMNS({Dataset}, true, @MyColumnsVariable)
Example:
In the below example we have a dataset containing instances of Definition Person with attributes Income and Scope but we want to only show the rows that have a distinct value in both the Income and Scope columns.
Here is the default view of the dataset in a result matrix
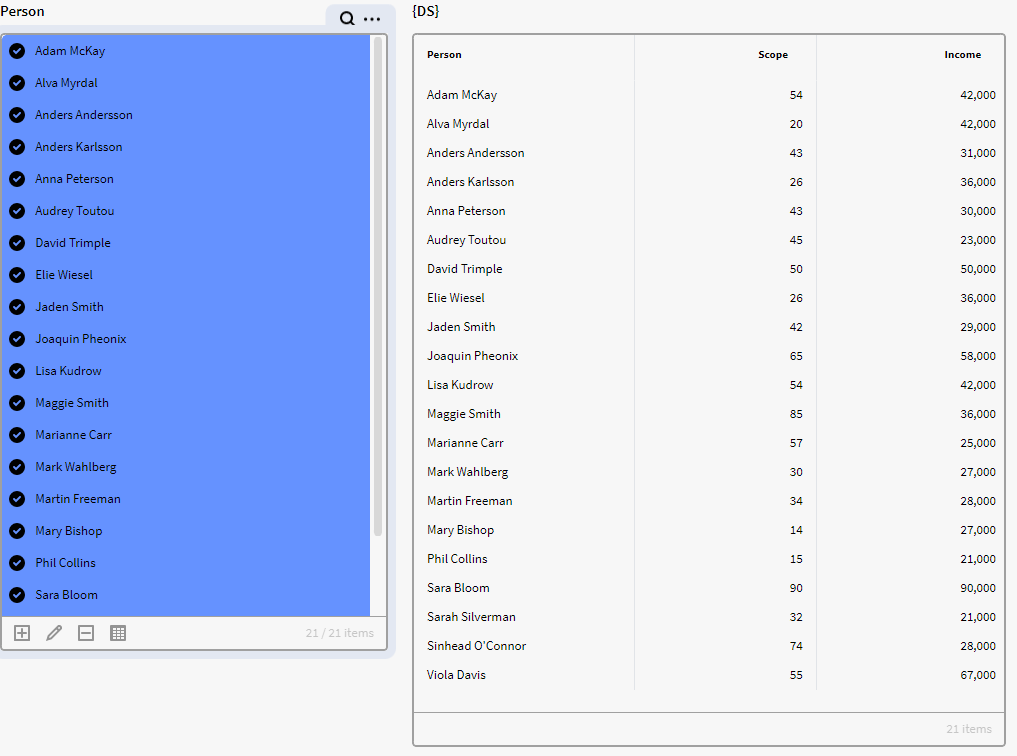
So, we add the below expression to a matrix and the result is 19 rows compared to the previous 21 rows from the dataset.
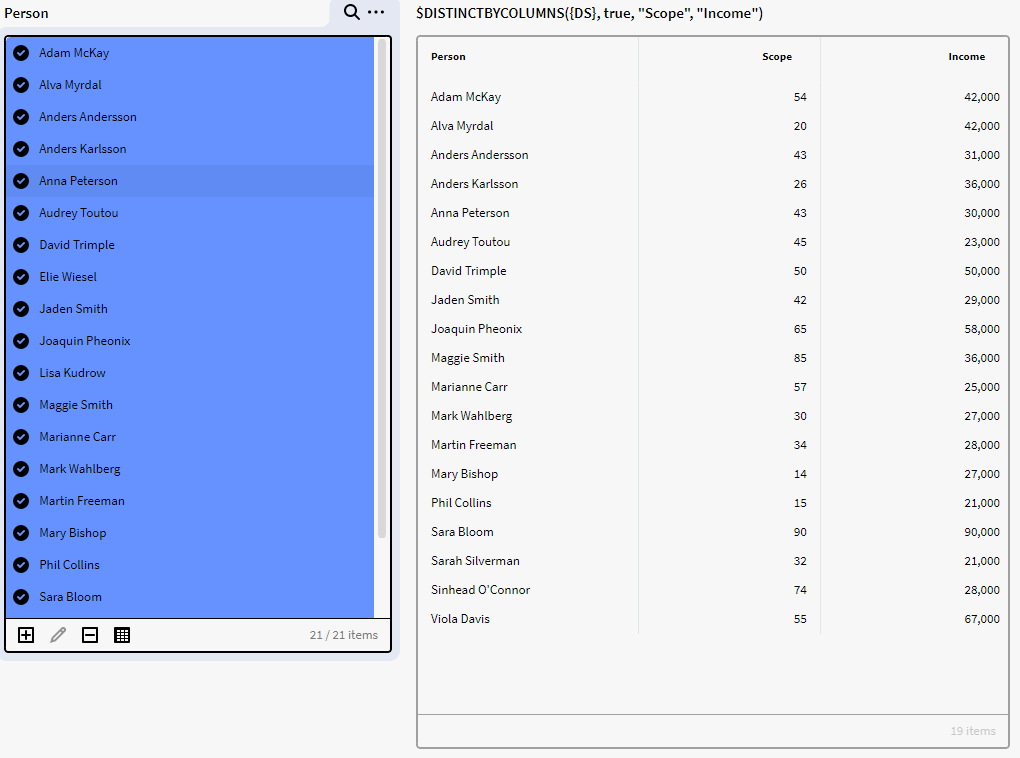
The reason we get 19 rows is that we have 2 different sets of duplicate values for Income and Scope in the dataset (Lisa Kudrow & Adam McKay and Anders Karlsson & Elie Wiesel). Lastly, as we have added true to our input in the expression, we get the first row found for the duplicates (Adam McKay and Anders Karlsson) and Lisa Kudrow and Elie Wiesel is excluded from the list resulting in 19 rows.
$DISTINCTBYCOLUMNS({DS}, true, "Scope", "Income")
$FILTER
Performs a filter operation on a collection of items.
The expression will be evaluated for each item in the input list.
The item can be referenced in the expression by {record}.
Input:
- A collection of items. Each item can be of any type supported by the filter expression.
- A Boolean expression for filtering the items.
Output:
A list of items for which the supplied expression returned true.
Usage:
$FILTER({Dataset}, $GET({record}, "Age") > 50)
$FILTER({p0}, $GET({record}, "Employment")="Inpraxius")
Example 1
We have a dataset (DS) containing instances of the Definition Person with the attributes Employment, Gender and Age. We want to filter out the rows of people with an age below 29.
Here is the default dataset DS in a result matrix
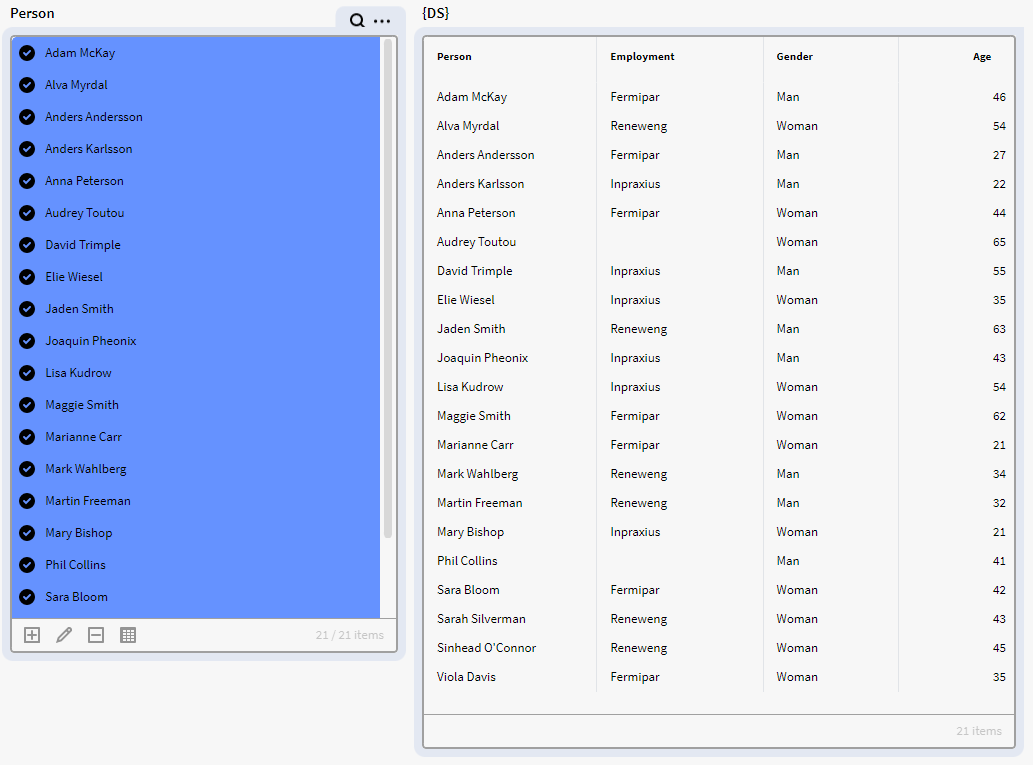
We add the below FILTER expression to a result matrix, which will only output the rows in DS that have an Age attribute value higher than 29. As you can see we now only have 17 rows compared to the previous 21.
$FILTER({DS}, $GET({record},"Age") > 29)
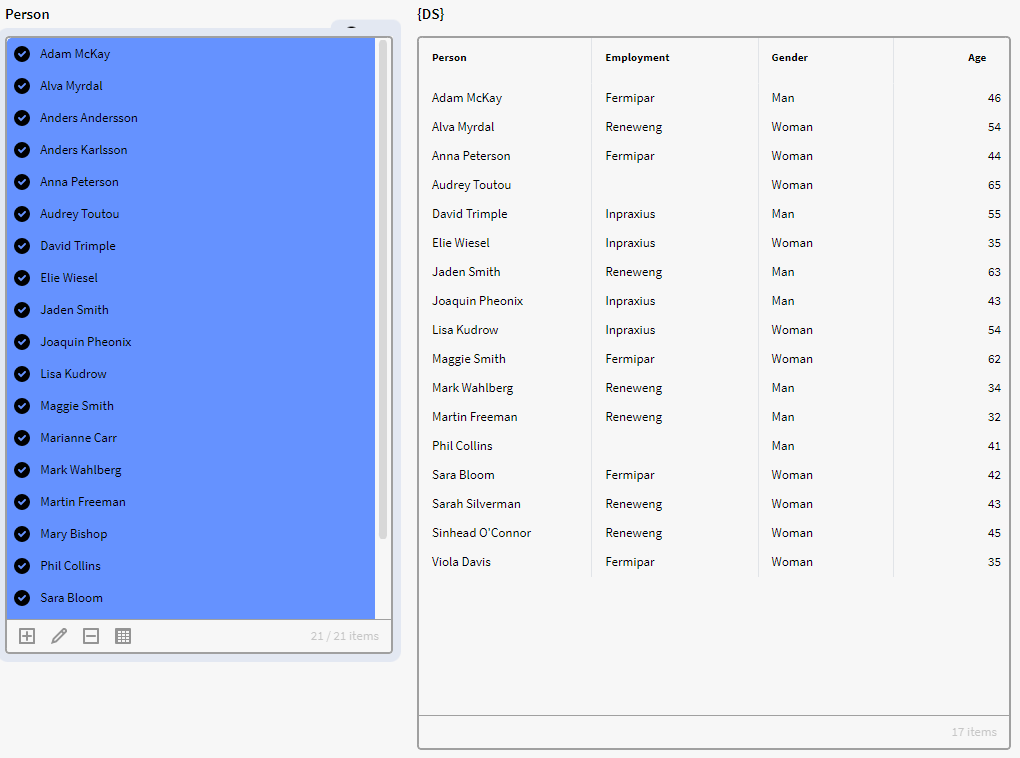
Example 2
Here we have the Filter box p0 containing instances of the definition Persons with the attribute Gender. We want to only show the instances with an attribute value of "Woman" as an output in a calculation box. So what we can do is the the expression below:
$FILTER({p0.all}, $GET({record}, "Gender") = "Woman")
This expression will filter all items in p0 and only return those records/items that have Gender set as Woman
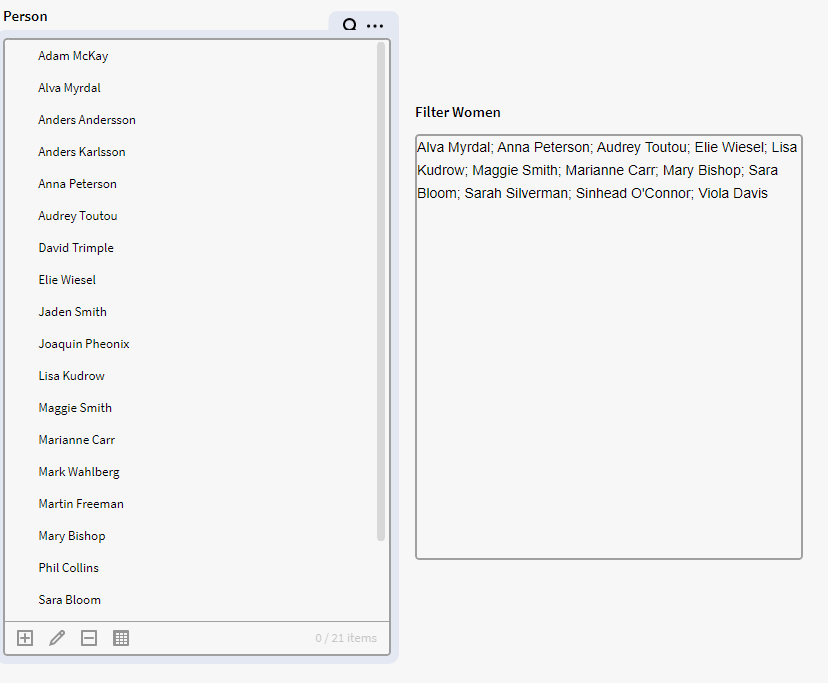
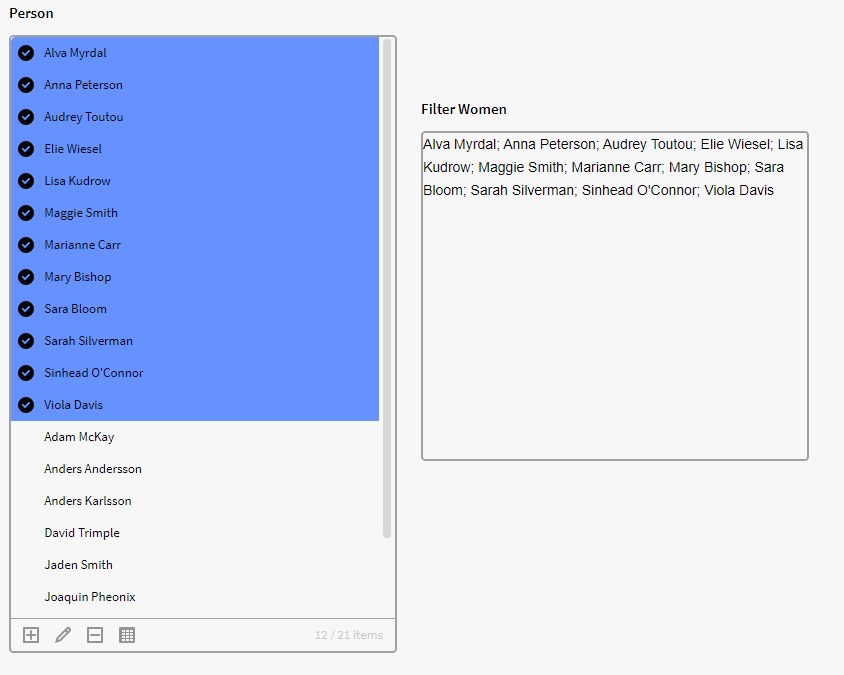
Note: if you want to add an initial selection filter to p0 that will select these person in the filter box, you can add the below expression. Simply add the previous filter expression to "{record} ="
{record} = $FILTER({p0.all}, $GET({record}, "Gender") = "Woman")
$FILTERNULL
This function removes null values.
Input:
- A collection of items.
- Optional attribute to check if list contains items supported by $GET.
Output:
List, Dataset.
Usage:
$FILTERNULL(@DataSet, "Gender")
$FILTERNULL(@ListOfNumbers)
$FILTERNULL(@p0, "Age")
Example:
We have a filterbox p0 that contains a list of instances of the definition Person with different attributes (see image below), among these is the attribute Employment. What we want to do in this example is filter out those persons/rows with no Employment attribute value.
This is the default output we get if we simply get all the instances from p0 via the below expression. As you can see we also get persons with no chosen Employment (null) in the dataset.
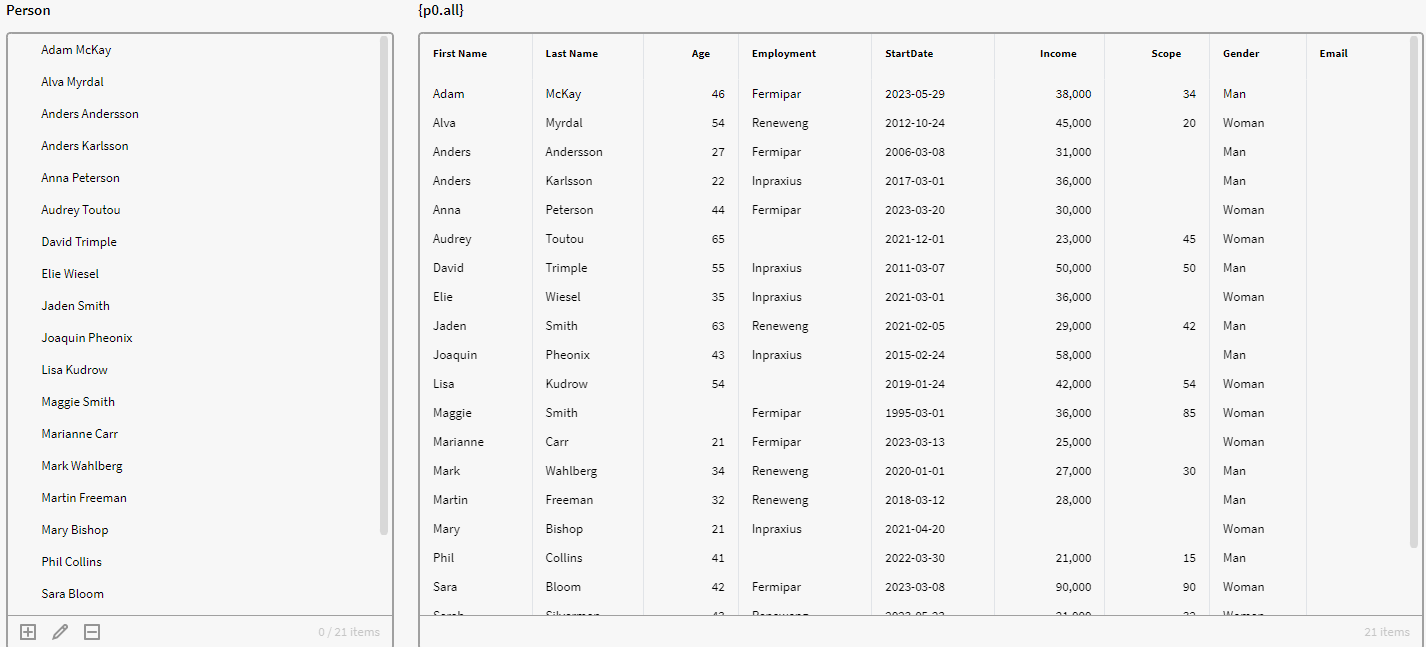
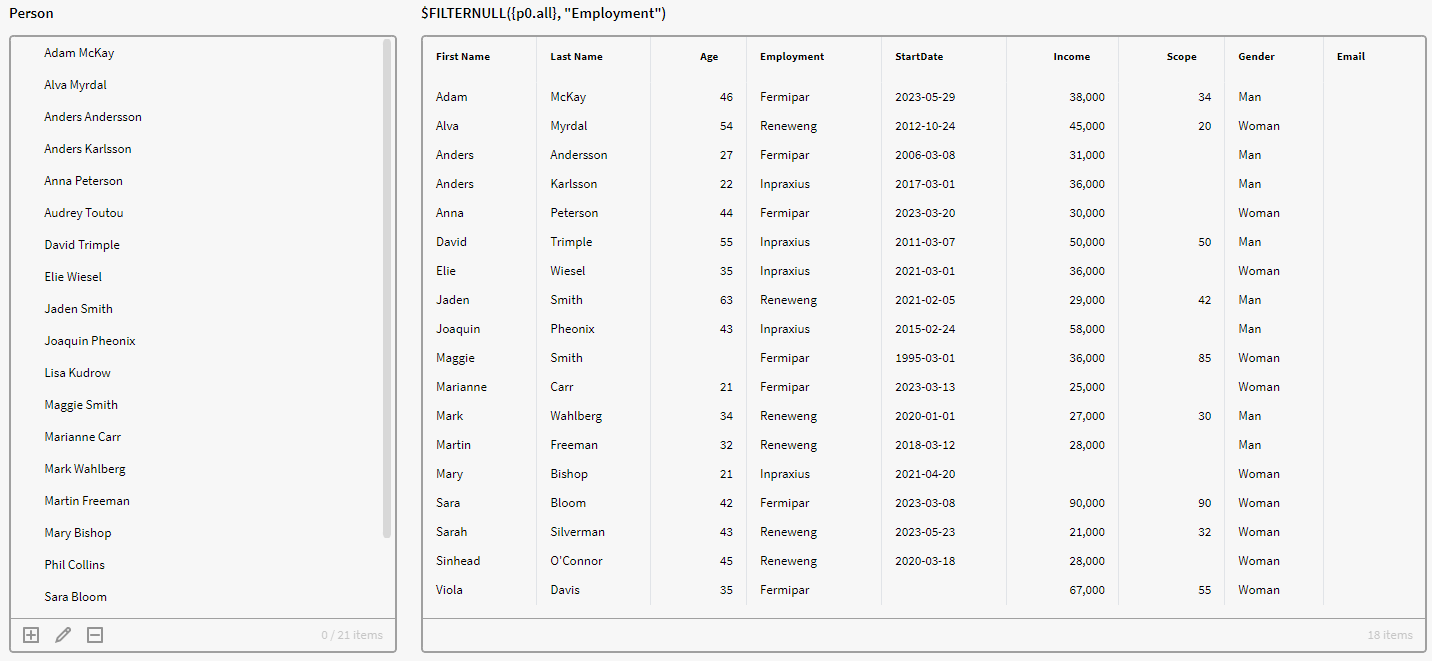
In the below image we have used the FILTERNULL expression, which removes the rows/persons that have a null value in the Employment attribute. Notice that we now only receive 18 items compared to the previous 21 items, even though we still specified p0.all
$FILTERNULL({p0.all}, "Employment")
$FOREACH & $LOOP
Executes an expression for each item in a collection of items.
Note! $FOREACH and $LOOP does the same thing. So you can use either to receive the same result.
Input:
A collection of items. Each item can be of any type supported by the filter expression.
An expression to evaluate for each item.
The item can be referenced in the expression by {record} or {item}
Output:
A list of values created by the supplied expression.
Usage:
$FOREACH({p0},$get({record}, "value")*2)
$LOOP({p0},$get({record}, "value")*2)
Example 1:
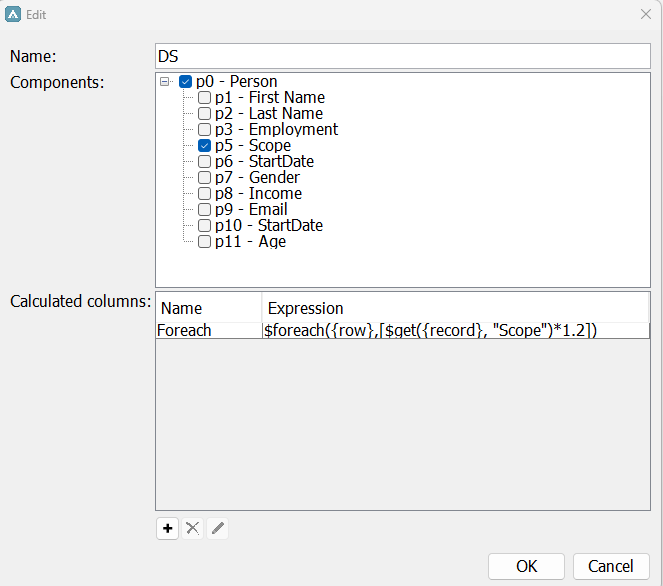
In the below example we have a dataset (DS) containing instances of the definition Person with the attribute Scope.
We want to see what numbers we would get for each person if we add 20% to each person’s scope attribute value. We therefore add a foreach expression to a calculated column in the dataset:
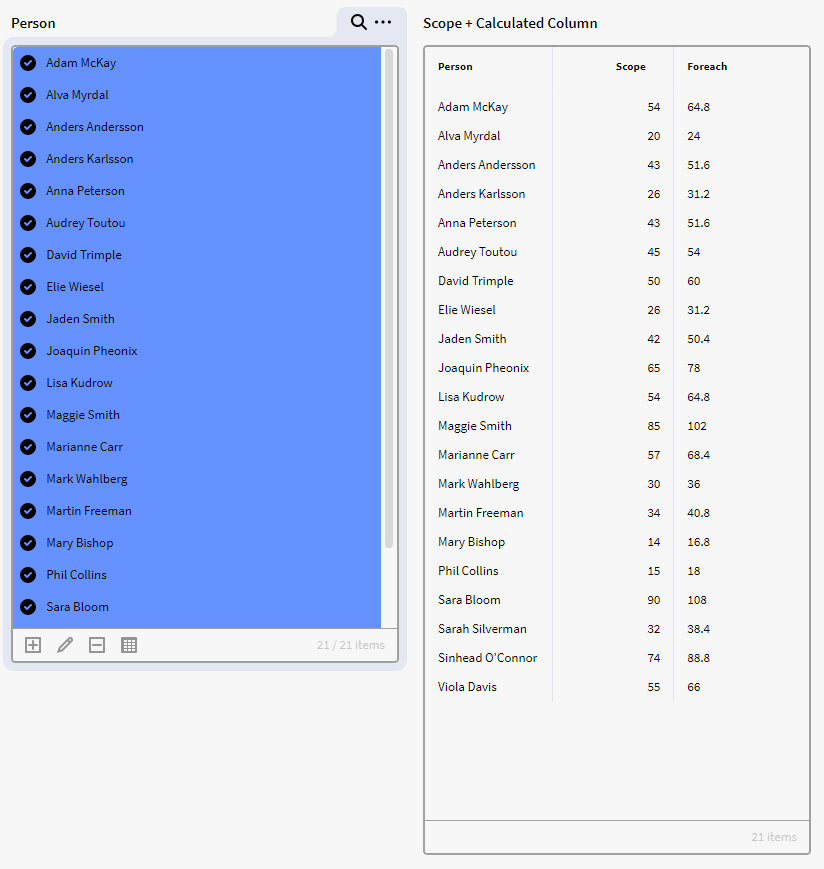
$foreach({row}, $get({record}, "Scope")*1.2)
Dataset
Result in a Matrix
Example 2
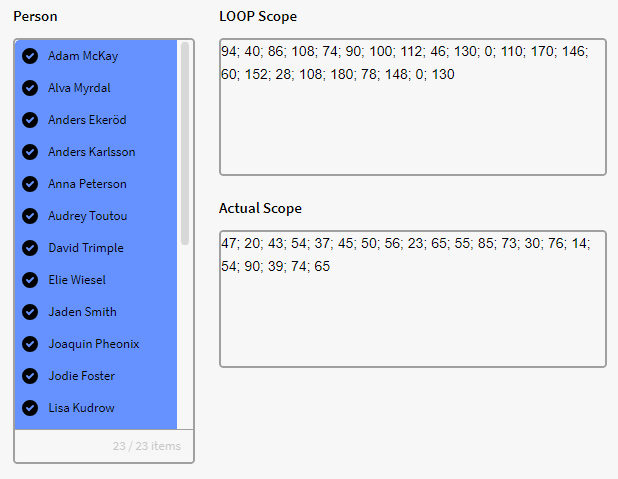
We have a filter box p0 containing instances of the definition Persons with the attribute scope but let's double the scope of each person in p0. What we can do here is use the below expression as it will execute on each item in p0:
$LOOP({p0.all}, $get({record}, "Scope")*2)
Here is the actual age (top calculation box) compared to the loop result showing in the lower Calculation box:
$NTH
Returns the n:th object in a list or the n:th letter in a string.
Index is zero based so it will start at zero.
Input:
Collection/String, Integer
Output:
Any/String
Usage:
$NTH({p0}, 0) First object in p0.
$NTH("Hello", 1) "e".
Example:
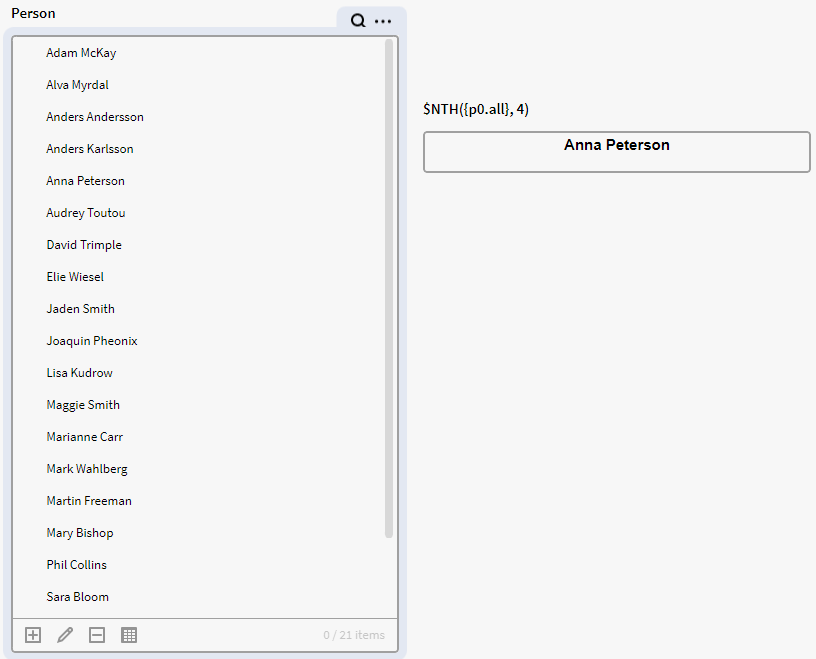
In this example we want to see the 5th item in the p0 filter box. We therefore use the below expression. Notice that we used p0.all so the expression is executed on the whole list in p0. If we used simply p0 we would get the 5th item of the selected items in p0.
$NTH({p0.all}, 4)
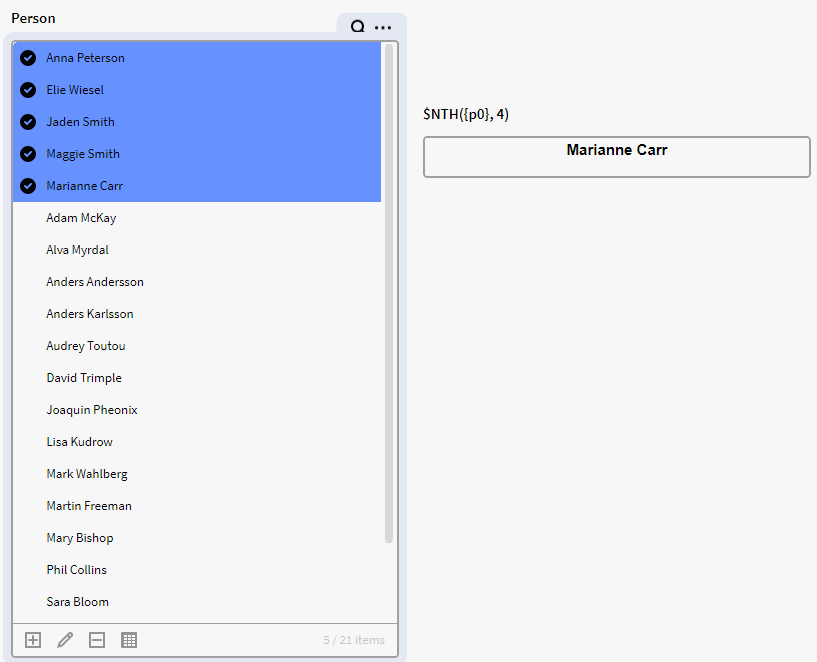
Using p0 instead of p0.all
$PACK
Returns a list of the arguments supplied.
This function is useful for when you want to pack different attribute values together into one parameter.
Usage:
PACK("A","B","C"...)
$PACK($GET({p0},"Last Name"), $GET({p0},"Employment"))
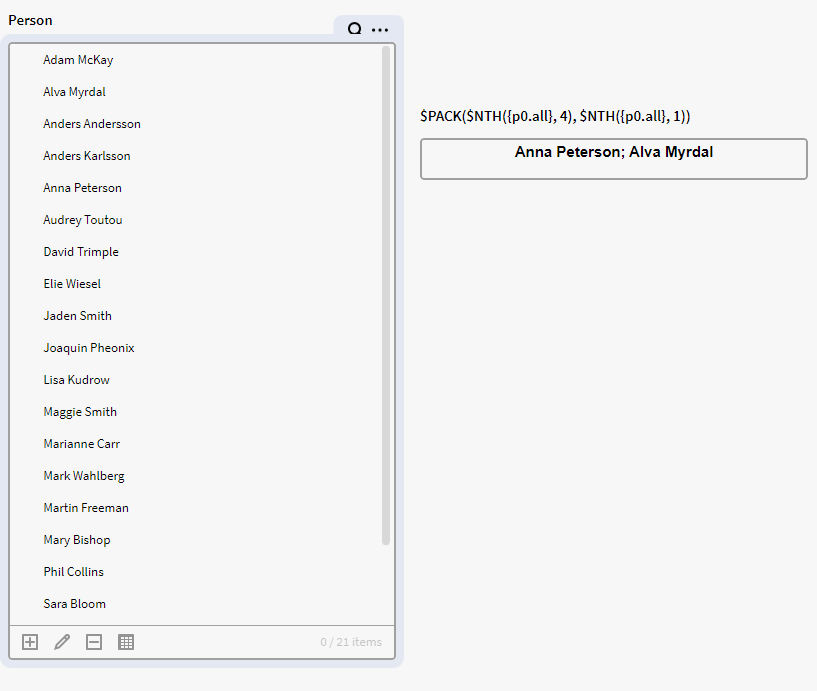
Example 1:
Let's say we want to pack the 5th object in p0 with the 2nd object in p0. For this we can use the $NTH function with the $PACK function.
$PACK($NTH({p0.all}, 4), $NTH({p0.all}, 1))
This expression pack them both together into one output:
Example 2:
In this example we have a Base table in Knowledge Set Builder containing instances of the definition Person with attributes Employment and Age.
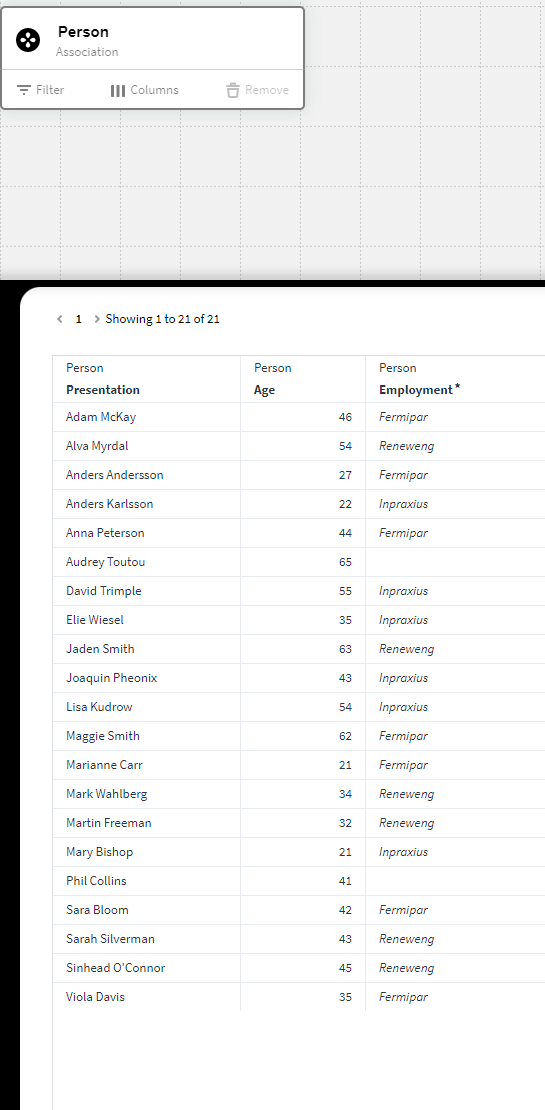
We want to add a calculated column to this dataset which should show both Employment and Age value in one cell for each person. We can for this use the below expression in a calculated column:
$TOSTRING($PACK({cell.Age}, {cell.Employment}))
This expression will pack both the current rows age and employment attribute value into one cell in the new calculated column in the Result table:
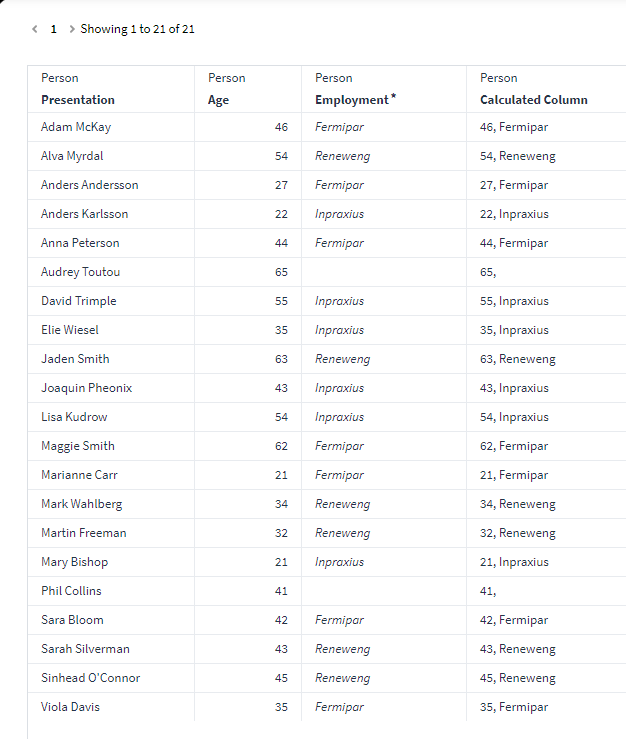
Example 3:
In the below image we have a dataset (DS) in Application Builder containing instances of the Definition Person with the attributes Age, Gender, Income and Scope.
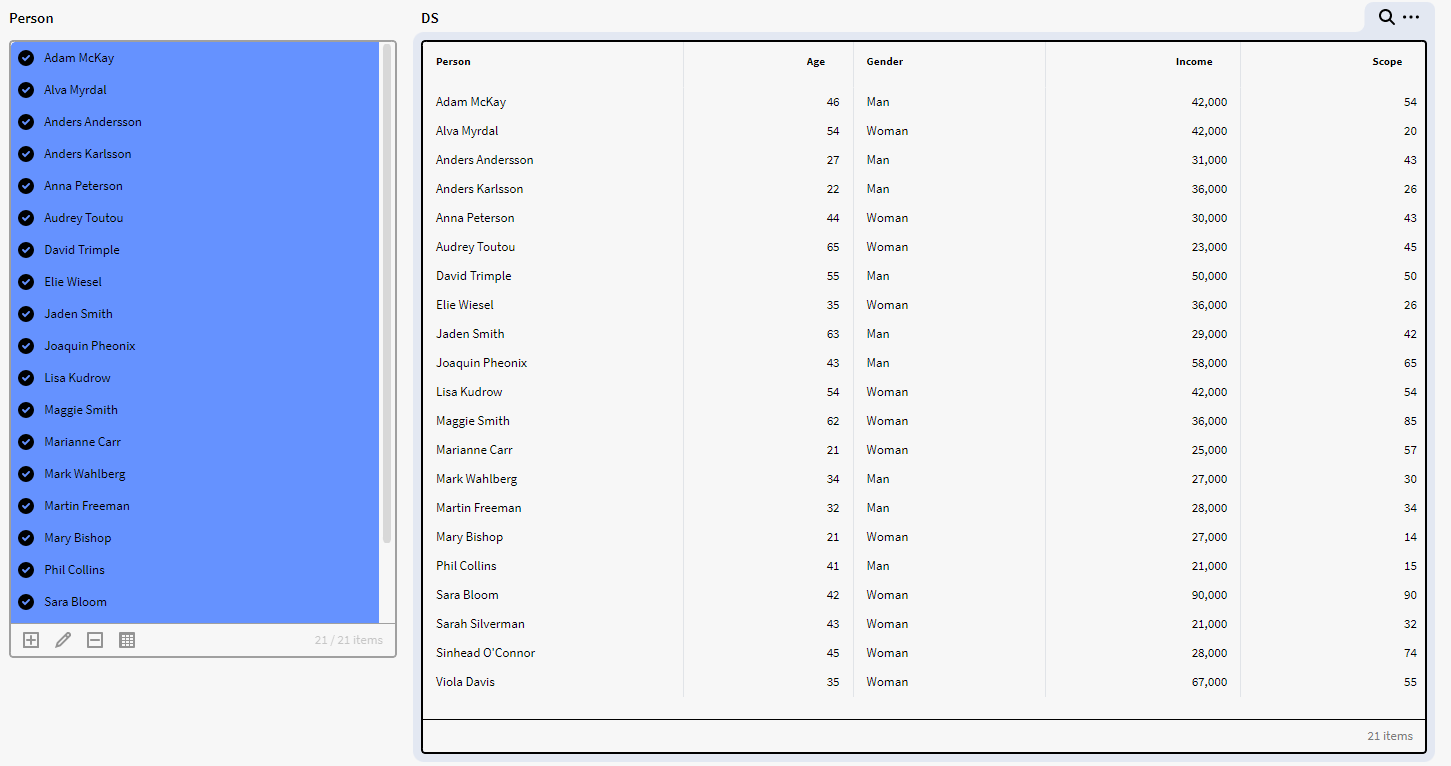
We want to add two other columns which should show the percentage for each person’s income and scope according to the total income/scope for people of the same Gender and Age. So, if two people/rows have the same age and gender the percentage will show according to the total sum of these two incomes and scopes. To achieve this we can use the below expression in a result matrix:
$PERCENT({DS}, $PACK("Income","Scope"), "Gender", "Age")
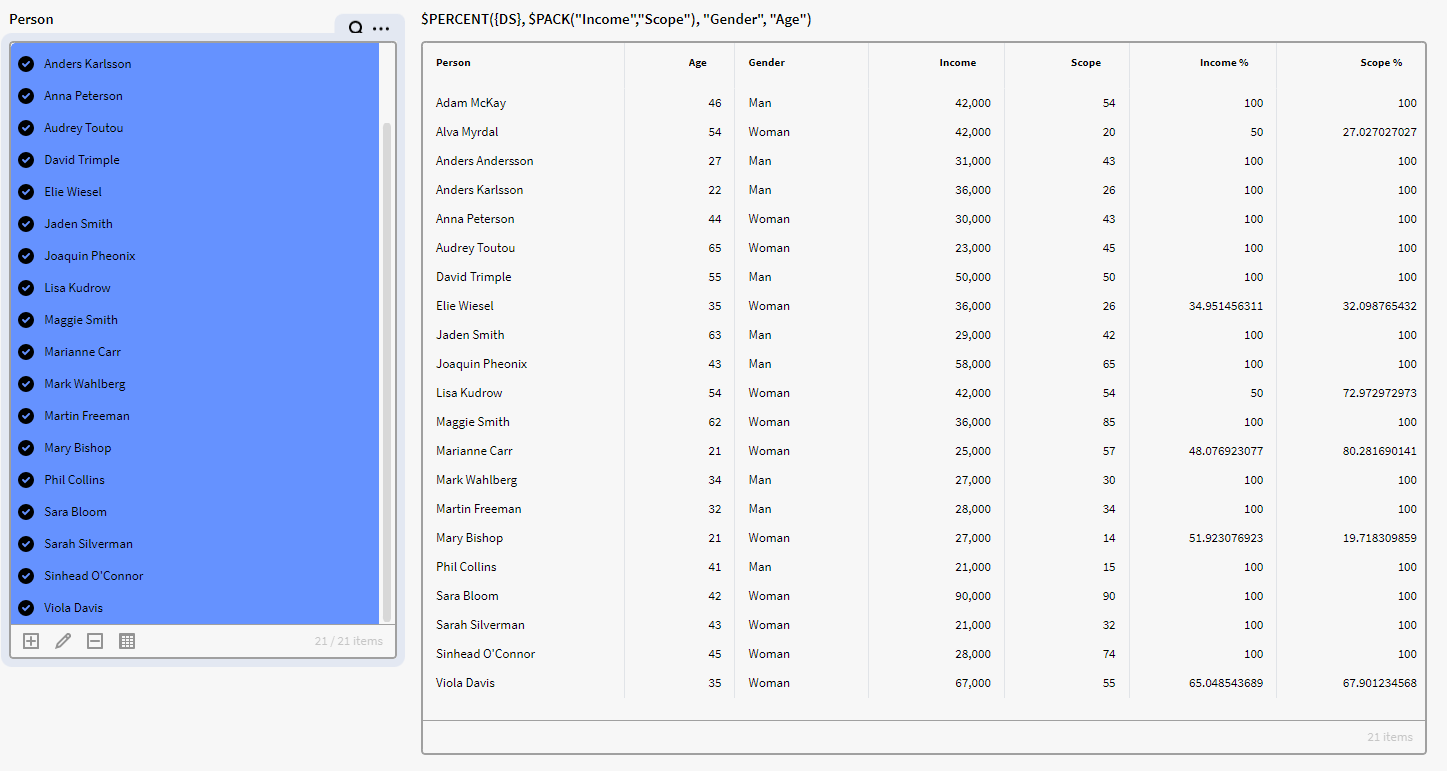
Note that If we didn’t use $PACK in the expression, Inorigo would not be able to understand that we want both Income and Scope as Value columns.
Scope would instead be read as a total grouping column and the below expression would check if there were any persons with identical values in Scope, Age and Gender before returning the percentage of total income of these people/rows.
$PERCENT({DS}, "Income", "Scope", "Age", " Gender ")
See $PERCENT for more information about the usage this expression.
$SELECT
Select rows and columns from a Dataset or a List of Dataset rows.
This function allows you to use simple variable names for cells. (e.g {cell.age} instead of $GET({record},"age").
Note:
- An empty filter parameter will make the function return all rows.
- No columns parameter will make the function return all columns.
- "*" as a column parameter will make the function return all columns.
Input:
Rows and columns from a Dataset or a List of Dataset rows.
Output:
A new dataset
Usage:
$SELECT({MyDataset}, {cell.age} > 21, "name","age").
$SELECT({MyDataset}, $GET({record},"age") > 21, "name","age").
$SELECT({MyDataset}, , "name","age").
$SELECT({MyDataset}, , $PACK("name","age")).
Example:
We have a dataset containing instances of the definition Person with attributes, Age, Scope, Gender, Income and Start Date.
Here is the default dataset DS tin a result matrix
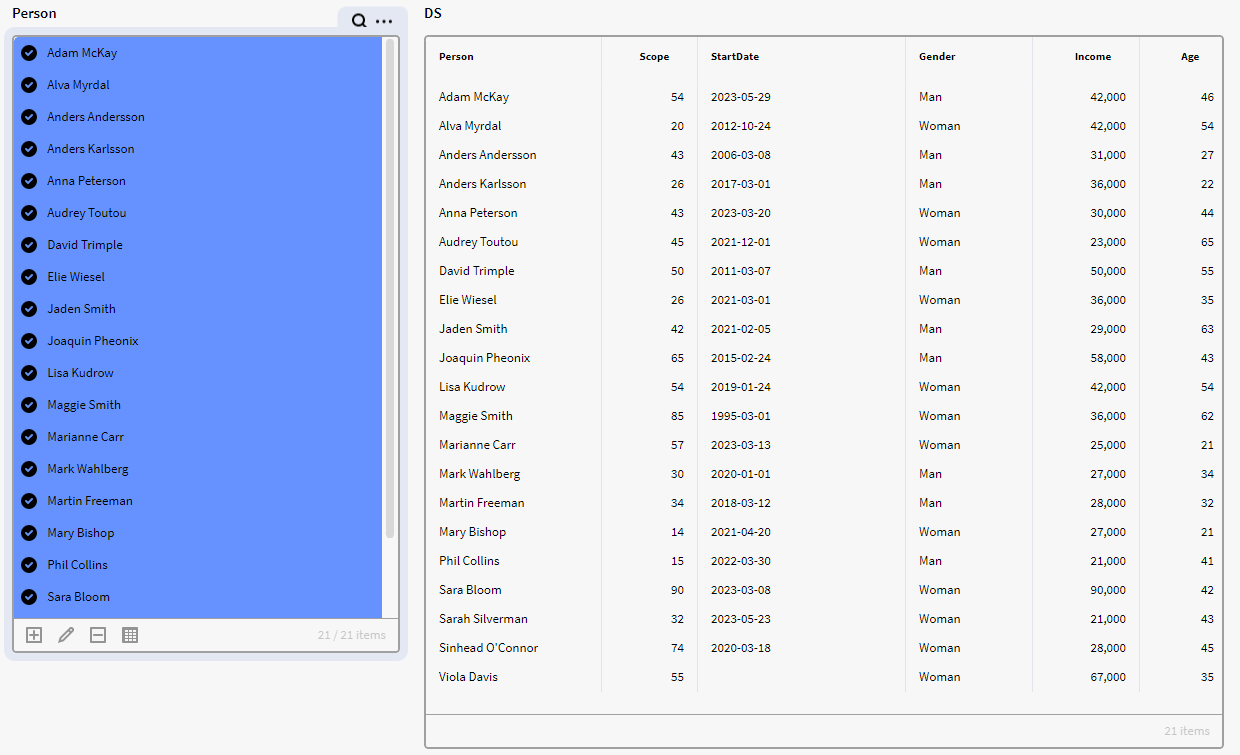
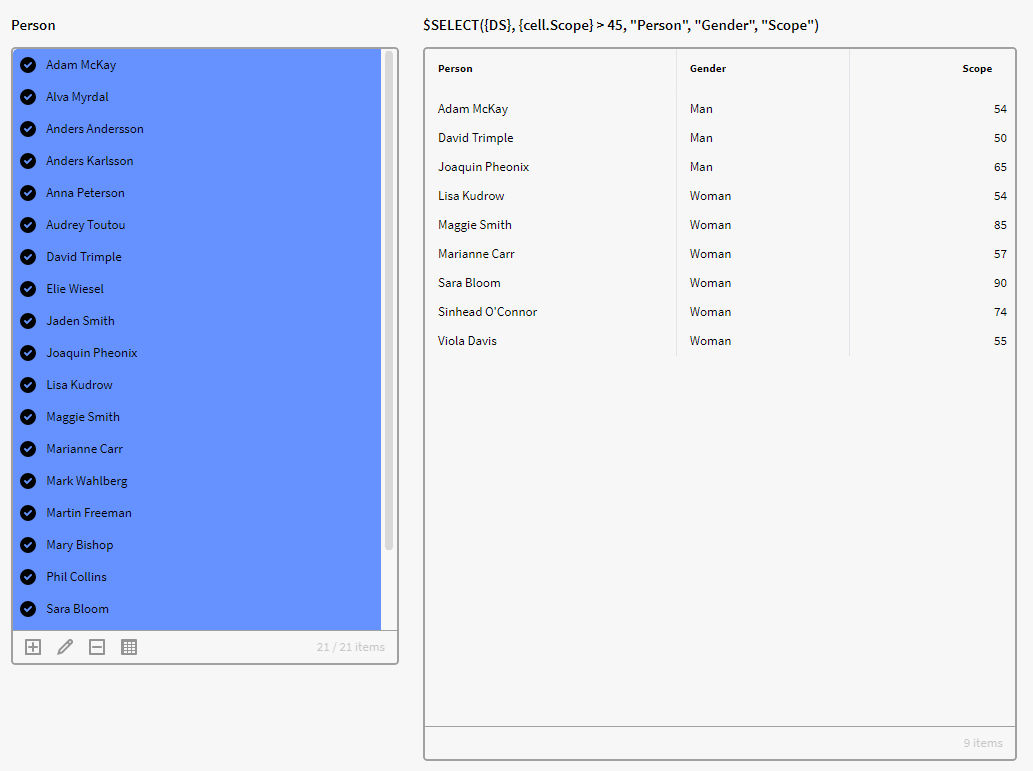
But we want to only see the people with a Scope attribute value above 45 with the columns Person, Gender, and Scope in our result matrix. So, we add the below expressionto achieve this:
$SELECT({DS}, {cell.Scope} > 45, "Person", "Gender", "Scope")
$SIZE
Performs a size operation on a value.
Input:
Array / Collection / List / String.
Output:
The size as an integer.
Usage:
$SIZE({Dataset}) ->Size of a collection.
$SIZE("Hello") ->Size of a string.
$SIZE({p0}) ->number of selected items in a filter box
Example 1:
To check if any item is selected in p0 we can use the below expression. Note that it will be a Boolean expression since we add the > operator. So, we add the expression into a calculation box and it will return true or false depending on whether any object is selected in p0.
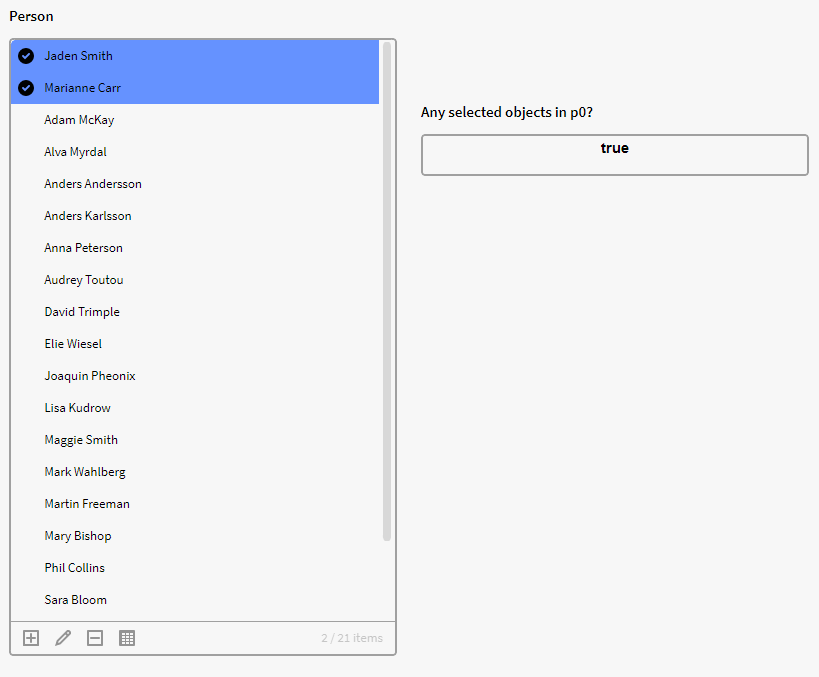
We are asking Inorigo if the size/number of the selected objects in p0 is larger than zero.
$Size({p0}) > 0
Not selected
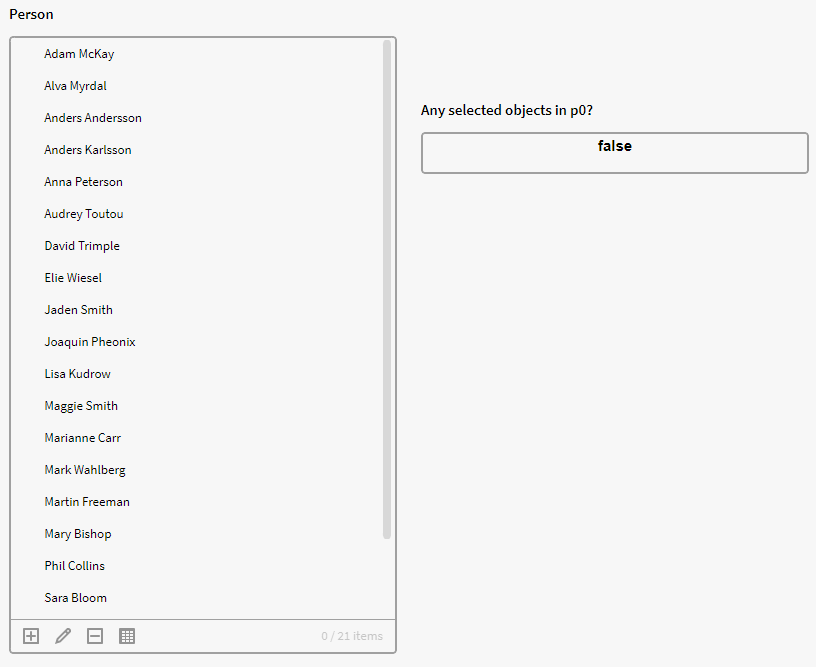
Selected
Example 2:
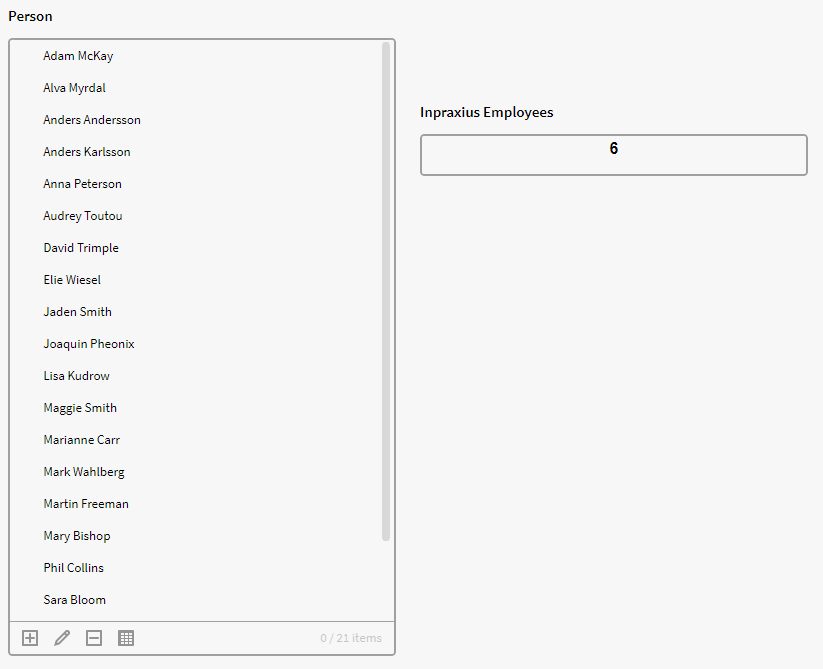
Here we want to see how many in p0 that has the attribute value "Inpraxius" in the attribute Employment. We therefore use the SIZE function together with a GET and FILTER function.
This expression is telling Inorigo to filter the whole list in p0 (p0.all), to only output the rows that has an Employment equal to the string "Inpraxius" and then count the number of objects from the result with SIZE
$SIZE($FILTER({p0.all}, $GET({record}, "Employment") = "Inpraxius"))
$SORT
Performs sorting on a collection of items.
Input:
Items. A collection of items
Optional - Descending. Default is false (i.e ascending).
Optional - Case sensitive. The default is true.
Optional - Attributes for sorting instances on specified attributes.
Output:
Sorted list.
Usage:
$SORT({p0}, false, true)
$SORT({p0}, false, true, "Amount", "Category")
$SORT(@ListOfNumbers)
Example:
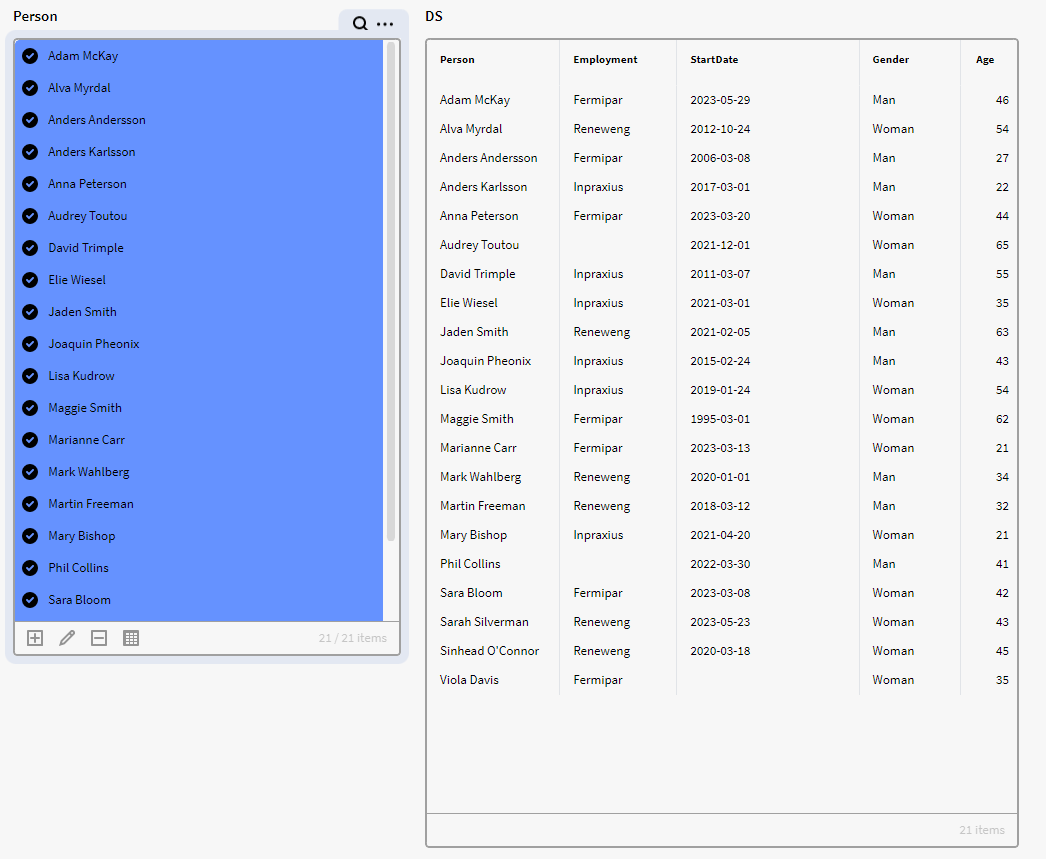
We have a dataset (DS) containing instances of the definition Person with the attributes Age, Gender, Employment and StartDate.
Default dataset "DS" in a Matrix
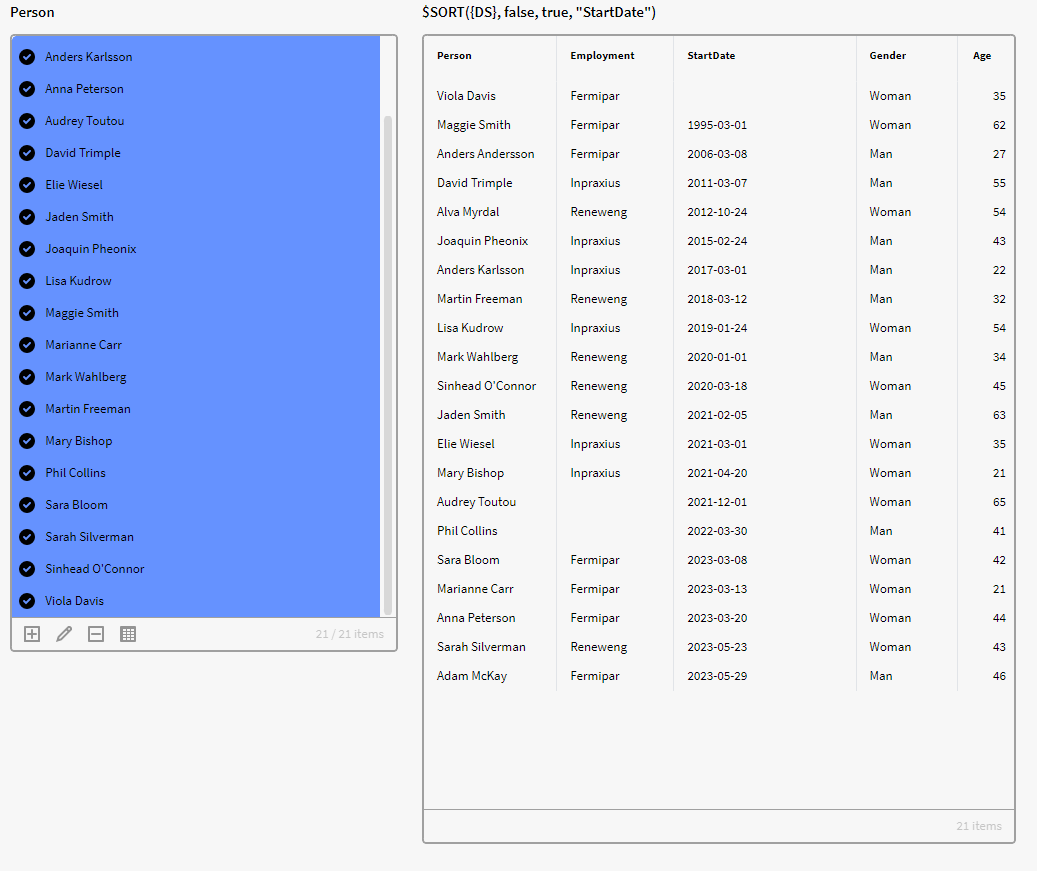
We want to sort this dataset from earliest start date to latest start date in a result matrix. We therefore use the expression below, which will sort the StartDate column in ascending order. Note also that we added true to the case sensitive option.
$SORT({DS}, false, true, "StartDate")
Result of our SORT Expression
$TOARRAY
Creates an array of the supplied input.
Some functions need their input in an array or list. This function can therefore be combined with these functions to convert the input into the correct data type.
- No input or a null first input will return a zero-length array.
- If one single input is iterable (collection/dataset/array), this will be converted into an array.
Input:
Any object(s).
Output:
Array of objects.
Usage:
$TOARRAY("a","b","c"...).
Example:
$SORT($TOARRAY("Aab", "aAc", "Aaa"), true, false) will get the result [aAc, Aab, Aaa]
$TOLIST
Creates a List of the supplied input.
Some functions need their input in an array or list. This function can therefore be combined with these functions to convert the input into the correct data type.
- No input or a null first input will return a zero-length list.
- If one single input is an array this will be converted into a list.
- If one single input is a collection this will be returned as a list.
Input:
Value(s). Any object.
Output:
List of objects.
Usage:
$TOLIST("a","b","c"...).
``
$SORT($TOLIST("Aab", "aAc", "Aaa"), true, false) will get the result [aAc, Aab, Aaa]
$OBJECT
Returns an GlobalID using the supplied identification.
Input:
Global ID or Type and ID.
Output:
GlobalID.
Usage:
$OBJECT(@MyGID).
$OBJECT("CoProduct",@MyID).
$TODATE
Parse argument to timestamp.
Null argument is returned as null. Invalid arguments will cause function to return null.
Input:
Object (java.util.Date, Long or String), String (date pattern), String (locale), java.util.Date (default date), String (time zone)
Output:
DateTime
Usage:
$TODATE("10/13/2014", "mm/dd/yyyy")
$TODATE("2022-12-28")
Example:
Expression below will convert "2022-03-21" to a date and then add two days, resulting in the date 2022-03-23 as an output:
$ADDDAY($TODATE("2022-03-21"), 2)
$TODATETIME
Parse argument to timestamp.
Note! Null first argument will return now. Invalid arguments will cause function to return null.
Input:
String/DateTime
Output:
DateTime
Usage:
$TODATETIME("10/13/2014", "mm/dd/yyyy")
$TODOUBLE
Parses argument to double
Input:
String/Number or Collection of String/Number
Output:
Double
Usage:
$TODOUBLE(42) == 42.0
$TODOUBLE("34.5") == 34.5
$TODOUBLE(@MyNumericString)
$TOGLOBALID
Creates a GlobalID.
Usage:
$TOGLOBALID(Class [as string], UUID [as string])
$TOGLOBALID(GlobalID [as string])
$TOINT
Parse argument to integer
Input:
String/Number or Collection of String/Number
Output:
Integer
Usage:
$TOINT(42) == 42
$TOINT("34") == 34
$TOINT(@MyNumericString)
$TOLONG
Parse argument to long.
Long is a datatype similar to integer but can hold larger values.
Input:
String/Number or Collection of String/Number
Output:
Long
Usage:
$TOLONG(42) == 42
$TOLONG("34") == 34
$TOLONG(@MyNumericString)
$TOSTRING
Returns a string representing the object
Note! Null first argument will return empty string.
Input:
Any
Output:
String
Usage:
$TOSTRING(42.0) -> "42.0"
$TOSTRING(@MyGlobaID) -> Default presentation string for the identified entity.
Example:
In this example we have a Filterbox (p13) in Application Builder containing several Knowledge Sets. We want to be able to see the IDs for each of these so we add the expression below to a Calculation Box:
Result on web
$TOULONG
Parse argument to unsigned long (BigInteger)
Input:
String/Number or Collection of String/Number
Output:
Unsigned Long
Usage:
$TOULONG(42) == 42
$TOULONG("34") == 34
$TOULONG(@MyNumericString)
DateTime Functions
Whats is a DateTime Function?
These functions performs an action or calculation on a date and time value
$DATE_LONG
Formats a timestamp according to Datatimelayout DATE_LONG format: "EEE, d MMM yyyy"
Input:
Date to be formatted
Output:
String
Usage:
$DATE_LONG(@MyDate).
$DATE_SHORT
Formats a timestamp according to DataTimeLayout DATE_SHORT format: "yyyy-MM-dd"
Input:
Date to be formatted
Output:
String
Usage:
$DATE_SHORT(@MyDate).
$DATEADD
Adds to a given date depending on DatePart.
Note! Use a negative number to subtract. Only numeric DateParts are supported.
Input:
DateTime, DatePart, Integer
Output:
DateTime
Usage:
$DATEADD("HOUR", @MyDate, 36).
$DATEADD("WEEK", @MyDate, 4).
$ADDDAY(@NOW, 2) → Adds two days to todays date
$DATEFORMAT
Formats a timestamp as a string.
Note! Month is specified by capitalized MM and Minute by lowercase mm**
Input:**
Date to be formatted
Output:
String
Usage:
$DATEFORMAT(@MyDate, "DATE_SHORT").
$DATEFORMAT(@MyDate, "DATETIME_LONG").
$DATEFORMAT(@MyDate, "yyyy-MM-dd").
$DATEFORMAT($NOW(), "MM/dd yyyy").
$DATEFORMAT($NOW(), "MM/dd yyyy").
$DATEPART
Returns the desired date part of a timestamp.
Input:
DateTime, DatePart
Output:
Integer/String
Usage:
$DATEPART(@MyDate, "MONTH").
$DATEPART(@MyDate, "QUARTER").
$DATEPART(@MyDate, "YEAR_QUARTER").
$DATEPART($Now(),"Year") -> (e.g.) 2015
$DATETIME_LONG
Formats a timestamp according to DataTimeLayout DATETIME_LONG format: "EEE, d MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss"
Input:
Date to be formatted
Output:
String
Usage:
$DATETIME_LONG(@MyDate).
$DATETIME_LONG($NOW()).
$DATETIME_SHORT
Formats a timestamp according to DataTimeLayout DATETIME_SHORT format: "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
Input:
Date to be formatted
Output:
String
Usage:
$DATETIME_SHORT(@MyDate).
$DATETIME_SHORT($NOW()).
$DAY
Calculate the day of a date, or the current day if no date argument is passed.
Input:
DateTime
Output:
Integer
Usage:
$DAY(@MyDate)
$DAY()
$DAY(@NOW) → If today is 2023-05-30 it will output 30
$DAYNAME
Calculate the day name of a date, or the current day name if no date argument is passed.
Input:
DateTime
Output:
String
Usage:
$DAYNAME(@MyDate)
$DAYNAME()
$DAYNAME(@NOW) → will output for example "Tuesday", if today is a tuesday.
$HOUR
Calculate the hour of a date, or the current hour if no date argument is passed.
Input:
Datetime
Output:
Integer
Usage:
$HOUR(@MyDate)
$HOUR()
$HOUR(@NOW) → will output for example 10 if now is 10:00 o'clock
$MILLIESECOND
Calculate the millisecond of a date, or the current millisecond if no date argument is passed.
Input:
DateTime
Output:
Integer
Usage:
$MILLISECOND(@DATE)
$MILLISECOND()
$MINUTE
Calculate the minute of a date, or the current minute if no date argument is passed.
Input:
DateTime
Output:
Integer
Usage:
$MINUTE(@MyDate)
$MINUTE() → will for example output 3 if the current time is 10:03
$MONTH
Calculate the month of a date, or the current month if no date argument is passed.
Note! Index is zero based so it will start at zero: January = 0
Input:
DateTime
Output:
Integer
Usage:
$MONTH(@MyDate)
$MONTH()
$MONTH($TODATE("2023-12-12")) → 11
$MONTHNAME
Calculate the month name of a date, or the current month name if no date argument is passed.
Input:
DateTime
Output:
String
Usage:
$MONTHNAME(@MyDate)
$MONTHNAME()
$MONTHNAME() -> (e.g.) June
$NOW
Calculates the current date and time.
Usage:
$NOW()
$QUARTER
Calculate the quarter of a date, or the current quarter if no date argument is passed.
Input:
DateTime
Output:
Integer
Usage:
$QUARTER(@MyDate)
$QUARTER()
$QUARTER($TODATE("2023-12-12")) → 4
$QUARTERNAME
Calculate the quarter name of a date, or the current quarter name if no date argument is passed.
Input:
DateTime
Output:
String
Usage:
$QUARTERNAME(@MyDate)
$QUARTERNAME() → eg. Q2
$SECOND
Calculate the second of a date, or the current second if no date argument is passed.
Input:
DateTime
Output:
Integer
Usage:
$SECOND(@MyDate)
$SECOND()
$TIME_SHORT
Formats a timestamp according toDateTimeLayout - Time Short
Usage:
$TIME_SHORT(@MyDate).
$TIME_SHORT($NOW()). eg. 13:19:14
$TIME_SHORT_MILLIES
Formats a timestamp according to DateTimeLayout - TIME_SHORT_MILLIES format: "HH:mm:ss.SSS"
Usage:
$TIME_SHORT_MILLIES(@MyDate).
$TIME_SHORT_MILLIES(@NOW). eg. 13:20:06.518
$TIMESPAN
Calculates the timespan between two timestamps or a duration.
Input:
DateTime date1, DateTime date2, String Datepart
Output:
Timespan/Long
Usage:
$TIMESPAN(@MyDate1, @MyDate2) returns a Timespan object, useful for output like "8h 5m 34s".
$TIMESPAN(date1, date2, "WEEK")
An example using dataset: $LOOP({DATASET},[$timespan($get({record},"p37"),$get({record},"p38"), "WEEK")])
Example:
The below expression will return the time between 2023-01-08 and 2023-02-09:
$TIMESPAN($TODATE("2023-01-08"), $TODATE("2023-02-09"))
$WEEK
Calculate the week of a date, or the current week if no date argument is passed.
Input:
DateTime
Output:
Integer
Usage:
$WEEK(@MyDate)
$WEEK()
$WEEK($TODATE("2023-12-12")) → 50
$YEAR
Calculate the year of a date, or the current year if no date argument is passed.
Input:
DateTime
Output:
Integer
Usage:
$YEAR(@MyDate)
$YEAR()
$YEAR($TODATE("2023-12-12")) → 2023
$YEAR_QUARTER
Calculate the year and quarter name of a date, or the current year and quarter name if no date argument is passed.
Input:
DateTime
Output:
String
Usage:
$YEAR_QUARTER(@MyDate)
$YEAR_QUARTER() eg. 2023 - Q2
Deprecated Functions
Whats is a Deprecated Function?
These functions is no longer relevant and users are discouraged to use these functions.
$LOAD
Returns an entity using the supplied identification.
Input:
- Global ID or Type and ID.
Output:
- GlobalID.
Usage:
$LOAD(@MyGID).
$LOAD("CoProduct",@MyID).
Entity Functions
$GET
Returns an Attribute Value. Can also be used to get a hash map value.
The index parameter is optional
Input:**
DataObject,String[, Integer]
Output:**
Any
Usage:**
$GET(entity, attribute name [, index])
$GET(entity, attribute id [, index])
Example:
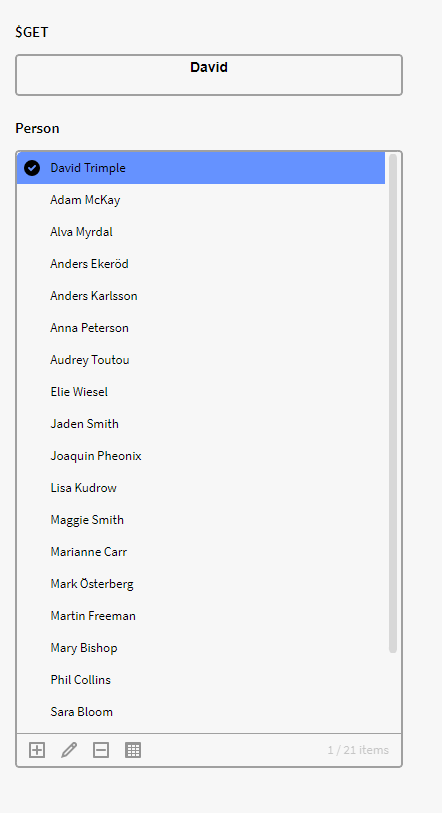
In this example we have a filter box (p0) containing instances of Person with the attributes First Name and Last Name. We want to get the Last name in a calculation box. We therefore use the below expression:
$GET({p0}, "First Name")
Logic Functions
What is a logic function?
These functions are used to manipulate and evaluate boolean values or conditions.
$CASE
Returns the first argument following a boolean true argument.
Input:
condition, val, condition2, val2, ...
Output:
Any
Usage:
$CASE(false, 42, true, 12) -> 12
$CASE(true, 42, true, 12) -> 42
$CASE(false, 42, false, 12) -> null
Example 1:
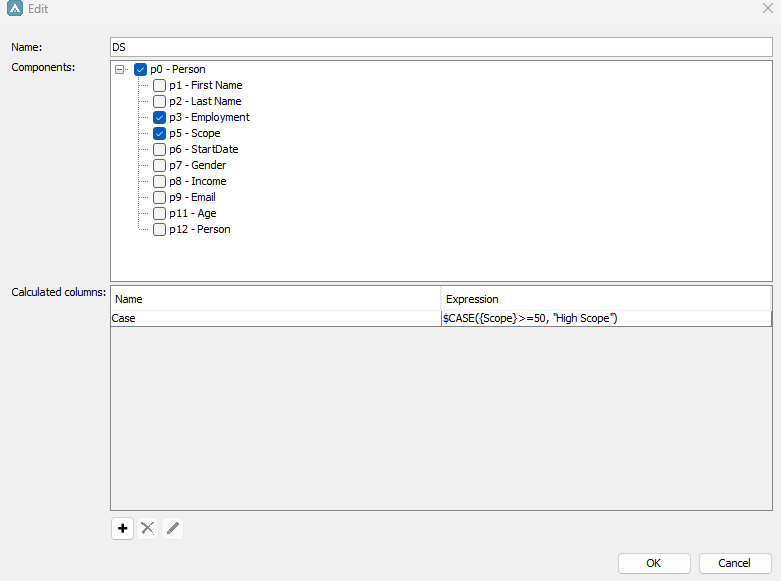
In the below example we have created a dataset which consists of the Definition node Person with the attributes Employment and Scope. We want to check the people in the dataset have a high scope (equal or above 50) or a low scope (lower than 50), we therefore create a calculated column in our dataset with the expression:
$CASE({Scope}>=50, "High Scope")
Adding the DS dataset in a matrix will then result in below image when opening on the web. Showing the Person instances.
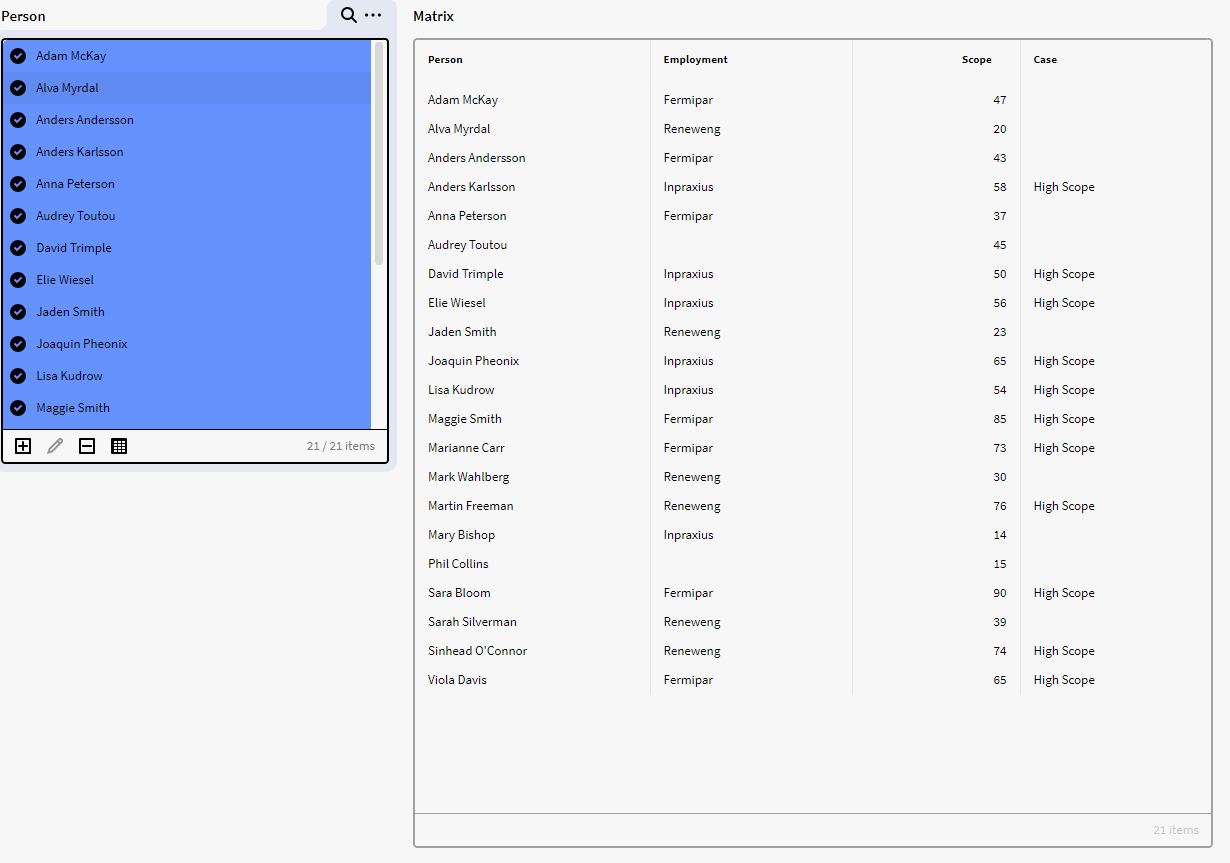
This is a very basic demonstration of the CASE function works. Which is similar to that of the IIF function, with the difference that we only supply a value for a true boolean argument.
Example 2:
You can do simple expressions with the Case function as above but what $CASE is truly useful for is longer more complex case expressions. Such as below:
$CASE({Scope} > 20 && {Employment} = "Fermipar", "High scope [Fer]", {Scope} > 40 && {Employment} = "Inpraxius", "High Scope [Inp]", {Scope} > 60 && {Employment} = "Reneweng", "High Scope [Ren]")
- What the function will do here is first check if the first condition is true, is Scope value higher than 20 and is the employment equal to Fermipar. If true then return the first argument, which is the string "High Scope [Fer]".
- If the first condition is not true, it will check if the second condition is true, is Scope value higher than 40 and is the employment equal to Inpraxius. If this second condition is true it will return the second argument, which is the string "High Scope [Inp]".
- But if the second condition is also not true it will then check the third condition and so on.
So you can create a very long case expression which will check a large number of conditions and return your desired argument for each condition (if true). But if the condition is false it will check the next condition.
If we now put this more complex expression containing the $CASE Function into the same dataset and calculated column as the first example, we will get the below view instead.
$IFNULL
Returns second or third argument, depending on whether first argument is null.
Input:
Expression to test whether null.
value if null
value if not null.
Output:
The value specified depending on if expression is null or not.
Usage:
$IFNULL(@NULL, 42, 12) -> 42
$IFNULL("yxa", 42, 12) -> 12
Example:
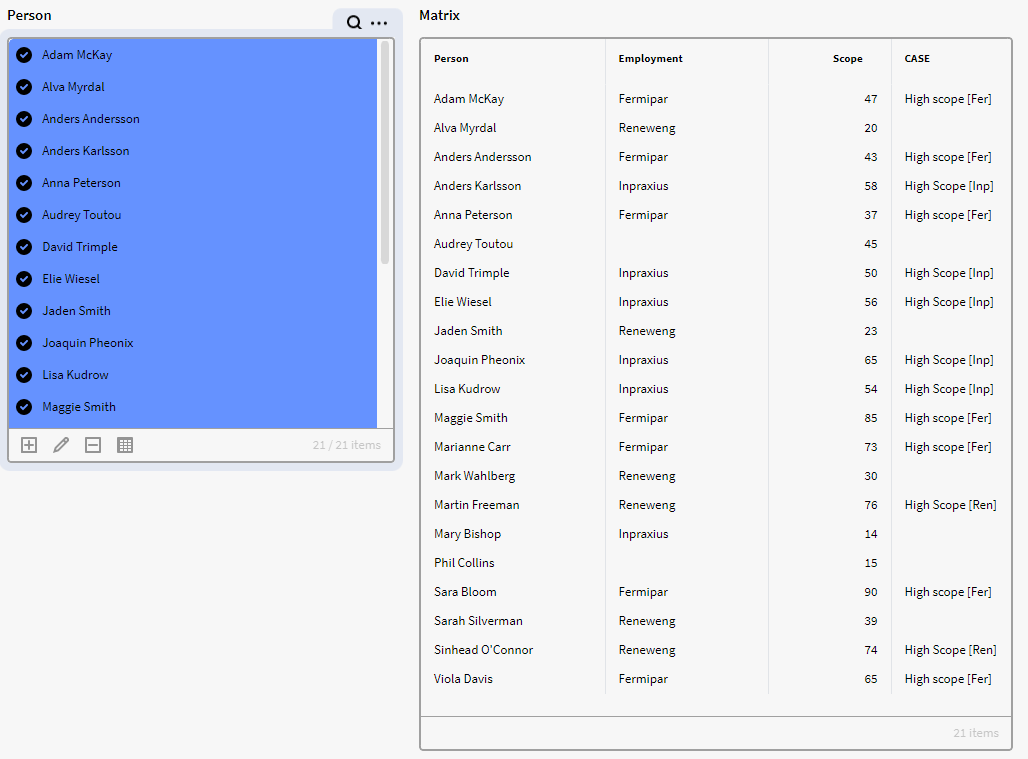
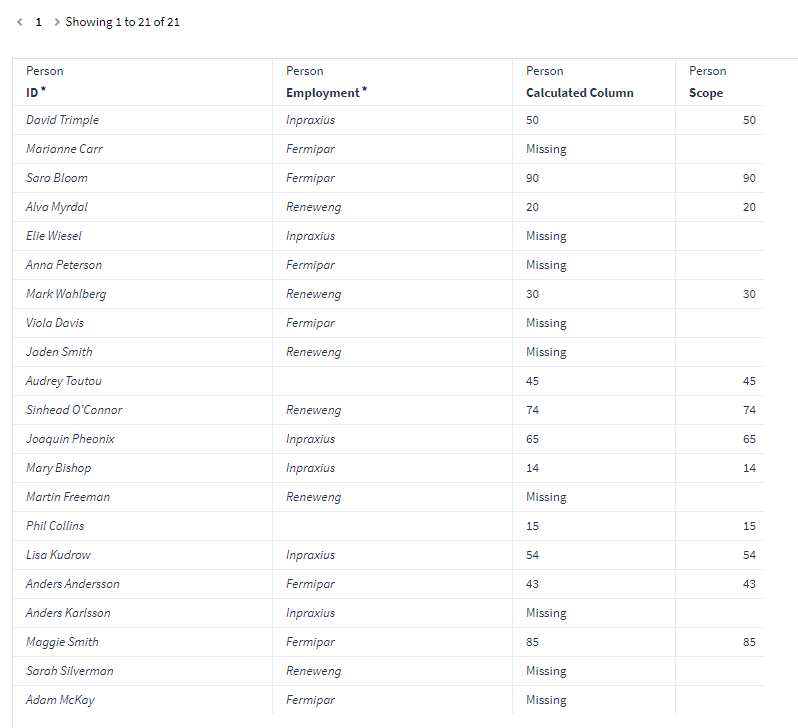
In the below example we have created a dataset in Knowledge Builder which consists of the Definition node Person with attributes Employment and Scope. But as you can see some people are missing Scope Attribute values in the list:
We want to check if we are missing any data in the attribute “Scope” in the dataset, so we add a calculated column and add our expression:
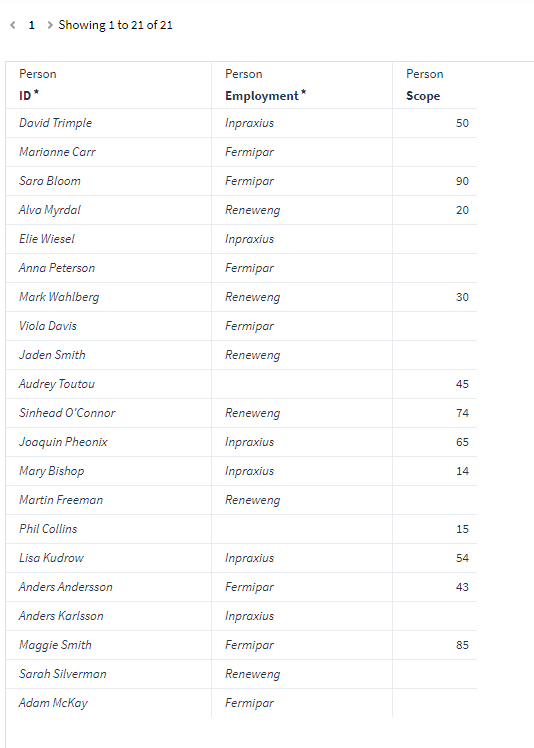
$IFNULL({Scope}, "Missing", "")
This expression will check each row in the dataset to see if there are any null values (empty) in the “Scope” attribute, if so, it will add a string called “Missing” and if any other value is found it will return blank (“”).
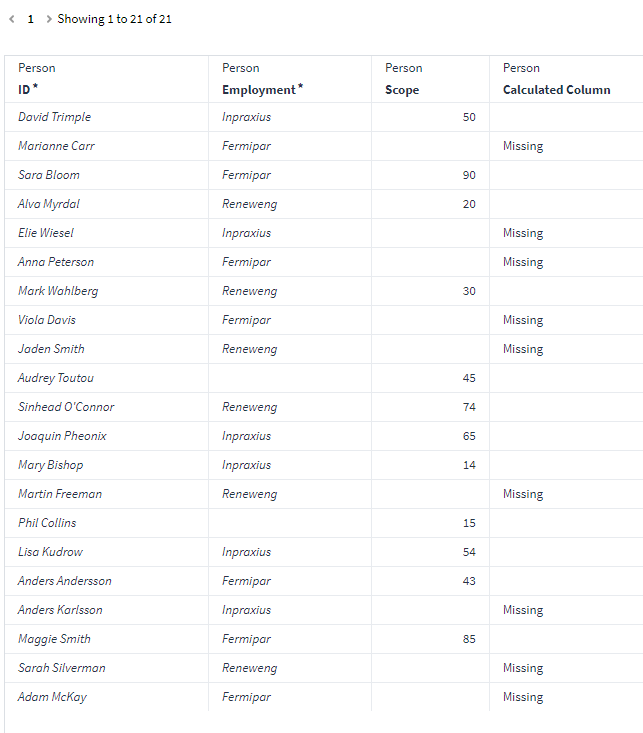
But lets say we want the "missing" text in the same column as the Scope attribute values. So if person has a value it will show the scope value but if null it will return "missing" in the cell.
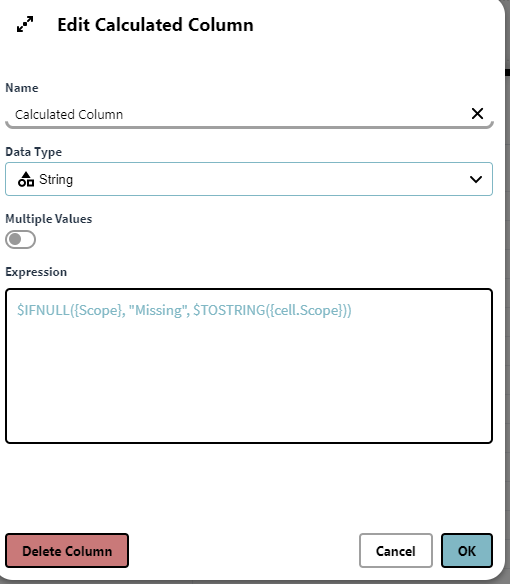
What we can do here is edit our calculated column and change the expression to the below. This will check if any row in the Scope column is null, and if true it will return "missing" but if false it will return the Scope attribute value. Notice also that we convert the if false argument to a string as we have the data type as String.
$IFNULL({Scope}, "Missing", $TOSTRING({cell.Scope}))
Now we click okay and Run the program. Which will result in the below view with all the info in one column:
$IIF
Returns second or third argument, depending on boolean first argument.
Input:
condition
value if true
value if false
Output:
Any
Usage:
$IIF(true, 42, 12) -> 42
\ `$IIF(false, 42, 12) -> 12`\
$IIF($EXPR("50 > 12"), 42, 12) -> 42
Example 1
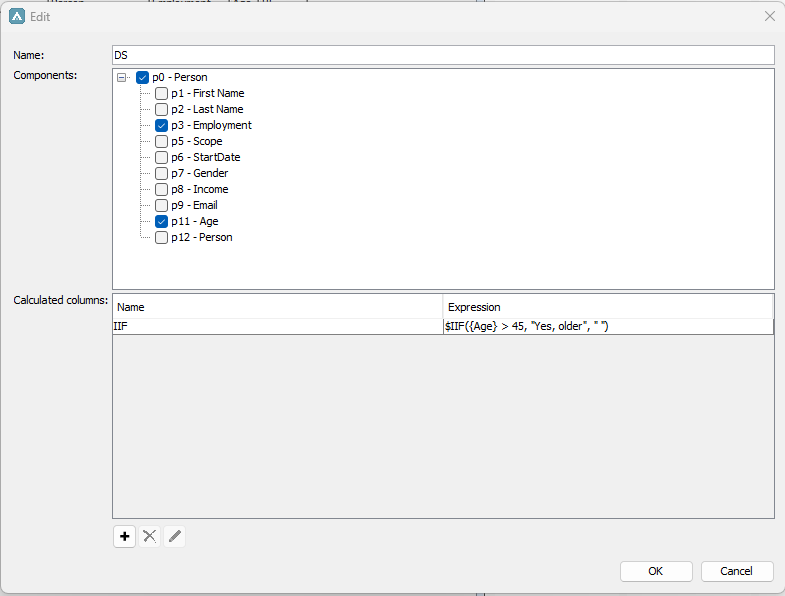
In the below example we have created a dataset in Application Builder which consists of the definition Person with the attributes Employment and Age.
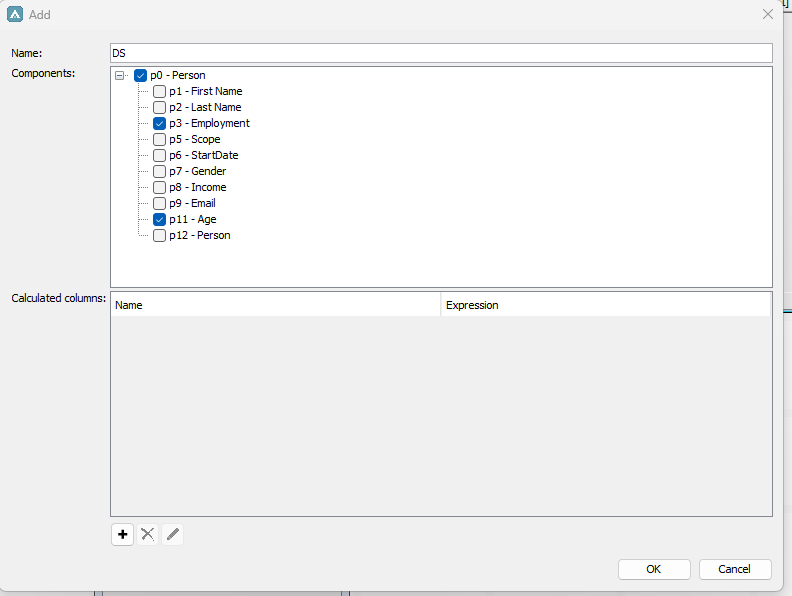
We want to quickly check if we have any persons older than 45 in the dataset, so we add a calculated column in our dataset and add our below expression:
$IIF({Age} > 45, "Yes, older", " ")
This expression will check if there are any rows with a value larger than 45 in the “Age” attribute, if so, it will add a string called “Yes, older” in the calculated column. If any other value is found it will return blank.
Lastly, we open the DS dataset in a result matrix:
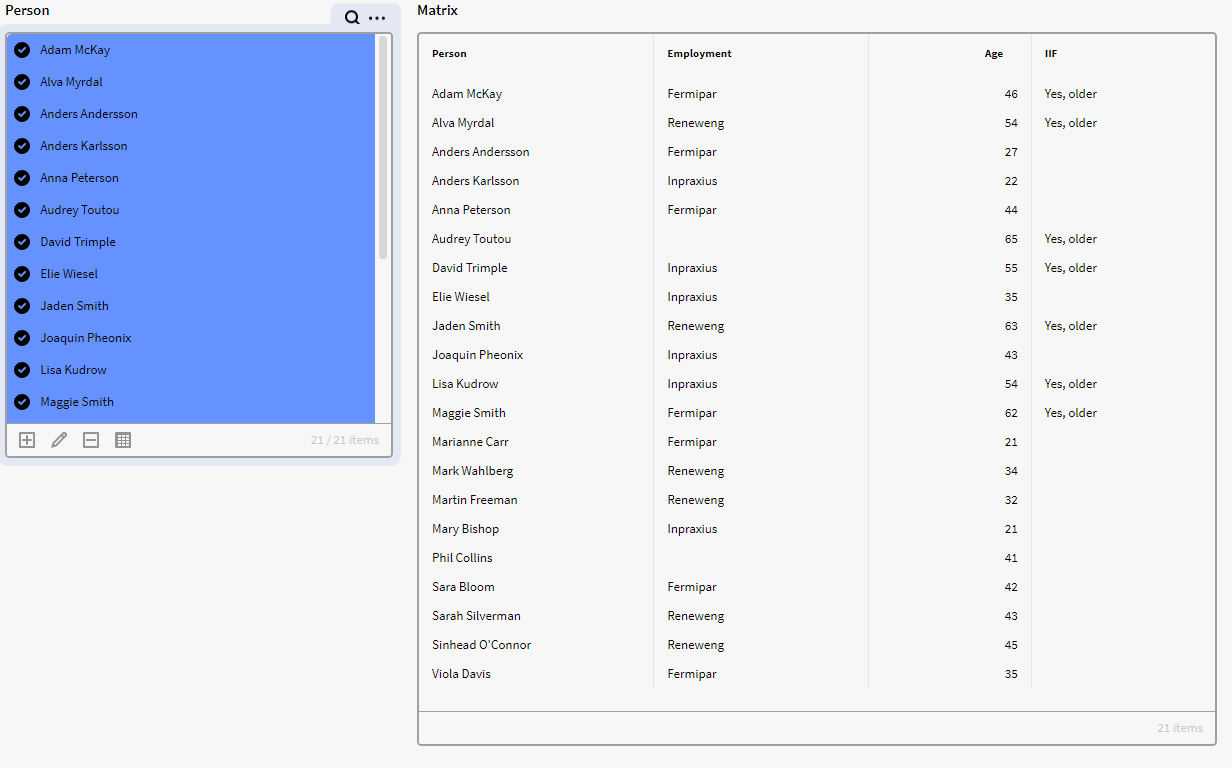
Example 2
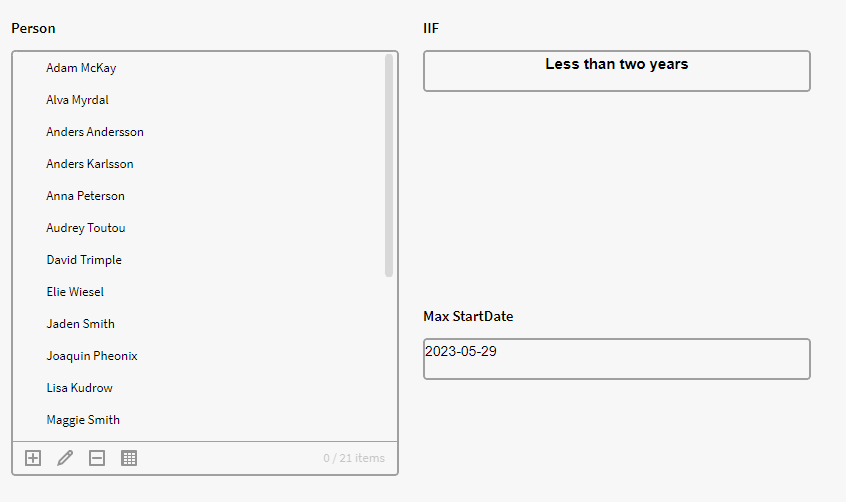
We have a filter box containing the instances of the definition Person with the attributes Employment and Start Date. We want to check if the latest employed person have been employed for 2 years or more. To check this, we can add a the below expression to a calculation box:
$IIF($MAX($get({p0.all},"StartDate"))>=$AddYear($NOW(), -2), "Less than two years", "More than 2 years")
Step by step explanation:
- *This expression will get the max value on the attribute StartDate (latest date) from all items in the p0 list.
$MAX($GET({p0.all},"StartDate"))* - *Then compare if it’s equal or later than 2 years ago
>=$AddYear($NOW(), -2)* - *If true the expression will output “Less than 2 years”, and if false it will output “More than 2 years”.
$IIF($MAX($get({p0.all},"StartDate"))>=$AddYear($NOW(), -2), "Less than two years", "More than 2 years")*
Result:
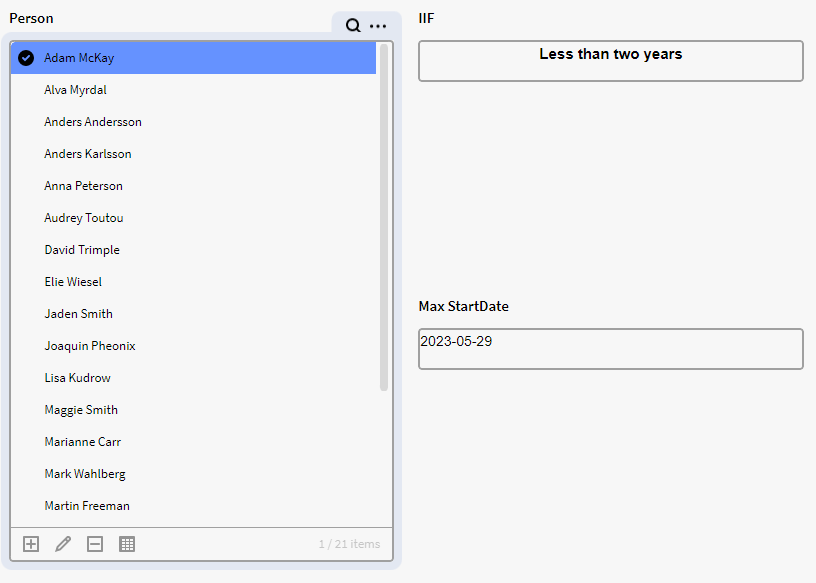
Extra: Initial Filter for item with latest start date
If we want to add a selection filter to p0 that will also select the Person with the latest start date in p0, we can add the below expression to the "Initial Selection" expression text box for p0:
{record} = $FILTER({p0.all},$GET({record}, "StartDate") = $MAX($GET({p0.all}, "StartDate")))
$ISNULL
Returns wether first argument is null.
The $ISNULL function works similar to the $IFNULL function with the difference that ISNULL is strictly boolean that will return either true or false.
Input:
Expression to test if null.
Output:
True or false depending on if expression is null or not.
Usage:
$ISNULL(@NULL) -> true
$ISNULL("yxa") -> false
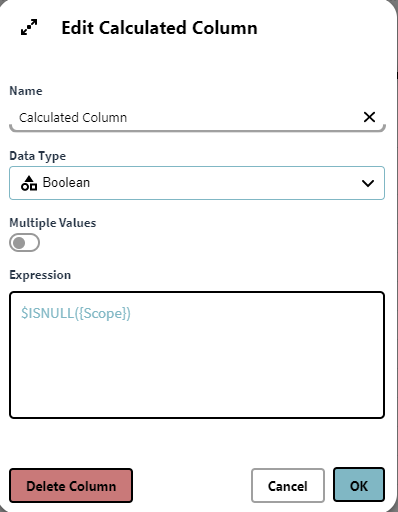
Example 1:
Working with a Dataset containing the Instances of the Definition Person with the attributes Employment and Scope in Knowledge Builder, we want a new calculated column containing true or false depending on whether the same row has any value in the Scope column:
$ISNULL({Scope})
This is the result of the expression in a calculated column:
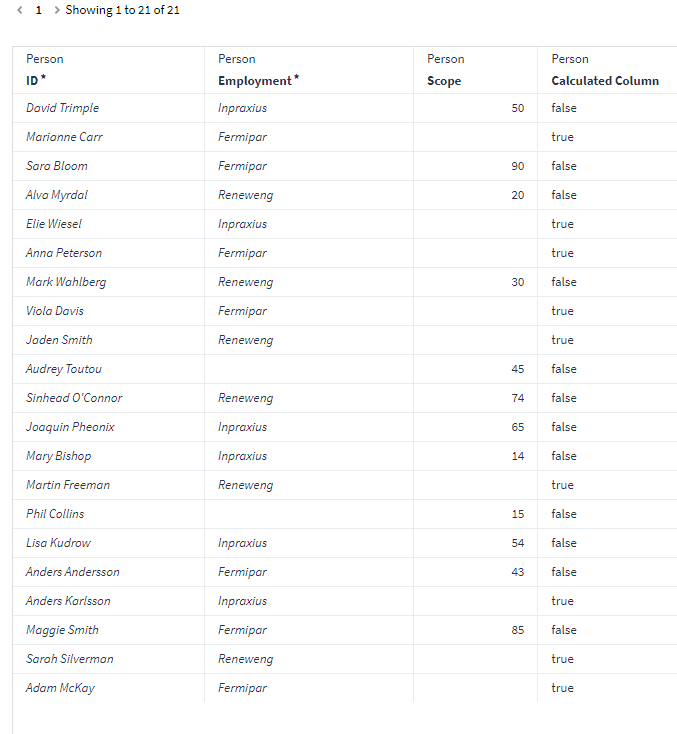
It can be useful to use this function as an argument in anther function such as $IIF, as $IIF requires a boolean argument as an input. So, if Scope is null/true then return something else.
Example 2:
In this example we have the same dataset with the definition Person and attributes Employment and Scope. But now we want to check if the Scope value is null and if the employment is equal to Fermipar, as these are the only ones that actually required Scope values. What we can do here is is the below expression:
$IIF($ISNULL({Scope}) && {Employment} == "Fermipar", "Part of Fermipar. Missing Scope", " ")
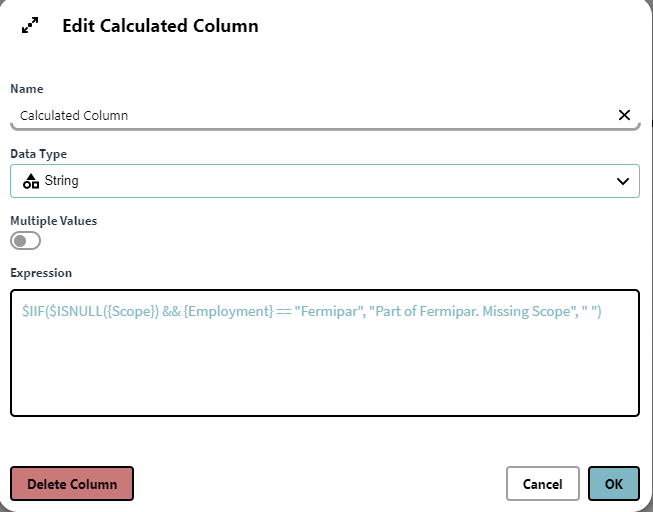
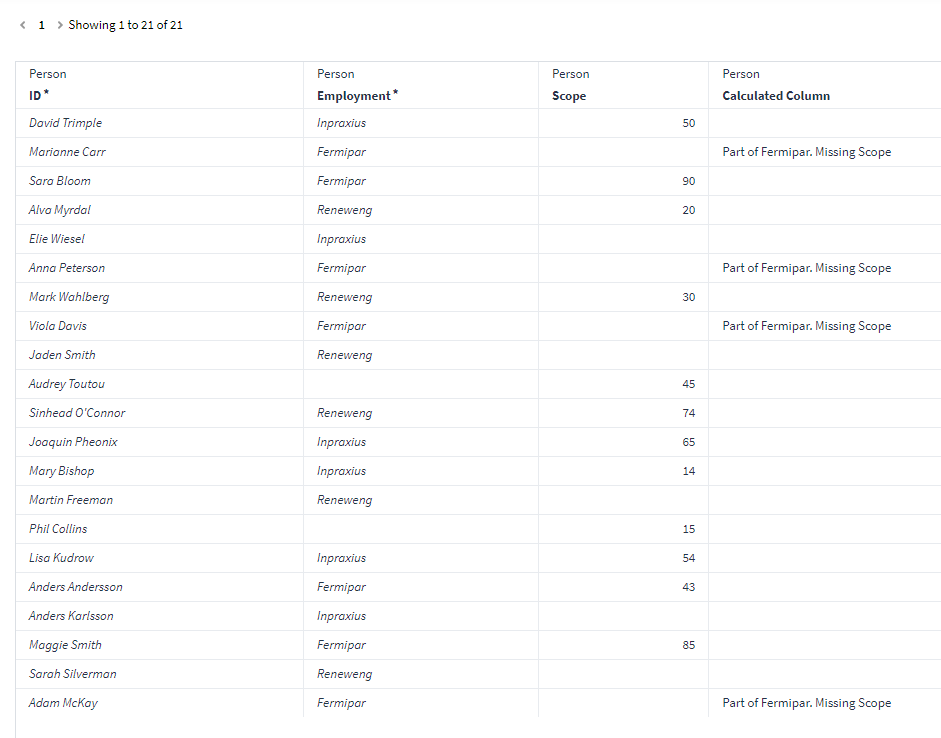
This expression will check if the scope value is empty and employment is equal to Fermipar, if true it will return the string "Part of Fermipar. Missing Scope", and if false it will return nothing " ". Resulting in the below result table view:
Math Functions
What is a Math function?
These functions can be used to to work on math calculations.
$ABS
Calculates the absolute value of a double value.
The non-negative value of x without regard to its sign. For example, the absolute value of 5 is 5, and the absolute value of −5 is also 5
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$ABS(@myNumber)
$ABS(-20) -> Returns value 20.
$ACOS
Calculates the arc cosine of a number.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$ACOS(@myNumber)
$ACOS(0) ->1.570796327
$ASIN
Calculates the arc sine of a number.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$ASIN(@myNumber)
$ASIN(1) →1.570796327
$ATAN
Calculates the arc tangent of a number.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$ATAN(@MyNumber)
$ATAN(1) ->0.785398163
$CIEL
Calculates the smallest (closest to negative infinity) double value that is greater than or equal to the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$CEIL(@myNumber)
$CEIL(132.32)->133
$COS
Calculates the cosine of a number.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$COS(@myNumber)
$COS(2)→ -0.416146837
$COSH
Calculates the hyperbolic cosine of a number.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$COSH(@myNumber)
$COSH(2)->3.762195691
$COT
Calculates the cotangent of a number (1/tan(n)).
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$COT(@myNumber)
$COT(2) → -0.457657554
$CSC
Calculates the cosecant of a number (1/sin(n)).
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$CSC(@myNumber)
$CSC(2.23) → 1.265053788
$E
Calculates the double value that is closer than any other to e, the base of the natural logarithms.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$E()
$EVALUATE
The function can replace method calls and enhance performance substantially, particularly if used in a calculated column in a knowledge Set with many rows.
It is used to evaluate expressions and supports an unlimited number of arguments (parameters) with the format:
$EVALUATE(<expression>, <p0>, <p1>, …<pn>)
Sample- Formula:
$EVALUATE("{p0} - {p1}", 10, 9)
This example calculates the difference between parameters {p0} - {p1} Input values are 10 and 9 so the output = 1
$EXP
Calculates Euler's number e raised to the power of a number.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$EXP(@myNumber)
$EXP(2.123) → 8.356168428
$FLOOR
Calculates the largest (closest to positive infinity) double value that is less than or equal to the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$FLOOR(@myNumber)
$FLOOR(2.123) → 2
$LOG
Calculates the natural logarithm (base e) of a number.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$LOG(@myNumber)
$LOG(2.321) → 0.841998127
$LOG10
Calculates the base 10 logarithm of a number.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$LOG10(@myNumber)
$LOG10(2.321) → 0.36567514
$PI
Calculates the double value that is closer than any other to pi, the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$PI()
$PI(2.321) → 3.141592654
$POW
Calculates the double value of the first number raised to the power of the second number.
Input:
Double, Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$POW(@myFirsNumber,@mySecondNumber)
$POW(3.343, 2.34) → 16.845314407
$ROUND
Rounds the first argument to the number of decimals specified by the second argument, using the HALV_EVEN rounding mode. If the second argument is null or zero, the value is rounded to the nearest long.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$ROUND(@Number,@Precision)
$ROUND(3.342312, 1) → 3.3
$SEC
Calculates the secant of a number (1/cos(n)).
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$SEC(@myNumber)
$SEC(2.231) → -1.630582582
$SIN
Calculates the sine of a number.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$SIN(@myNumber)
$SIN(2.3421)→ 0.717002527
$SINH
Calculates the hyperbolic sine of a number.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$SINH(@myNumber)
$SINH(2.453) → 5.768564433
$SQRT
Calculates the square root of a number.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$SQRT(@myNumber)
$SQRT(2.41) → 1.55241747
$TAN
Calculates the tangent of a number.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$TAN(@myNumber)
$TAN(1.31) → 3.747080976
$TANH
Calculates the hyperbolic tangent of a number.
Input:
Double
Output:
Double
Usage:
$TANH(@myNumber)
$TANH(1.23) → 0.842579326
### Model Functions
$DEFINITIONS
Returns a list of definition IDs for one or several instances.
Usage:
$DEFINITIONS(@oneID).
$DEFINITIONS(@oneID, includeDefinitionSuperclasses).
$DEFINITIONS(@oneID, includeDefinitionSuperclasses, includeSuperClassDefinitions).
$DEFINITIONS(@listOfIDs).
$DEFINITIONS(@listOfIDs, includeDefinitionSuperclasses).
$DEFINITIONS(@listOfIDs, includeDefinitionSuperclasses, includeSuperClassDefinitions).
$DEFINITIONS(@p0).
$DEFINITIONS(@p0, includeDefinitionSuperclasses).
$DEFINITIONS(@p0, includeDefinitionSuperclasses, includeSuperClassDefinitions).
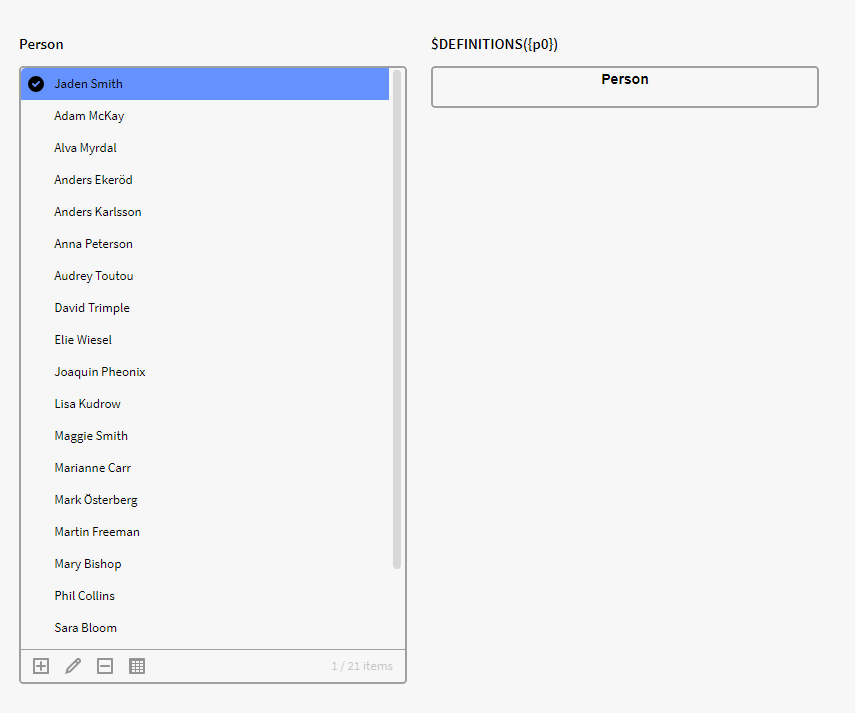
Example:
Here we have a list of Instances of the definition Person in Filter box p0. By using the below expression we can see what definition the selected Instance in p0 has:
$DEFINITIONS({p0})
$GID
Creates a GlobalID.
Usage:
$GID(Class [as string], UUID [as string])
$GID(GlobalID [as string])
$PARTNERS
Returns a list of partner Global Identifiers.
To be able to handle lists, it is common to include $LOOP
The type of relation parameter is only used in Legacy implementation
The relation parameter can be passed as text, unique identifier or entity.
Input:
DataObject/GID target, String relationClass, String relationName, Boolean upwards, Boolean digDeep, Boolean leafsOnly
Output:
Collection
Usage:
$LOOP({p0},[$PARTNERS($get({record},"sourceGID"), "CoNode", "Classifies", true, true)])
(the input from p0 is a Specific Unit, the GET function will catch the definition and the output is all generic units that classify the definition recursively)
$REFERENTS
Returns Attribute Value referents for a given instance.
Usage:
$REFERENTS(<targetID>,<type of referent>[,<attributeID>])
$SUBCLASSES
Returns a list of subclasses.
Usage:
$SUBCLASSES(<definitionID>,<recursive>)
$SUPERCLASSES
Returns a list of superclasses.
Usage:
$SUPERCLASSES(<definitionID>,<recursive>)
Search Functions
What is a search function?
These functions will search for objects in collections.
Note: Try to use GID when applicable
$FINDMANY
Returns all GlobalIDs matching the supplied criterias.
Input:
- Type of entity.
- Attribute - Value pair(s). At least one pair must be supplied, otherwise an empty list is returned.
Output:
- List of GlobalID.
Usage:
$FINDMANY("CoProduct", "code", "1234")
$FINDMANY("AsInstance","First Name", "Alfred", "Last Name", "Nobel").
Example:
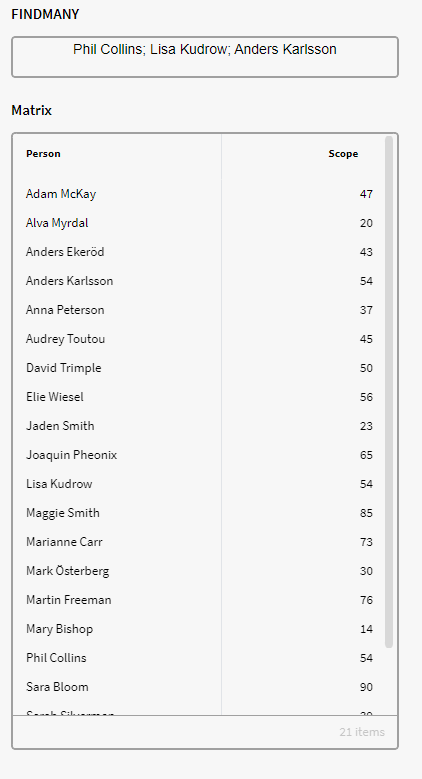
In this example we have instances of the definition Person with the attribute Scope. We want to see which of these persons has a Scope value of 54, and we want it to show several instances if they fit this description.
We can use the below expression for this, where we specify that the type of entity is "Asinstance", the attribute is "Scope" and 54 is the value to search for:
$FINDMANY("AsInstance","Scope", 54)
Notice that we didn't specified a collection of items and instead only specified the type of entity along with attribute name.
So the output result doesn't need to be from the Definition node Person in this case. This can be fixed by using the GID of the attribute instead.
$FINDONE
Returns one GlobalID matching the supplied criterias.
Input:
- Type of entity.
- Attribute - Value pair(s). At least one pair must be supplied, otherwise null is returned.
Output:
GlobalID.
Usage:
$FINDONE("CoProduct", "code", "1234")
$FINDONE("AsInstance","First Name", "Alfred", "Last Name", "Nobel")
Example:
In this example we have Instances of the definition Person with the attribute Scope. We want our expression to return one instance that fit our criteria: "Scope" is equal to 54.
We can use the below expression for this, where we specify that the Type of entity is "Asinstance", the attribute is "Scope" and 54 is the value to search for:
$FINDONE("AsInstance", "Scope", 54)
Notice that we didn't specified a collection of items and instead only specified the type of entity along with attribute name. So the output result doesn't need to be from the Definition Node Person in this case. If we want a result from only the definition person we can use the GID of the attribute instead.
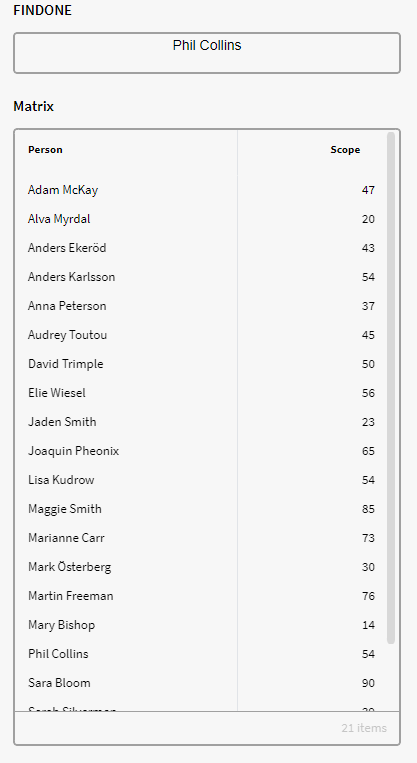
This Function works similar to that of FINDMANY with the difference that the FINDONE function only ever returns one entity, even if it finds several that fits the criterion.
$LOOKUP
Performs a lookup by attribute values. Attribute can be specified by name or ID.
It is always a better idea to refer to the GID rather than the name (attribute or other). So even if the name of the attribute is changed the expression will still work.
Input:
String type, String attribute, Any value, String attribute, Any value,...
Output:
Array
Usage:
$LOOKUP(type, attribute name, Attribute Value [, attribute name, Attribute Value...])
$LOOKUP(type, attribute id, Attribute Value [, attribute id, Attribute Value...])
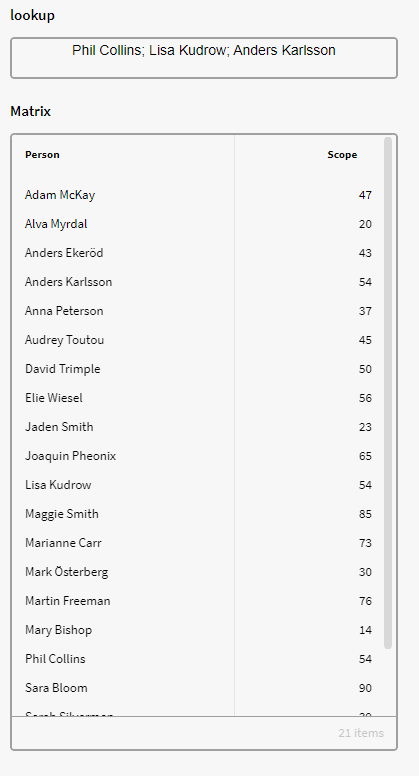
Example:
We want to find Instances that have Scope attribute value of 54. We can then use the below expression in a Calculation Box. Here we are using our GID of the attribute Scope:
$LOOKUP("AsInstance",GsVar:3077B276-B06B-2147-A44E-AFD200D26B80, 54)
Notice that we didn't specified a collection of items and instead only specified the type of entity along with attribute (and attribute value), but we reference our attribute with the GID so only instances within this attribute shows (Person).
If we had written the attribute name "Scope" instead, the expression will also return other instances if they have an attribute called "Scope" and the value of this is 54.
Text Functions
What is a Text Functions?
They can be used to analyze, rearrange, extract, and build text strings.
$ASCIITOSTRING
Returns a String object representing the specified decimal ASCII character.
Input:
Integer
Output:
String
Usage:
$ASCIITOSTRING(65) == "A"
*What is ASCII?*ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) is a character encoding format. This format is used to make blocks of texts more easily stored in a computer by assigning numbers for each character i.e., letters, numbers (0-9) and symbols.
$FINDSTR
Returns the index of a substring within a string.
- Optional starting point can be supplied as third argument.
- If not found it will output -1.
- It’s a good idea to convert the input to a string in the expression as well - $TOSTRING()
- Zero based index
Input:
String
Output:
Integer
Usage:
$FINDSTR("Hello world.", "world") -> 6
$FINDSTR("Hello world.", "yxa") -> -1
$FINDSTR("Hello Africa, Hello motherland.", "Hello") -> 0
$FINDSTR("Hello Africa, Hello motherland.", "Hello", 5) -> 14
Example:
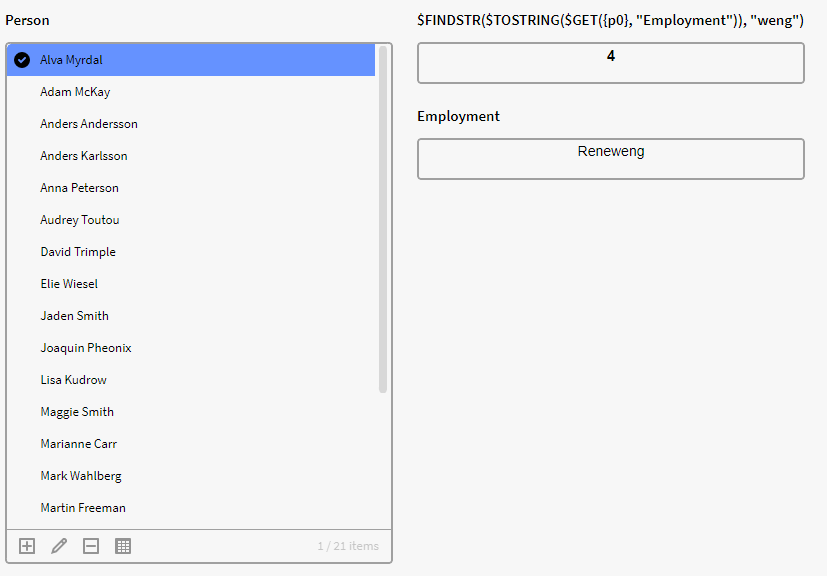
In this example in Application Builder we have Instances of the Definition Person with attribute Employment. We want to check if where the sub-string “weng” can be found in their employment attribute value. We can use the below expression in a calculation box for this:
$FINDSTR($TOSTRING($GET({p0}, "Employment")), "weng")
Result:
$FORMAT_DATE
Formats a timestamp as a string.
Input:
Date to be formatted
Output:
String
Usage:
$FORMAT_DATE(@MyDate, "DATE_SHORT").
$FORMAT_DATE(@MyDate, "DATETIME_LONG").
$FORMAT_DATE(@MyDate, "yyyy-MM-dd").
$FORMAT_DATE($NOW(), "MM/dd yyyy").
Example:
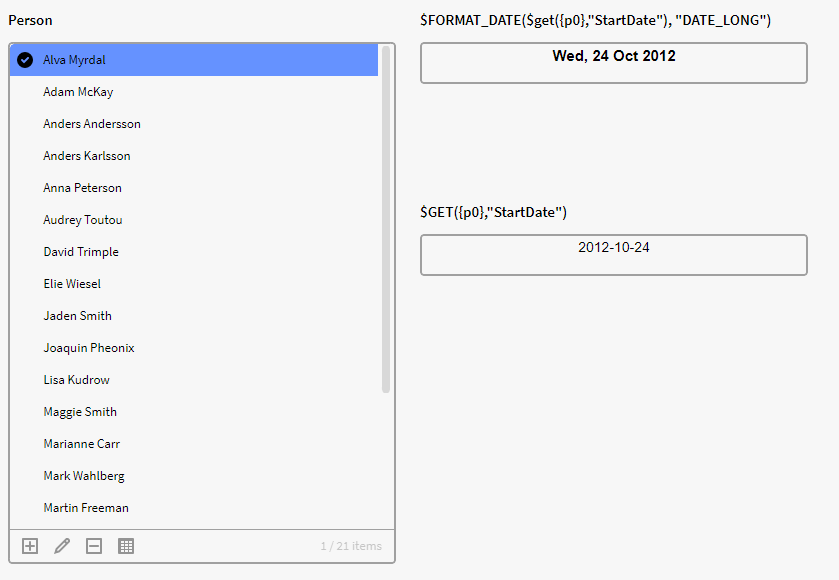
We have here a filter box containing Instances of the definition Person with the attribute Start Date. We want to format the attribute value in Start Date to a longer format, so we use the below expression in a Calculation Box to achieve this:
$FORMAT_DATE($get({p0},"StartDate"), "DATE_LONG")
Result:
$FORMAT_NUMBER
Formats a number using into a string.
Input:
Number to be formatted.
Precision (integer) or Java Decimal Format Pattern (string).
Output:
String representation according to input. Result will be rounded automatically when applicable.
Usage:
$FORMAT_NUMBER(5.1234, 2) -> "5.12"
$FORMAT_NUMBER(5, 3) -> "5.000"
$FORMAT_NUMBER(364565.1454, "#,###,##0.00") -> "364,565.15"
$FORMAT_NUMBER(9.95, "000.###") -> "009.95"
Example:
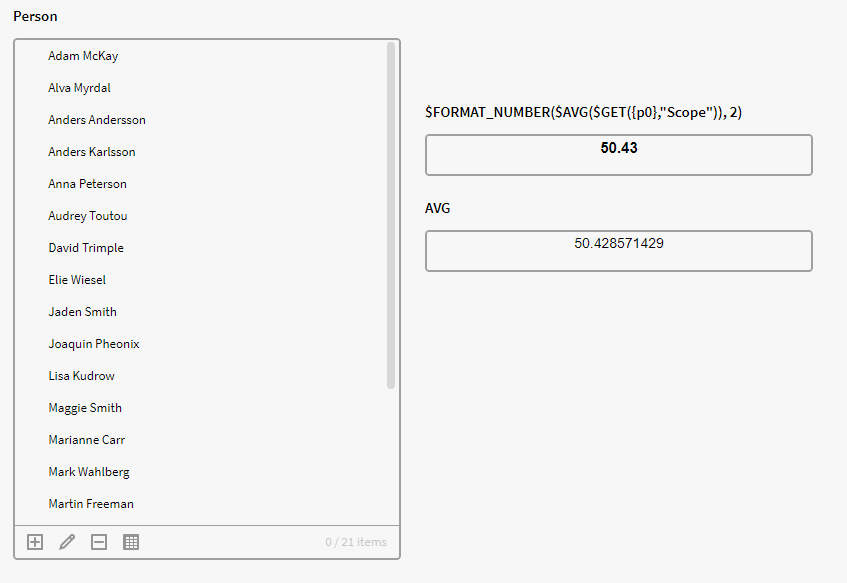
We have a filter box containing Instances of Person with attribute Scope. We want to extract the average number of the attribute Scope from all instances in p0 and then format that number to only contain 2 decimals. What we can do to receive that result is the below expression to a calculation box:
$FORMAT_NUMBER($AVG($GET({p0.all},"Scope")), 2)
$HTML_ENCODE
Makes a string safe to present on web.
Useful for presenting raw HTML and XML
Usage:
$HTML_ENCODE(@MyString).
$HTML_ENCODE("Hello World").
$HTML_ENCODE($TOSTRING($GET({p0}, "Last Name")))
$LEFT
Returns the leftmost n characters of a string.
Input:
String orig, Integer length
Output:
String
Usage:
$LEFT(string, n)
Example:
$LEFT("Hello", 2) will return “He” since it’s the first two string characters. If I had written the expression $LEFT("Hello", 3) it would return “Hel”.
$REPLACEREGEX
The function can replace method calls and enhance performance substantially.
It is used to replace parts of a string using a regular expression.
Syntax: $REPLACEREGEX(string_to_search, search_regex, replacement_string)
Example:
$REPLACEREGEX("JC-SERIAL/1234.56 AB+", "[^a-zA-Z0-9]", "") Output Result = "JCSERIAL123456AB"
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| input text | "JC-SERIAL/1234.56 AB+", The text in which to match |
| match regex expression | "[^a-zA-Z0-9]",The Regular expresion to look for in the text |
| replacement string | "" The pattern with which to replace the parts matching the regular expression. |
| Output result in the sample | JCSERIAL123456AB |
For a more comprehensive explanation of the syntax please visit the regex101 and the Java Section:
$REPLACESTR��
Replaces part(s) of a string.
Note that this function does not change the original string but returns a new string.
Input:
String target, String to Replace, String replacement.
Output:
String
Usage:
$REPLACESTR("Hello world.", "world", "cruel world") → Hello cruel world
Example:
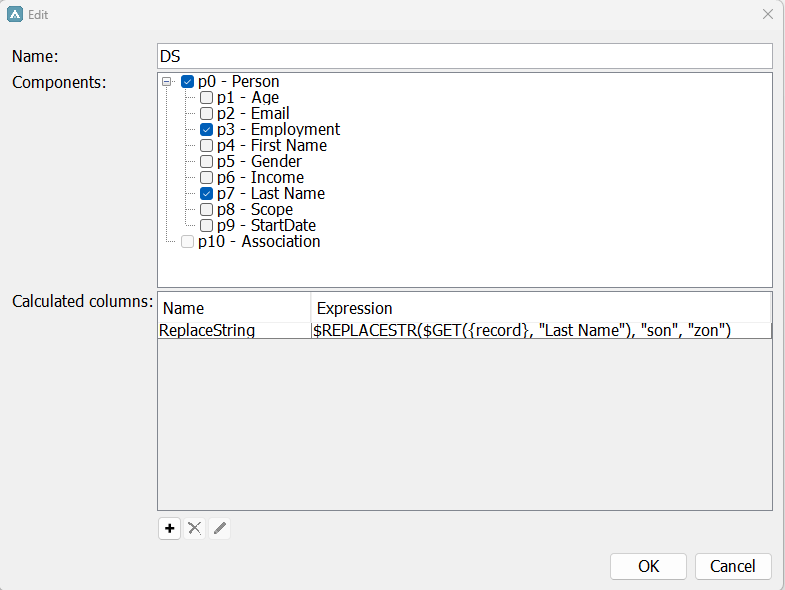
In this example we have a dataset (DS) containing Instances of the definition Person with an Employment and Last Name attribute.
We want to replace the substring "son" with "zon" in all the last names in a result matrix. For this, we can use the below Expression in a calculated column in our dataset DS:
Here we are specifying that our string target is every row with a Last Name Attribute in the dataset with $GET({record}. "Last Name", and then we specify that "son" should be replaced with "zon".
Result:
$RIGHT
Returns the rightmost n characters of a string.
Input:
String orig, Integer length
Output:
String
Usage:
$RIGHT(string, n)
Example:
$RIGHT("Hello", 2) will return “lo” since it’s the first two string characters.
If I had written the expression $RIGHT("Hello", 3) it returns the below result:
$STRING_JOIN
Returns a string built from a list of items, with specified delimiter and optional prefix and suffix.
Notes:
- An empty list will return an empty string.
- Each item will pass a standard formatting method where for instance a GlobalID will be replaced by its presentation and null by an empty string.
Input:
A collection of items.
Delimiter.
Suffix (optional).
Prefix (optional).
Output:
String
Usage:
$STRING_JOIN($GET(@p1,"ID"), "&p1=")
$STRING_JOIN($GET(@p1,"Name"), "</DIV><DIV>", "<DIV>", "</DIV>")
Example:
We have a filter box containing Instances of the definition Person (p0). We want to list a selection of the Instances in a Calculation Box with the suffix #. We can use the below expression to achieve this:
$STRING_JOIN({p0}, " # ")
Result:
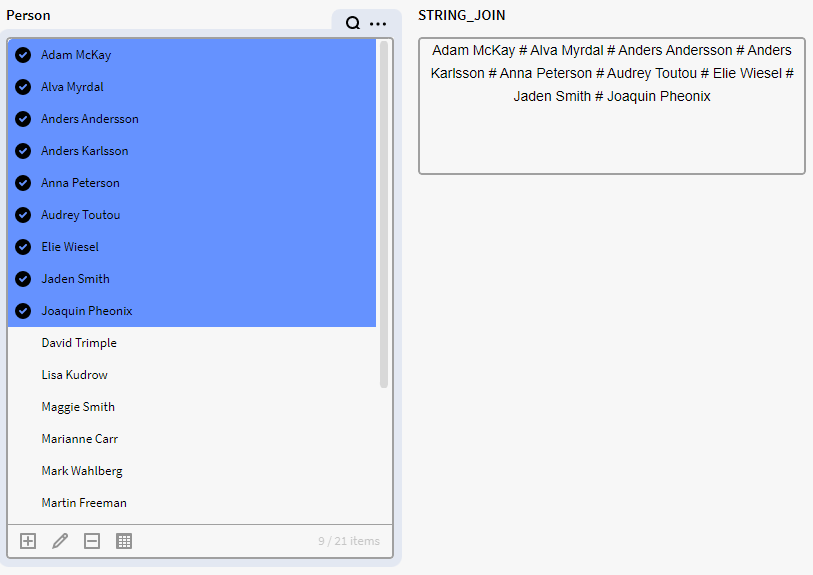
$STRINGFORMAT
Performs a string.format() operation. Useful for complex string output.
This function can be used to convert and format other data types into a string via Format Specifiers
Input:
String, Object...
Output:
String
Example:
The below expression will return a string showing how many objects are selected in the p0 filter box.
$STRINGFORMAT("There are %d selected objects in box p0", $SIZE({p0}))
%d allows you to add numbers in a formatted string. The %d in the above example will add the Integer we got from $SIZE({p0}), which is the number of selected items in p0.
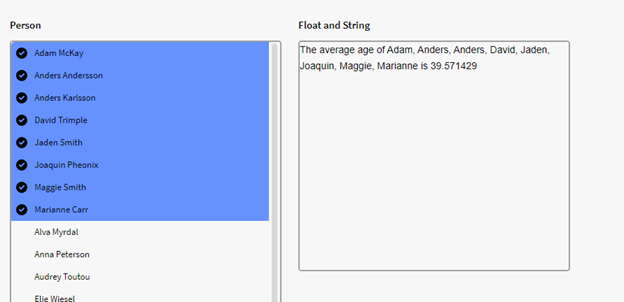
$SUBSTR
Returns a substring of the first input string.
Null input will return an empty string.
Input:
Source string. Start position (Zero based). Optional Length.
Output:
String
Usage:
$SUBSTR("Hello World",6) = "World".
$SUBSTR("Hello World",0,5) = "Hello".
$TOLOWER and $TOLOWERCASE
Turns a string into lower case.
Note: TOLOWER and TOLOWERCASE do the same thing.
Input:
String
Output:
String
Usage:
$TOLOWER("Hello World."). -> hello world
$TOLOWERCASE("Hello World."). -> hello world
$TOUPPER and $TOUPPERCASE
Turns a string into upper case.
Note: TOUPPER and TOUPPERCASE do the same thing.
Input:
String
Output:
String
Usage:
$TOUPPER("Hello world."). ->HELLO WORLD.
$TOUPPERCASE("Hello World."). ->HELLO WORLD.
$TRANSLATE
Translates a text.
Input:
String
Output:
String
Usage:
$TRANSLATE(Text)
$TRANSLATE(Text, "INFORMATION") default
$TRANSLATE(Text, "DATA")
$TRANSLATE(Text, "ERROR")
$TRANSLATE(Text, "ACTION")
$TRANSLATE(Text, "TOOLTIP")
$TRANSLATE("YOU_HAVE_TO_SPECIFY_FIRST_AND_LAST_NAME")
$TRANSLATE("OPEN_IN_NEW_BROWSER_WINDOW")
$TRANSLATE("Searchable.searchFor")
Example:
We have our Language setting to Swedish in Model Builder in the below example and we are using a Hard ID as the text input. Which will result with a Swedish String result:
$TRANSLATE("YOU_HAVE_TO_SPECIFY_FIRST_AND_LAST_NAME")
Result:
But if we now change language to English in Model Builder (and log out and in again) the text will translate to English:
$TRIM
Removes leading and trailing spaces from a string.
Input:
String
Output:
String
Usage:
$TRIM(" Hello ") -> "Hello"
Formatting Expressions
Notes
- All functions must be prefixed with a dollar sign ($).
- All function names are case insensitive.
- [] (Lazy evaluation) are no longer necessary to use.
- Try to use {} instead of @ - i.e. {Dataset} instead of @Dataset. This will ensure the validity of the Expression regardless of Attribute name changes and use of Attribute aliases.
If you still use @ to format variables, you must replace non-letter characters with underscore (_), for example @My attribute -> @My_attribute. Below non-letter characters need to be replaced with underscore:
- (space)
- -(dash)
- *(asterisk)
- ((left parenthesis)
- )(right parenthesis)
- .(dot)
- ,(comma)
If you use an attribute name within quotes, e.g. $GET("My Attribute", "name"), you should not replace the non-letter characters. The replacement is done automatically when retrieving the value from the property bag.
Results from your expressions might not load correctly, or at all, in Application Builder, you will therefore need to open the application on the web to confirm if your expression worked properly.
{Record}, {Item} or @Y_Object?
{Record}, {Item} or @Y_Object all refers to each item in a list, but you should in almost all cases use {Record}.
- {Record} = Used in most cases for expressions.
- {item} = Used in calculated filter boxes and maps.
- @Y_Object = Used only in matrixes (old variant which should not be used unless necessary) - Same functionality as {rowSource}
$GET Function
If you wish to manipulate attributes values, use the GET function together with a suitable operator.
The $GET function is one of the most useful functions to learn. If you want to return an attribute value from a filter box or in a dataset you need to use this function.
For example, to get the attribute Age from filter box p0 use:
$GET({p0},"Age")
%d, %s and %f
Placeholder for string, float, and integer values in more complex strings.
It can be useful to use format specifiers when building a string that is more complex than usual such as the STRINGFORMAT function , as it will return an integer, float, or string from another argument in the same expression.
- Arguments are separated by comma (,).
- Use $STRINGFORMAT as the most outwards function to return the format specifier values.
When a %d is encountered it will take the next argument and return it as an integer.
When a %s is encountered it will take the next argument and return it as a string.
When a %f is encountered it will take the next argument and return it as a float – float is basically the same as a double with the difference that a double can hold much larger numbers.
Usage:
$STRINGFORMAT("Hi, this is a text %s", "example")Result: Hi this is a text example
$STRINGFORMAT("The current month number is %d", $MONTH(@NOW))Result: The current month number is 4
$STRINGFORMAT("Hello %s your number is %d", "David", $TOINT(322))Result: Hello David your number is 322
Note that you can add several format specifiers in the same expression. The first string format specifier (%s) will use the result from the first argument and the second string format specifier will use the result from the second argument and so on.
The same logic applies to integer format specifiers (%d) and float format specifiers (%f).
$STRINGFORMAT("%s, this is a text %s. Today is the year %d ", "Hi", "example", $YEAR($NOW()))
Result: Hi, this is a text example. Today is the year 2023
$STRINGFORMAT("The average age of %s is %f", $TOSTRING($GET({p0}, "First Name")), $AVG($GET({p0}, "Age")))
Result:
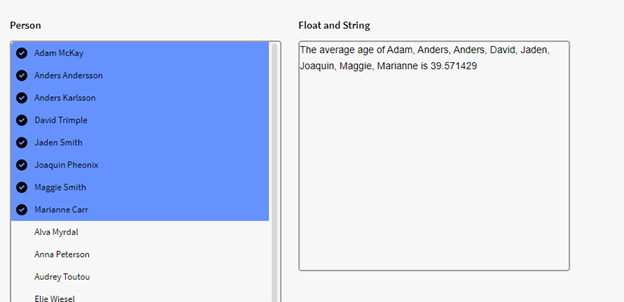
Example:
The below expression will return which selected person in p0 has the earliest start date along which said start date. Notice how we convert our arguments to string to make sure that we get the correct input to use the %s format specifiers when we call the arguments.
$STRINGFORMAT("The longest employed person is %s, who has worked here since %s", $TOSTRING($FILTER({p0},$GET({record}, "StartDate") = $MIN($GET({p0}, "StartDate")))), $TOSTRING($MIN($GET({p0}, "StartDate"))))
First argument:
$TOSTRING($FILTER({p0},$GET({record}, "StartDate") = $MIN($GET({p0}, "StartDate"))))
Filter only the item in the p0 list whose attribute value in StartDate equals that of the minimum attribute value of StartDate in p0.
Second Argument:
$TOSTRING($MIN($GET({p0}, "StartDate")))
The minimum (earliest) attribute value in Startdate in p0.
Result:
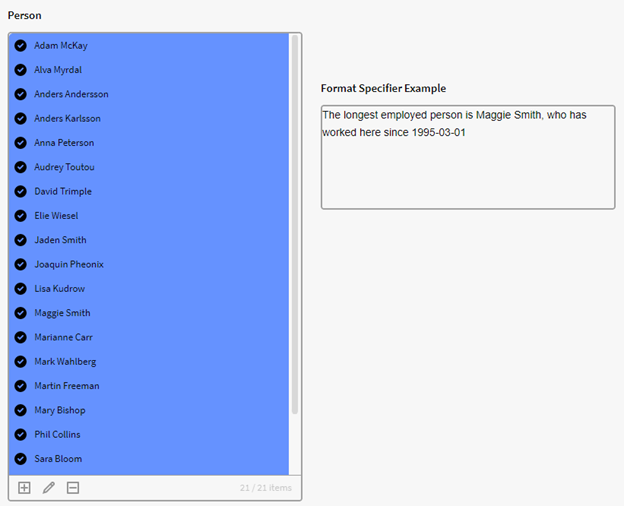
Combined Expression
When we combine functions into one expression, we are using the result of the inner functions as arguments for the outwards functions.
It can be helpful to combine functions into one expression to get the result you want.
For example, a TEXT function such as $FORMAT_DATE can be combined with the Entity function $GET to get a date attribute value from a filter box and then return the date in a specific format:
$FORMAT_DATE($GET({p0},"StartDate"), "DATE_SHORT")
Try to write and test functions separately and it’s a good idea to start building it from the center and work the expression outwards.
Example 1
So, let’s say we have a filter box p0 that contains Instances of the definition Person with the attributes First Name, Last Name, Age, Employment and Gender. We want to see the average age of women in a certain company (Inpraxius) in p0.
This will require us to combine different functions ($GET, $FILTER and $AVG) into one expression.
1. First, we input the data collection we want to filter, i.e all items in p0 and then specify the attribute value(s) from this data collection to filter.
$FILTER({p0.all}, $GET({record}, "Employment") = "Inpraxius")The {record} variable will make sure the expression references each row in a list/dataset for our $GET function. A record in this case will be each row with an Employment attribute. The $FILTER function will make sure to return only the rows with employment attribute value set to “Inpraxius” from our list in p0.
2. We add our second filter parameter (the row {record} must also have the attribute Gender value equal to “Woman”) to this filter expression.
$FILTER({p0.all}, $GET({record}, "Employment") = "Inpraxius"
Note that when we add an equal sign to a $GET function it will simply return true or false. Which is what we want since the $FILTER expression requires a Boolean input.
3. We want to see the age average of this filter result, so we enclose our $FILTER function with an $AVG function with the “Age” attribute as the last input parameter:
$AVG($FILTER({p0.all}, $GET({record}, "Employment") = "Inpraxius" && $GET({record}, "Gender") = "Woman"), "Age")
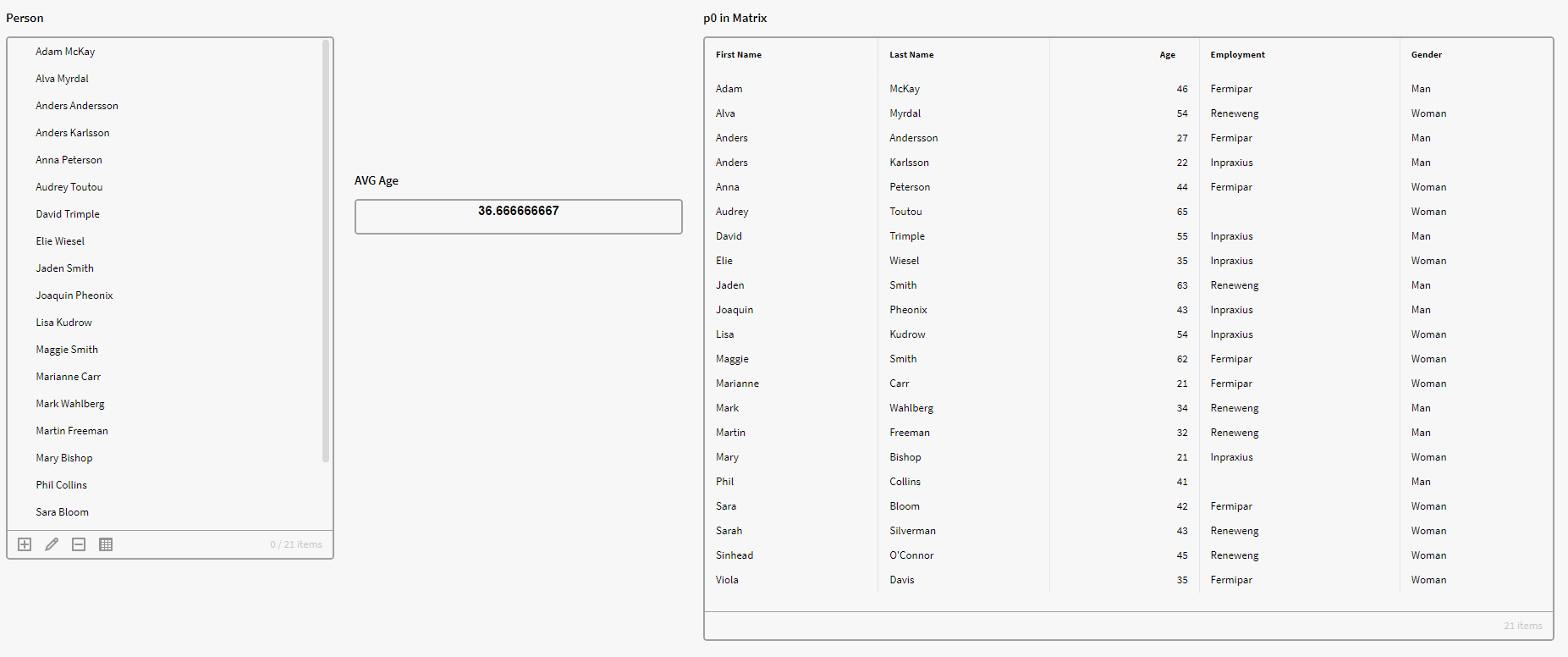
Note that simply executing the $GET({record}, "Employment") = "Inpraxius" function will not yield any results. This is because we don’t specify any collection of data for which it should check if each item/row has an Employment value equal to “Inpraxius”. To yield a test result, you can replace {record} with a data collection that contains an attribute titled “Employment”.
Example 2
We have a dataset containing Instances of the definition Person with the attributes Employment and Scope in Knowledge Set Builder. Some people in our dataset do not have any Scope values (image below) and we want to add a new column in our Result Matrix. This new column should show the average of the total Scope values if the Scope attribute value is empty.
What we can do is add the below expression to a calculated column for the Base table named Person:
$IIF({cell.Scope}=@null, $ROUND($AVG($Get({dataset}, "Scope"))), {cell.Scope})
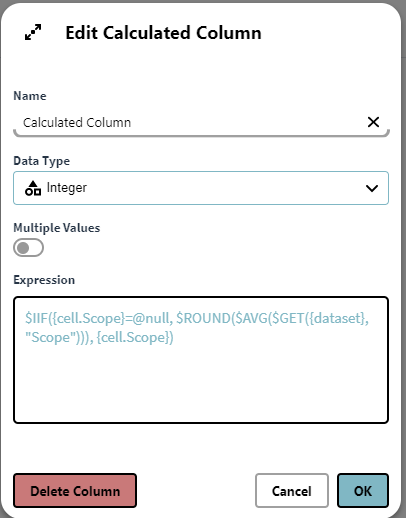
In this example we have 4 combined expressions, $GET, $AVG, $ROUND and $IIF. More can be added of course but for this example we will go through them step by step to show how they work together:
Step by Step tutorial:
- This $GET expression gets the Scope attribute value in current dataset.
$GET({dataset}, "Scope") - The $AVG expression returns the average of the Scope attribute values.
$AVG($GET({dataset}, "Scope")) - The$ROUNDexpression rounds up the average of the Scope attribute values.
$ROUND($AVG($GET({dataset}, "Scope"))) - The $IIF expression will check if the value of Cell "name" of the current Dataset row (in this case the “Scope” column) is null. If true, it will return the result of our previous expression $ROUND($AVG($GET({dataset}, "Scope"))) if not true (has any value) it will return the value in the cell in the current Dataset row of “Scope” ({cell.Scope}).
$IIF({cell.Scope}=@null, $ROUND($AVG($GET({dataset}, "Scope"))), {cell.Scope})
By adding this expression to a calculated column in our Person dataset we will get the below result in the “Calculated Column"-column:
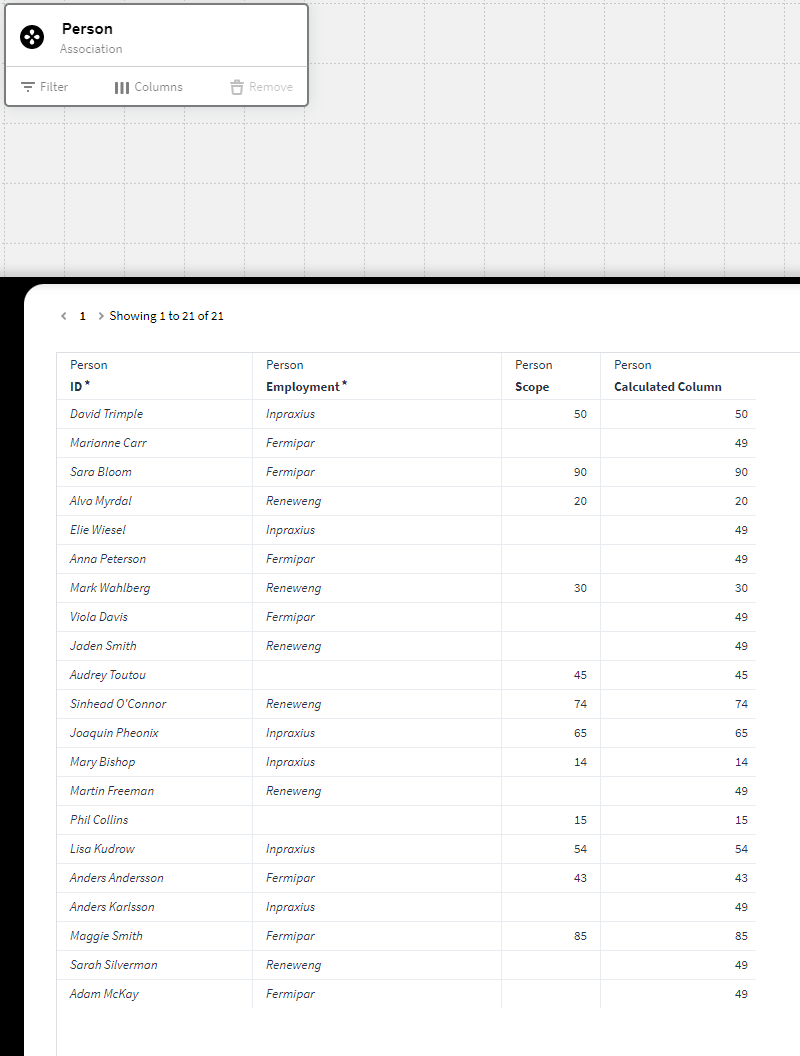
Expression Troubleshooting
Check the examples and usage for each function to see how to set up your expression correctly.
Ask yourself the following questions if a function is not working as intended:
- What datatype does the function require as an input? Am I providing the function the correct datatype?
- Am I formatting the syntax for the expression correctly? Am I missing a mandatory input?
- Am I missing a start or closing parenthesis?
- Am I spelling my attribute, dataset, or variable correctly?
Note also that results from your expressions might not load correctly in Application Builder, you will therefore need to open the application on the web to confirm if your expression worked as intended.
Global ID and Class
What is a GID?
A Global identifier or GID is a way for Inorigo to identify objects in the system. Every time you create a new Attribute, Instance, Definition Node and so on, it is assigned a GID.
These IDs do not change, even if you change name for the object. It is therefore a good idea to reference your objects via this GID in Expressions as Inorigo will always know what object you are referencing to.
Retrieving the GID of an Attribute in Model Builder:
A global ID can be formated with both Class and ID or or just an ID. If you specify with class as well you should use this format Class:ID
Specifying class and ID:
AsDefinition:95CFD186-2398-09B0-4054-AFA100E0DE1A
Only ID:
95CFD186-2398-09B0-4054-AFA100E0DE1A
What is a Class?
A class is a data type for objects in Inorigo. Specifying the class when referencing a GID will shorten the time it takes for Inorigo to find said object, as Inorigo will know where to search for it.
Operators
| Operations | Result | |
|---|---|---|
| * | Multiply | |
| + | Add or Concatenate | |
| - | Subtract | |
| % | Remainder | |
| | | Or | |
| && | And | |
| = | Equals | |
| == | Equals | |
| < | Less than | |
| > | Greater than | |
| >= | Greater than or equals | |
| <= | Less than or equals | |
| != | Not Equal |
Optional inputs
Certain function parameters are not required, which gives us the option to pass function arguments when we call the function.
If you don’t want to use an optional input in an expression, you can simply add a blank space if there are multiple optional inputs. If it’s the last input in the expression you do not need to add blank space, simply end the expression with “)”.
Optional input at the end of expression
For example, the last input “Gender” in the below PERCENT expression is optional, it is used to group the percentage according to, in this case, gender. So, each row’s percentage of income is according to the total income of that gender group.
$PERCENT({DS},"Income", "Gender")
If I want to remove Gender from the expression, I can simply delete it like below:
$PERCENT({DS},"Income")
Optional input in the middle of expression
In this example we have 3 different optional inputs (orange). I want to remove the first true input which makes the list descend (we want it ascending).
$SORT({DS}, true, false, "StartDate")
We therefore remove this input and replace with a space as below. As this optional input is false by default it will return it as false (ascending)
$SORT({DS}, , false, "StartDate")
Type of Entity
Type of entity is the same as Class in Model Builder.
In some expressions you need to reference an object with a type of entity as an input parameter. The $FINDONE() function is an example of this and which syntax is as follows:
$FINDONE(Type of Entity, Attribute, Attribute value)
Example:
$FINDONE("AsInstance", "Age", 65)
In the above example we are looking for an Instance that have a value of 65 in an attribute called Age.
By using this expression Inorigo would return the below Instance.
As you might notice the type of entity parameter is using an old name for the entity "AsInstance" even though the class is called "Association" in the Change log tab. This is because "Association" is simply a presentation name:
Reference a type of entity correctly:
To reference the object correctly in your expression you must use the entity name Inorigo has stored as reference. This you can find by searching for it in "Class"
Choosing your class:
Choosing your class:
Variables
A Variable is a holder of an expression that optionally can be created from the contents of the data in an Application.
Features of a Variable:
- Variables are defined per Application.
- Variables can hold any expression, even a reference to a Dataset.
- Possible to reference a Variable wherever an expression would apply.
- It is possible to reference one Variable from another (which amongst other things will increase expression readability).
- By using variables, expressions need only to be executed once, which will reduce response times every time a variable is used.
- Use Constant variable, ticking the check box in variable settings panel,
Available Dataset Variables
With inorigo 4.10 and ondwards its possible to write variables in the two following ways
Contained within Curly Brackets
Example:
or
Prefixed with an at sign (@). Spaces needs to be replaced with underscore.
Example:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| {any_user_specified_parameter} | Any user specified variable in tab Expression Variables in Application Builder |
| {BASE_PATH} | This holds the base path to the inorigo server. If installed as ROOT.war on the tomcat server this will be empty. Installed as inorigoProd.war this will contain "/inorigoProd". |
| {CLICK} | A number representing the current time in milliseconds when user clicked something. For instance used to make URL:s unique between calculations, in order to trigger reload of embedded Velocity pages. |
| {DATA_CONTEXT_ID} | Holds the ID of the current data context. |
| {Dataset} | Any user specified DataSet in the tab DataSets in application Builder settings |
| {NOW} | Returns the current date and time |
| {NULL} | Null Value |
| {pX.all} | Returns all items in filter component X |
| {PX} | Returns selected items in filter component identified by X |
| {record} | Representing current record when evaluationg Initial Filter and Initial Selection expressions |
| {rowindex} | Representing current index when evaluating Initial Filter and Initial Selection expressions. Zero based. |
| {USER_DISPLAY_NAME} | Holds the display name of logged in user |
| {USER_ID} | Holds the ID of the logged in user * |
| {USER_NAME} | Holds the name of the logged in user * |
| {verso.pX.all} | Same as pX.all |
| {VERSO_RUNTIME_ID} | The ID of the current instance of the application. If you look at the same application in two tabs or windows, each has it's own VERSO_RUNTIME_ID. This is only used for mirroring and also passed to Velocity pages in order for them to reference the same selections and so forth. |
| {VERSO_VIEW_ID} | The ID of the Application |
| {VERSO_VIEW_TITLE} | The title of the Application |
These additional are only available for Datasets (including Knowledge Sets), when adding Calculated columns.
| variable | Description |
|---|---|
| {cell<0..n> | Value of the Cell 0..n of the current DataSetRow |
| {cell | Value of Cell "name" of the current DataSetRow (i.e@cell.p1, @cell.Country, @cell.Home_Adress) |
| {columnCount} | Number of columns in hte current DataSet |
| {columnIndex} | Index of the current DataSetColumn in the DataSet |
| {columnTitle} | Title of the current DataSetColumn in the DataSet |
| {column} | The current DataSetColumn |
| {dataset} | Current DataSet (also referable by it's normal name) |
| {rowCount} | Number of rows in the current DataSet |
| {rowIndex} | Index of the current DataSetRow in the DataSet |
| {row} | The current DataSetRow |
Expression Variables
Besides the available dataset variables, you can also create your own variables from the contents of the data in an Application.
- To assign a value to a variable you use an expression, which will also set the value as a datatype such as Integer, list, string etc.
- You give your variable a name so that you may call it when in need of the stored value.
- Both the variable value, name and datatype can be changed (it’s by default not a constant).
- Note that variable names are case sensitive.
Why use Variables?
Variables are a great way to “clean up” your expressions as it will make it easier to read and less cluttered.
It makes it possible to call the stored value via the variable name in several places - it removes the need to write and run the expression multiple times.
Example
A simple variable can for example be X=6:
6 is the value,
X is the name,
Integer is the datatype (whole number).
Set value and variable name via the Control Panel in Application Builder:
We add an expression into a calculation box using our X variable + 2:
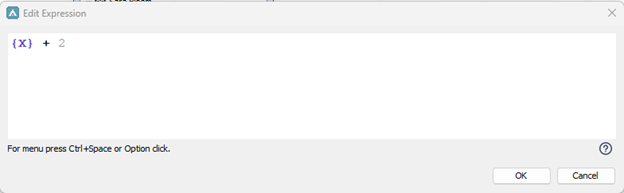
The result is the sum of the variable value (6) plus 2. Note that if we now decided to change the variable value from 6 in the Control Panel, the sum would also change in the result box.
Constant Variable Option
In the Variable configuration panel you can also find a check box called "Constant". Checking this means that the variable is NOT updated when calculations/selections are performed in the Application, only on Application Reload or browser refresh.
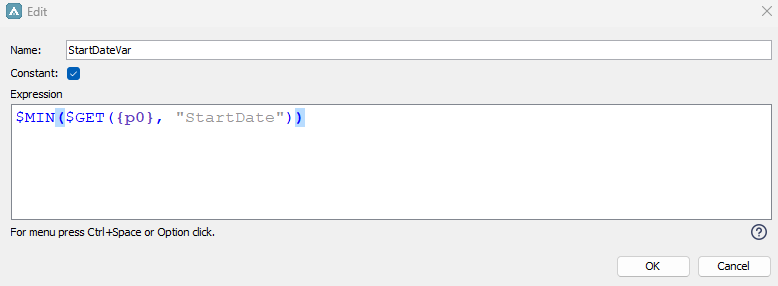
Dataset
Using a Dataset as reference in a constant variable will not work unless an Initial Selection is specified for Application, since the Dataset need input from a selection to calculate.
Visible values
- There is one case when the Application Reload button does not affect the constant variable; and that is when the value contained in the constant variable is not listed in any filter component.
- Depending on which behavior that is expected, one can control the Constant variable sensitivity by adding a filter component that lists one of the input values for variable, invisible if wished.
- In general, for all Applications, the sensitivity of the Reload is controlled by the filter components that exist in the Application, visible or not.
Vocabulary
BooleanA value that is either true or false.
DoubleA number with decimals, for example 22.343.
IntegerA positive or negative whole number, including 0.
ExpressionA combination of variables, constants, operators, and functions that are put together in a single statement to be evaluated.
FunctionAlways contains $ + Function name and a start and closing parentheses (). All functions are expressions but not all expressions contain functions.
GID
Global Identifier. A way for Inorigo to identify objects.
InputThe data we give to Inorigo to process.
Null
Means that something is undefined. It has no value but note it is not equal to zero.
OutputThe result we get back from Inorigo from the processing.
OperateAn action that is carried out to accomplish a given task
Inward functionA function that is enclosed within another function.
*Example*($GET(Outward functionThe surrounding function that encloses another function.
Example$FORMAT_DATE(
OperatorA character that represents a mathematical or logical action, such as +, -, = or >.
Parse
Converting information into a format. This so to make something understandable for Inorigo.
ParameterThe variable listed inside the parentheses in the function definition.
ArgumentThe value that are sent to the function when it is called.
Example
VariableContainer for storing data values.
ConstantA fixed value, for example the number 5. The value does not change and is predefined.
StringA sequence of characters, for example “Hello world”.
Substring
A string that is part of another string. "Hel" is for example a substring of "Hello World".
Syntax
The concept/rules of how different elements in an Expression should be combined in order for it to run correctly.
Zero based Index
A way of numbering in which the initial element of a sequence starts at the index 0 rather than the usual index 1.
© 2025 Inorigo AB. All rights reserved.